gametogenesis
Gametogenesis is the process by which gametes are produced
Spermatogenesis - formation of spermatozoa
Oogenesis - formation of eggs or ovaries
Cell division and gamete production
- Mitosis - produces diploid cells (genetically identical cells)
- Diploid - will have full set of chromosomes 46 in 23 pairs
- Haploid - half of the number of chromosomes 23 one of each pair
- Meiosis - produces cells that are genetically different
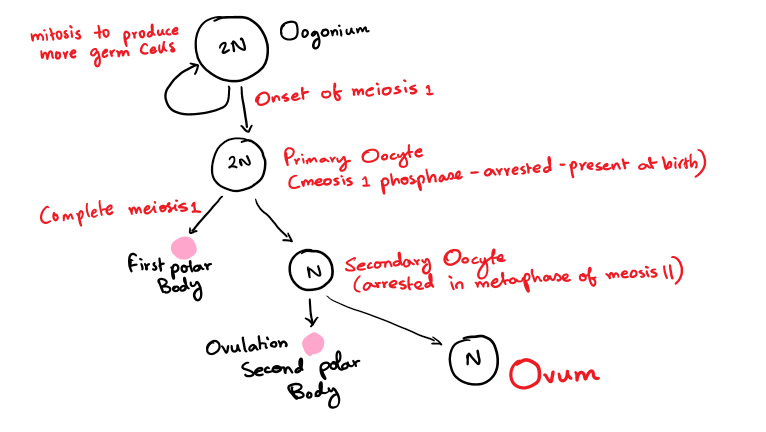
Oogenesis
spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis occurs in the testis
- These are large cells in the walls of seminiferous tubules that nourish the developing spermatids and protect them from the immune system
- These cells are stimulated by the secretion of testosterone from leading cells in the testis
oogenesis
- Follicle stimulating hormone(FSH) secreted by the pituitary promotes the growth of primary oocytes into follicles the oocyte is surrounded by epithelial cells usually only 1 follicle will develop into a graafian follicle which grows and moves to the surface if the ovary
- The follicle eventually bursts releasing the egg (ovulation)
- The empty follicle devolves into a corpus lutes
- This secretes the hormone progesterone for a while before starting to degenerate
Fertilization
- Less than 1% of sperm will reach the oocyte
- Sperm reach the oocyte by a mixture of peristaltic contractions and the swimming actions of the tails
- The oocyte also secretes chemical attractants
Capacitation
- Sperm undergo further maturation whilst in the female tract
- The membrane around the acrosome become fragile enabling the release of digestive enzymes
- The release of enzymes help the sperm penetrate the layer of follicular cells and the zona pellucida
- Sperm bind to receptors in zona pellucida and normally only 1 enters the oocyte syngamy
- Syngamy causes depolarisation of the membrane triggering the release of calcium ions
- Release of calcium triggers the vertical reaction preventing polyspermy
- Once the sperm has entered the oocyte this triggers the final meiotic division and this forms the female pronucleus
- The 2 nuclei fuse complementing fertilization
- After fertilization
- About 36 hours after the first division or cleavage takes place
- Division continues for the next few days to form a morula a solid ball of cells by the end of the 4th day
- By the 5th day morula has developed into a hollow ball of cells called a blastocyst
Implantation
- By day 6 the blastocyst has entered the uterus and after a short time it attaches to the endometrium with the inner cell mass next to the endometrium
- The trophoblast cells will go on to form the embryonic membranes and the placenta
- Embryonic development lasts for the first 2 months