Enzyme inhibition and case study

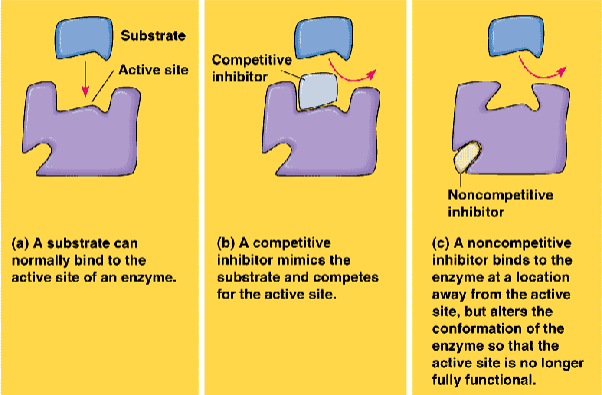
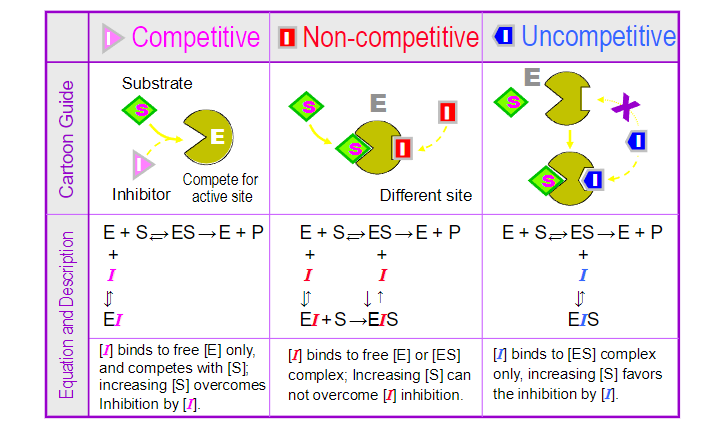
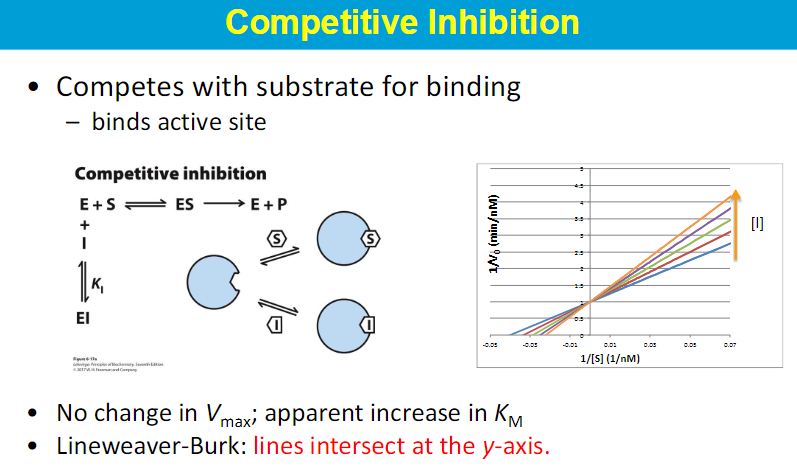
increase in km → weak binding of subtrate
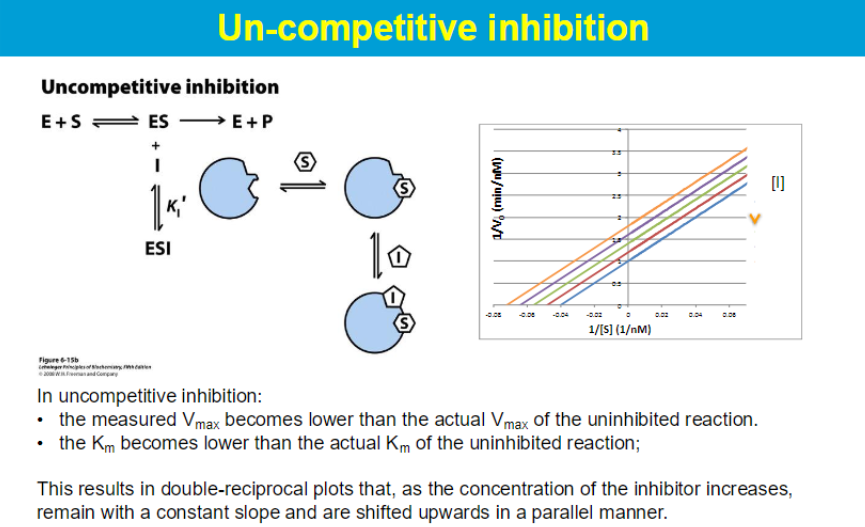
y int = 1/ Vmax
so when inhibited → Vmax is smaller making 1/Vmax bigger so the whole line is shifted up
km lower → so it binds tighter??
