Physical and Cognitive Development in Middle Childhood
Physical and Motor Development
Body Growth
Slower growth rate
Rapid growth for girls
Influence of genes and nutrition
Stunted growth
Motor Development
Advancement of gross motor skills
Development of new interest
Advancement of fine motor skills
Contextual influences
Exercise
CDC: 1 hour of exercise a day to moderate to vigorous physical activity
The U.S. Children are not getting enough
Linked to reduced fat, increased strength reduced blood pressure, and reduced risk for metabolic disease
Aerobic exercise also benefits
Children’s attention and memory
Effortful and goal-directed thinking and behavior
Creativity
Health, Illness, and Disease
time of excellent health
Accidents and injuries
Motor vehicle accidents are the most common cause of severe injury
Bikes, skateboards, skates, etc.
Overweight Children
17.5% 6-11 yo in U.S. are obese
heredity and environmental causes
consequences - diabetes, hypertension, elevated blood cholesterol levels, low self-esteem, teasing
intervention programs
combination of diet, exercise, behavior management
emphasize parents engaging in healthier lifestyles
healthier food family exercise
Cancer
2nd leading cause of death in children 5-14
The most common child cancer is leukemia
Children with cancer are surviving longer because of advancements in cancer treatment
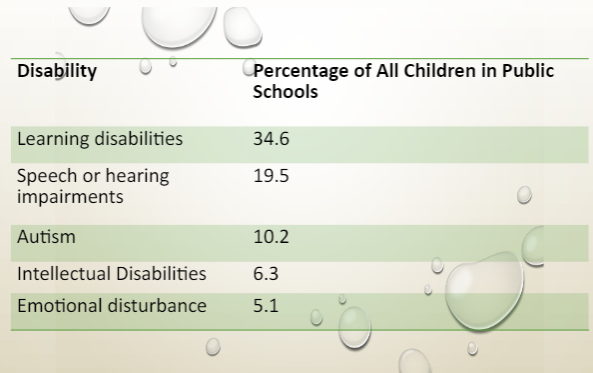 ADHD
ADHD
inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity
boys are twice as likely to receive ADHD diagnosis
possible causes
Genetics
Brain damage during prenatal or postnatal development
Cigarette and alcohol exposure during prenatal development
high maternal stress during prenatal development
low birth weight
Learning Disabilities
Dyslexia - Severe Impairment in the ability to read and spell
Dysgraphia: difficulty in handwriting
Dyscalculia: Developmental arithmetic disorder
Educational Issues
Individualized education plan: written statement specifically tailored for the disabled student
Least restrictive environment: setting as similar as possible to the one in which non-disabled children are educated
Inclusion: Educating a child with special education needs full-time in the regular classroom
Cognitive Development
Memory and executive function in children
Improved selective attention
improved wm, encoding, and recall from ITM
role of prior knowledge
Faster processing speed
Improvements due to the development of the prefrontal cortex
influence of schooling quality of relationships with teachers
Concrete Operational Stage
Ages 7 - 11
Children can perform concrete operations and reason logistically and can classify things into different sets
Inductive Reasoning: A logical process in which multiple premises are believed to be true are combined to obtain a specific conclusion
Intelligence
Ability to adapt and learn from experiences
Binet tests
mental age MA: Individual level of mental development relative to others
intelligence quotient IQ: a person’s mental age divided by chronological age multiplied by 100
normal distribution
Intelligence Tests
Wechsler Intelligence scale for children
10 subtests and five indexes
verbal and nonverbal abilities
supplemental subtests
IQ and academic achievement
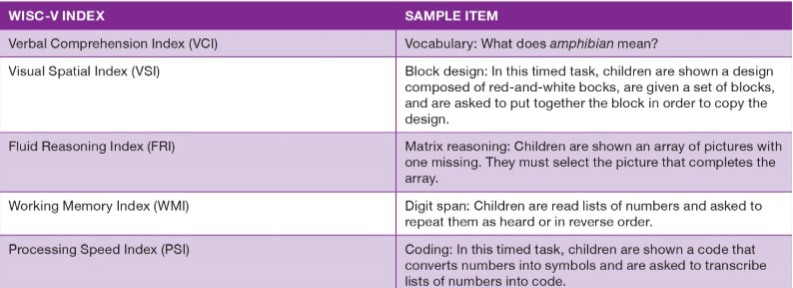 Alternative views of intelligence
Alternative views of intelligence
Sternberg Triachic Theory of Intelligence
Analytical, creative, and practical intelligence
cultural; the importance of intelligent behavior
Gardner’s Multiple Intelligences
eight independent kinds of intelligence
Binet general and specific intelligence
Sternberg Triarch theory of intelligence comes in the following forms
Analytical
creative
Practical
Agarders eight frames of mind
Learning and Schooling
transition to first grade
influences teachers’ and child perceptions
important role and interactions with teachers
foundation for child educational career
bilingual ism and learning a second language
Simultaneous bilingualism
second language learning
immersion
dual language learning
changing language preferences and dominance
Gifterd: above average intelligence (IQ of 130+) and /or subior talent for something
three characteristics
Precoiyt
march9ign to their own drum
mastery orientation
Gene-environment interaction
Domnain specific gistedness and development
Educationof children who are gisted
Moral Development
Kohlberg’s Level 1: Preconventional Reasoning
Morality not internalized
Stage 1: Heteronomous Morality
Moral decisions are based on fear of punishment.
Children obey because adults tell them to.
Stage 2: Individuals, Instrumental Purpose, & Exchange
Individuals pursue their own interests & let others do
the same. What is right involves equal exchange.
Kohlberg’s Level 2: Conventional Reasoning
Individuals abide by internal and external standards, forexample, parents, law
Stage 3: Mutual interpersonal expectations,relationships, and interpersonal conformity
Trust, caring, and loyalty to others valued as a basis formoral judgments
Stage 4: Social System Morality
Moral judgments based on understanding, social order,law, justice, duty