1.3 The Power of Geographic Data Notes
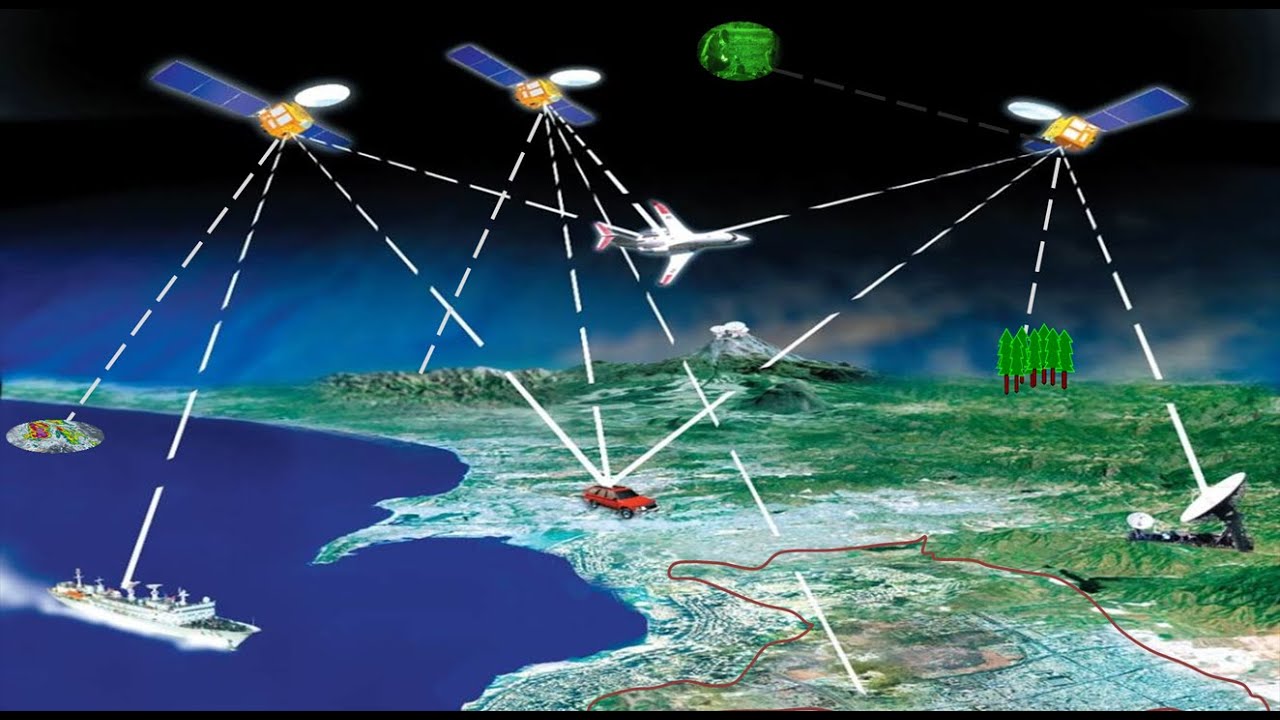
Geospatial data is data related to a specific point on the physical Earth. Geospatial data can be collected in two ways:
- GPS (Global Positioning System)- An example of this would be driving a car, to get from point A to point B
- GIS (Geographic Information Systems)- An example of this would be companies using GIS to analyze sites for future expansion
An example of geospatial data would be governments (of all scales) can make decisions about urban planning, transportation, infrastructure and funding programs.
1.3 IMPORTANT VOCABULARY
Geovisualization- 2D/3D interactive maps that allow people to zoom in or out to see the data in ways that were previously impossible
Global Positioning System (GPS)- These receivers use the locations of multiple satellites to determine and record a receiver's exact location
Geographic Information System (GIS)- Computer system that can store, analyze, and display information from multiple digital maps or geospatial data sets
Remote Sensing- The use of cameras or other sensors mounted on aircraft or satellites to collect digital images or video of the earth's surface