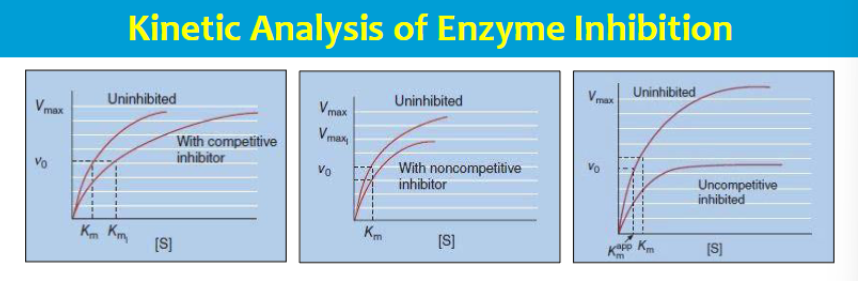
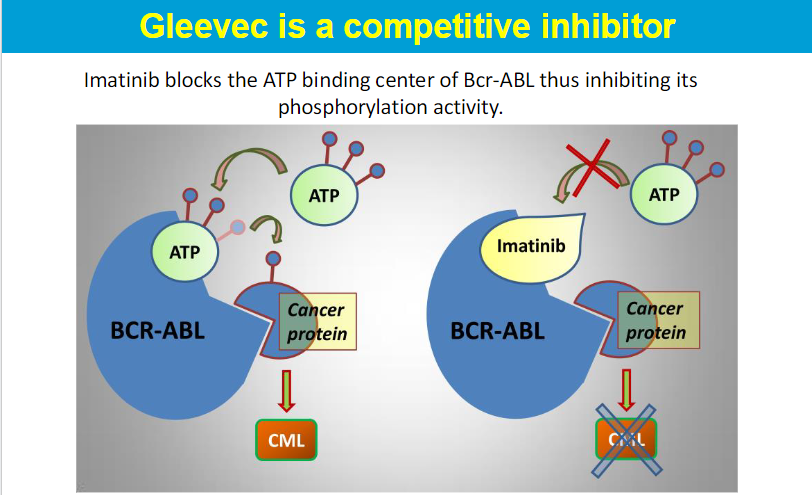
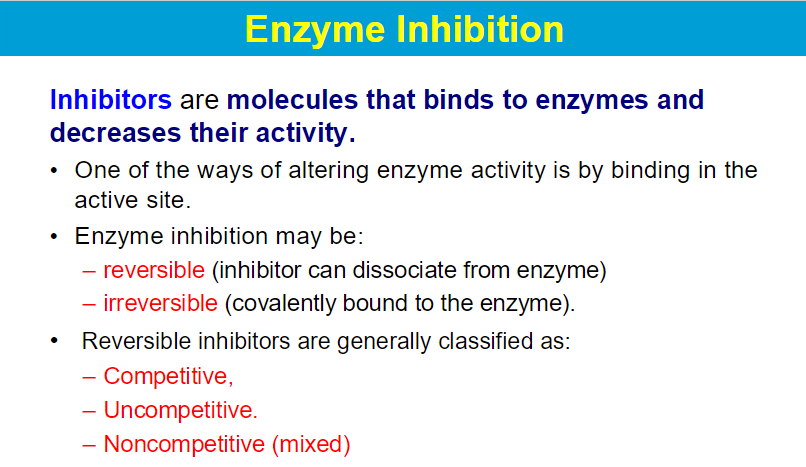
competitive inhbitor - inc in S can overcome the inhibitor
noncompetitive - no amount of S can overcome inhibitor
uncompetitive - inc in S favors inhibitor
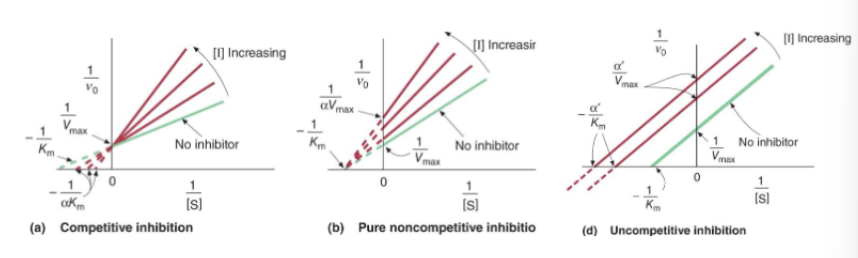
competitive - slope = Km/Vmax Km increases, Vmax stays same → bigger slope but y int stays the same
noncompetitive - Km stays the same; dec in V max → bigger slope and y - int increases
uncompetitive - more I → Km/ Vmax decreases constant so slope is the same y int. is increasing
