Lecture Review Flashcards
Digestion
Digestion locations:
Mouth: Sugars are digested in the mouth.
Stomach: Proteins are digested in the stomach.
Small Intestine: Carbohydrates are digested in the small intestine.
Course of food through the digestive system:
Mouth
Lower Esophageal Sphincter
Stomach
Pyloric Sphincter
Duodenum
Jejunum
Ileum
Colon
Rectum
Enzymes for Carbohydrate Digestion: amylase, proteases, lipases
pH Regulation
pH Homeostasis: Blood Buffers, Kidneys, Breathing
Neutral pH: 7
Labeling Structures
Digestive System
GU (Gastro-Urinary) System

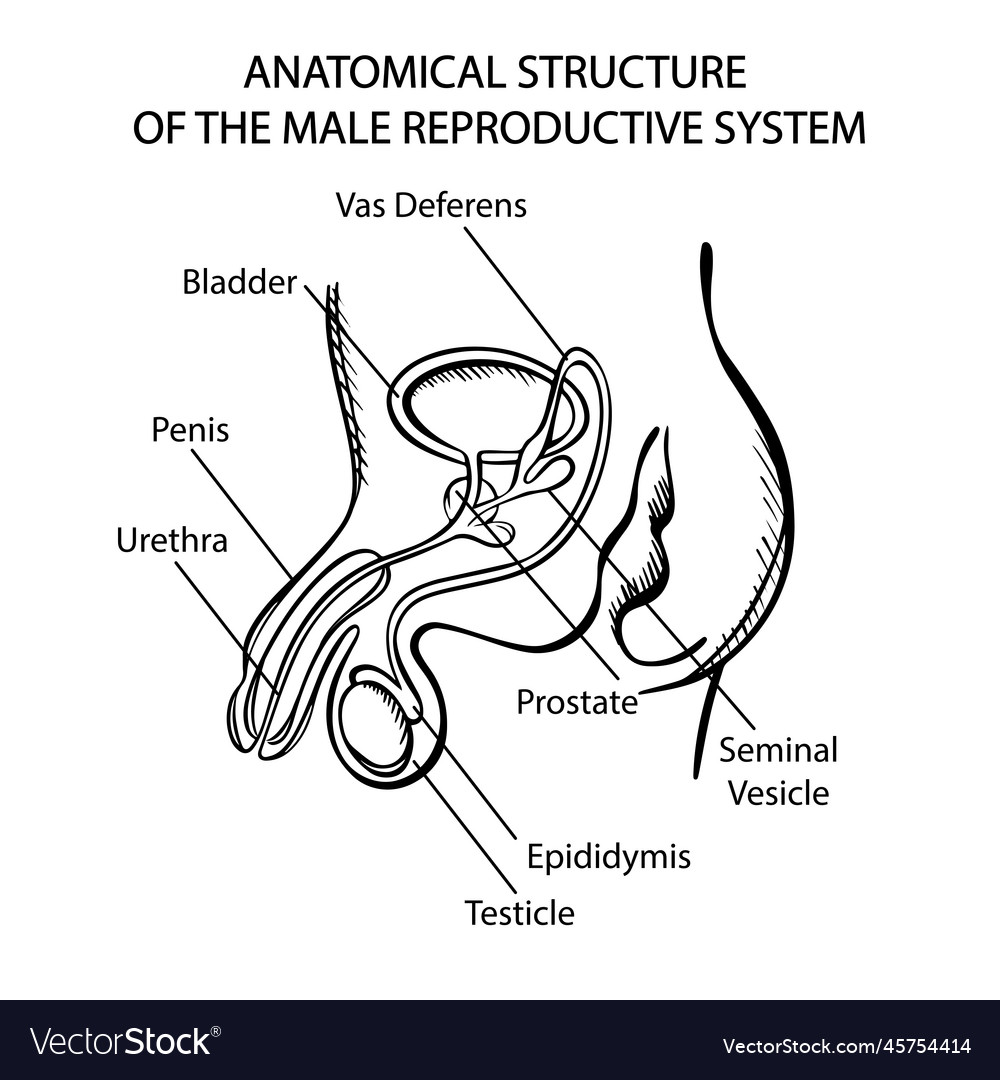
Male Reproductive System
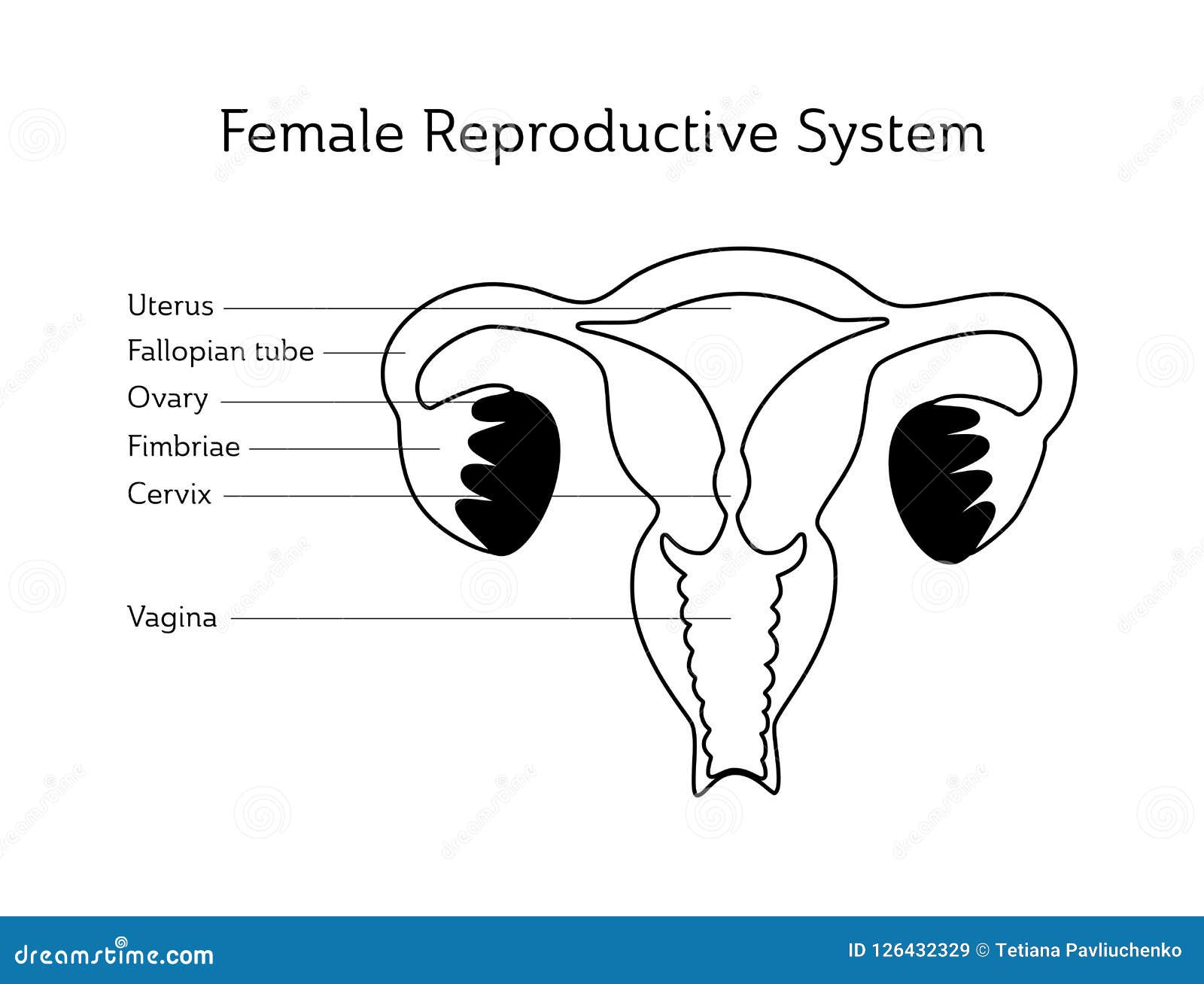
Female Reproductive System
Aldosterone and ADH
Function: Both cause the reabsorption of water.
Aldosterone: Salt-saving hormone; prevents sodium excretion (sodium is the most abundant extracellular ion).
Reabsorption occurs in the distal convoluted tubule.
ADH: Reabsorption occurs in the collecting duct.
Proximal Convoluted Tubule: Most normal fluid reabsorption occurs here.
Erythropoietin (EPO)
Kidney's Role: When red blood cells decrease, the kidney secretes erythropoietin (EPO).
EPO Function: Stimulates bone marrow to produce red blood cells.
Kidney Damage Implications: Patients with kidney damage or failure may become anemic due to decreased EPO production
