Atoms and the Periodic Table
Atoms (Review and NEW information)
Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter, consisting of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Subatomic Particles (TEST!!!)
Protons (positive charge) are in the nucleus.
Changes the identity of the element.
Neutrons (neutral charge) are in the nucleus.
Adds mass to the nucleus
Creates isotopes (example: C-12 and C-14)
Electrons (negative charge) orbit outside the nucleus.
Atomic number is defined as the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom, which determines the element's identity and its position on the periodic table.
Protons are ALWAYS equal to the atomic number
Examples
Lithium: Atomic # 3 = 3 protons
Palladium: Atomic #46 = 46 protons
Helium: Atomic #2 = 2 protons
Atomic mass is the weighted average mass of an element's isotopes, measured in atomic mass units (amu).
You can find the atomic number, element name, element symbol, and atomic mass on the periodic table.
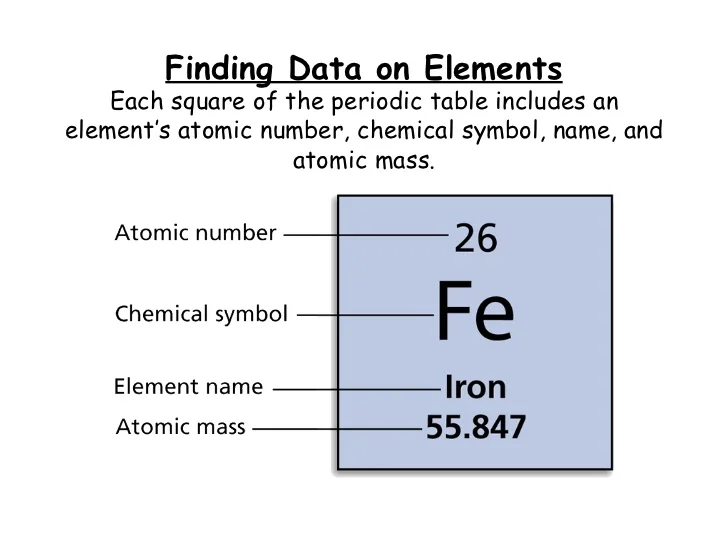
Isotopes (TEST!!!)
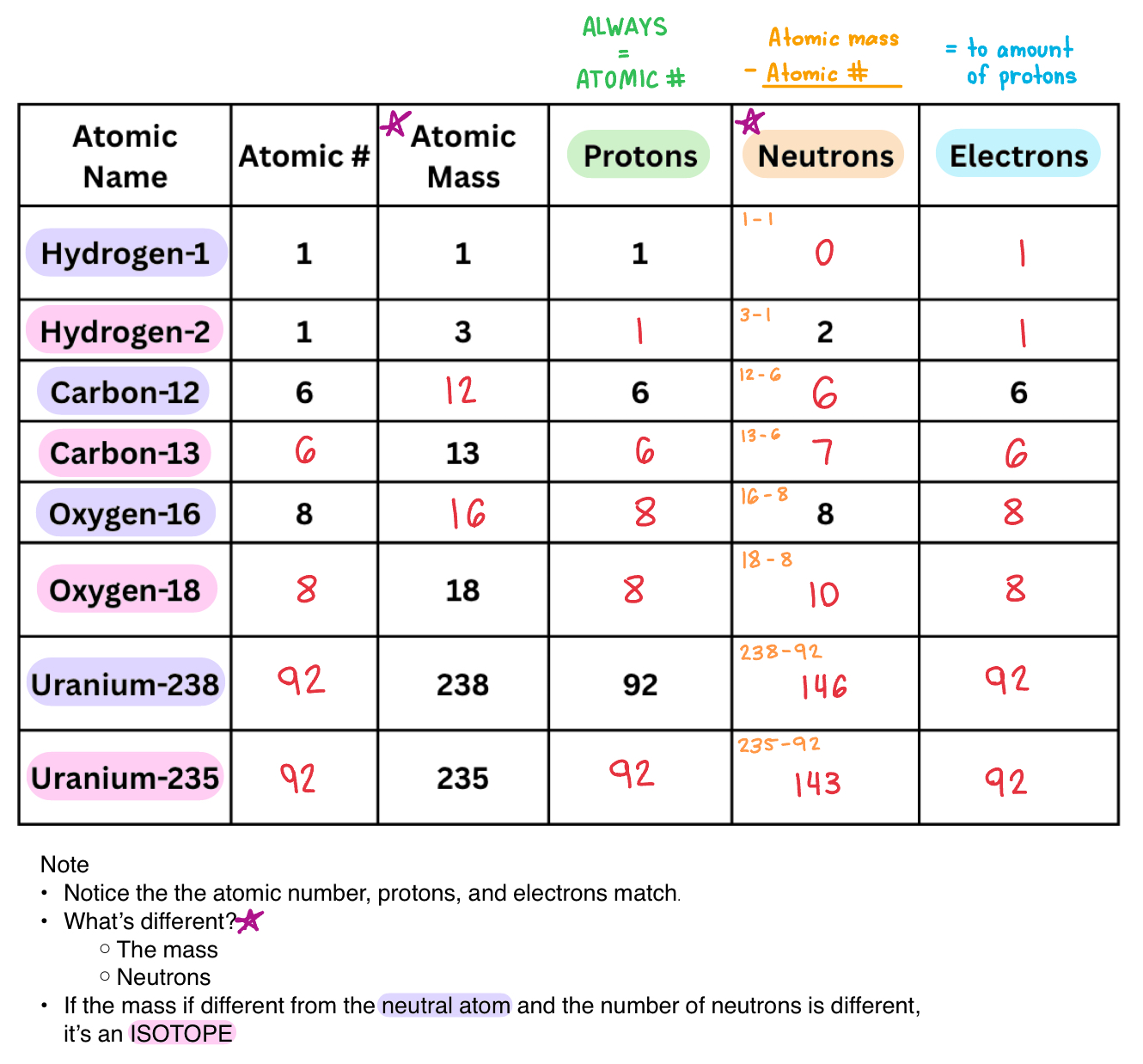
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with a different number of NEUTRONS.
Completing Isotope table examples (TEST!!!)
Helpful periodic table video: