NGSS Chemistry (ALL UNITS) - WIP
Highlight Key -
Key Vocab
Key Information
Key Formulas
Key Examples
BS Summary
***Collapse headers for best information experience
Unit 1
Significant Figures
All digits 1-9 inclusive are significant.
Example: 129 has 3 significant figures.
Zeros between significant digits are always significant.
Example: 5,007 has 4 significant figures.
Trailing zeros in a number are significant only if the number contains a decimal point.
Example: 100.0 has 4 significant figures.
100 has 1 significant figure.
Zeros in the beginning of a number whose only function is to place the decimal point are not significant.
Example: 0.0025 has 2 significant figures.
Zeros following a decimal significant figure are significant.
Example: 0.000 has 3 significant figures.
0.47000 has 5 significant figures.
Multiply/divide - Round to least number of sig figs in any of the factors.
eg: 23.0 cm x 432 cm x 19 cm = 188,784 cm3 The answer is expressed as 190,000 cm3 since 19 cm has only two significant figures.
Add/subtract - Round answer to least number of decimal places in any of the numbers that make up your answer.
eg: 123.25 mL + 46.0 mL + 86.257 mL = 255.507 mL The answer is expressed as 255.5 mL since 46.0 mL has only one decimal place.
Density
Less dense things → float
Denser things → sink
D = M/V
vvv - (Use Alg1 skills to figure out:)
M = DV
V = M/D
Matter
Temperature - Intensity of kinetic energy
Pressure - Amount of force applied to an object
Volume - Amount of space taken
Combined Gas Law
Combination of Boyle, Charles, and Amonton’s Law
P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2
Pressure and Temperature (PT) - Direct relationship
Volume and Temperature (VT) - Direct relationship
Pressure and Volume (PV) - Inverse relationship
Direct relationship - 1 thing increases, other thing increases
Inverse relationship - 1 thing increases, other thing decreases
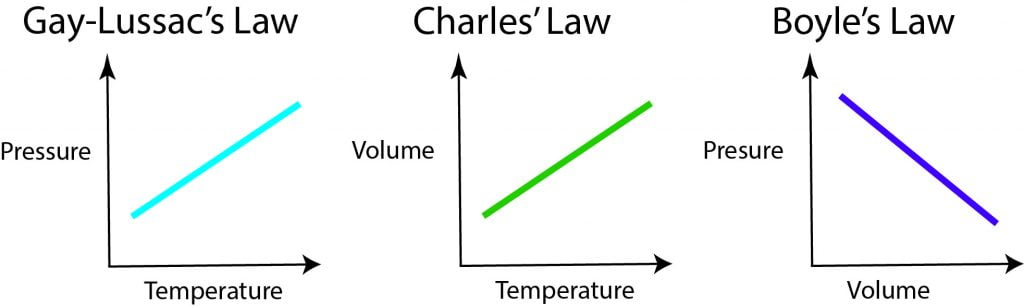
Ideal Gas Law
PV = nRT