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
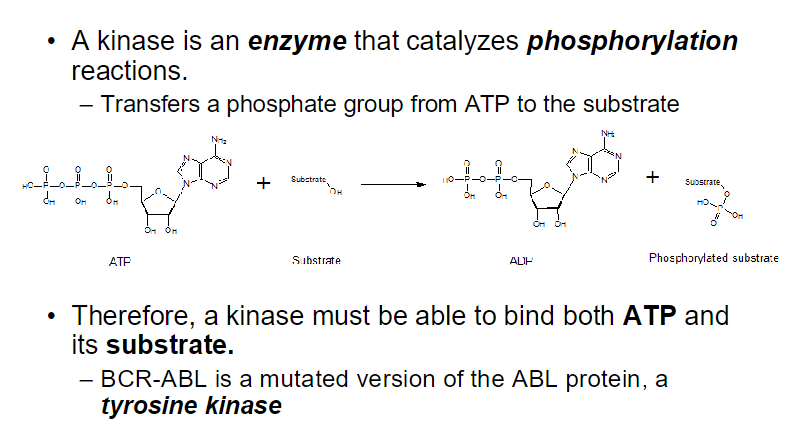
The BCR-ABL gene encodes a protein that is a constitutively active form of the ABL protein, a type of tyrosine kinase.
Tyrosine kinases are enzymes that catalyze the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to specific tyrosine residues on target proteins. This phosphorylation can lead to changes in protein function and signaling pathways.
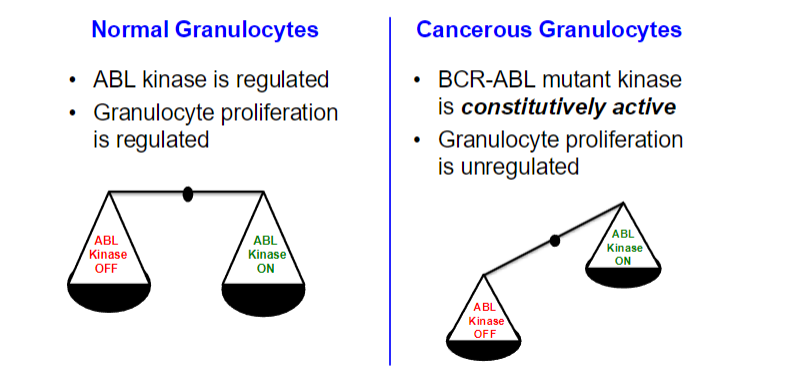
The BCR-ABL protein’s constitutive activity means that it is always "on," leading to uncontrolled cell division and the survival of granulocytes.