Genitourinary System Terminology
Polyuria: Excess amount of urine.
Anuria: No urine production.
Hematuria: Blood in the urine.
Bile
Synthesis: Bile is synthesized in the liver.
Storage and Secretion: Bile is stored and secreted from the gallbladder; the gallbladder concentrates it.
Nephron Function
Reabsorption: Movement of materials from the renal tubules (proximal tubule, distal tubule) back into the blood.
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System
Activation: Causes increased fluid reabsorption.
Effects:
Increases blood volume.
Increases blood pressure.
Movement of Food
Peristalsis: The process of food moving through the GI system.
Body Temperature Regulation
Cooling Down: Vasodilation
Increasing Temperature: Vasoconstriction
Other Key Points
Calcium: Required for bones, teeth, and (look up the additional function).
Folic Acid: Found in greens and liver.
Aerobic Phase of Glucose Metabolism: Occurs in the mitochondria.
Anaerobic Phase of Glucose Metabolism: Occurs in the cytoplasm.
Cellular Catabolism: Glucose + Oxygen → ATP + H2O + CO2
Vitamin K: Know its benefits and uses.
Blood Sugar
Low Blood Sugar: Give simple sugars for quick increase.
Examples of Simple Sugars: Fruits (e.g., apple, grapes, strawberries, peach), orange juice.