NOTES FOR RECI
2 functions of business
marketing
innovation
Marketing eras
1.0 - product centric
markets product than a specific need
2.0 - customer centric
customer needs and interests ex. skincare
3.0 - human centric
personal desire to form interactive connections and build meaningful relationships.
4.0 - traditional marketing coexisting with digital marketing
combines style with substance to build brands and fosters human-to-human connections for stronger consumer engagement.

5.0 - technology for humanity
market - regular gathering of people for the purchase and sale of provisions
marketplace - open square or place in a town where markets r held
main objectives business orgs should achieve:
attaining a position of comp advantage
enhancing a firm’s performance vs competitors
2 parts of definition of marketing
customer analysis
competitor analysis
customer value - level of satisfaction customers have with your product or service
4 PS
Product
price
place
promotion
7 PS
Product
Price
Place
Promotion
People
Physical Evidence
Process
Product Strategy
Vision
goals
Initiatives
3 drivers of customer value
need
want
demand
5 level of products
core product
basic product
expected product
augmented
potential
market skimming - high price, low volume
market penetartion - low price, high volume
status quo pricing - matching competitors price
prestige pricing - higher price of product when its unqieu
product line pricing - price steps between various products
psychological pricing - emotions fo customers
odd even pricingg - odd prices like 888
reference pricing - product is below a customer’s price
everyday low pricing - setting a low price for products consistently ex. walmart
multiple unit pricing - less payment for multiple units of same product
bundle pricing - package of goods or services for a lower price
differential pricing - pricing aligned w demand and supply ex hotels
product form pricing - different variants of the same product ex. car w diff color
image pricing - pricing is based on image differences of the same product ex. cheez whiz and its different packages
channel pricing - distribution channels as a factor in pricing
location pricing
time pricing
customary pricing - product price is consistent over time
price elasticity - change in demand with unit change in price
MODULE 8
The physical environment - where firm and customer interacts
Process - a series or steps taken to achieve a particular end
Service - can't be experienced until delivered. Demonstrated through testimonials, customer feedback, and referral business
intangibility- services cannot be seen, tasted, felt, heard, or smelled before purchase
inseparability- services cannot be separated from their providers
variability- quality of services depends on who provides them
perishability - services cannot be stored for later sale
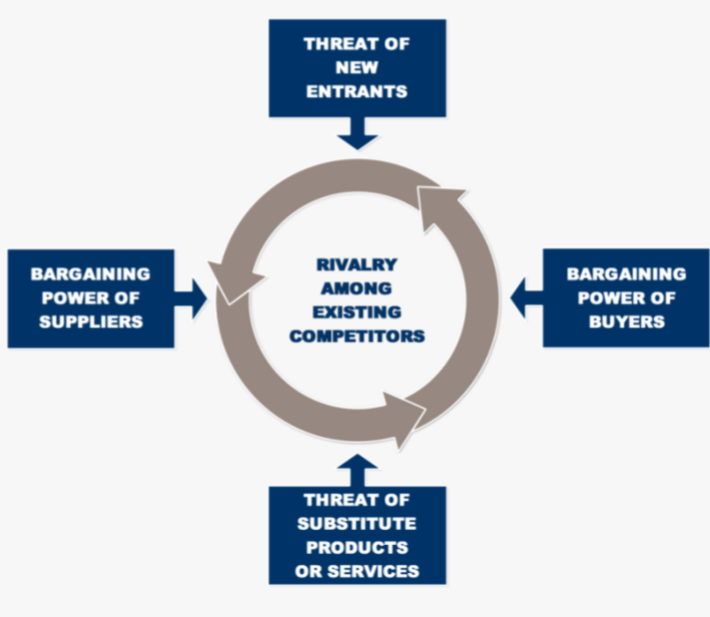
7 Ps of MARKETING: Product Price Place Promotion People Process Physical environment Porters generic strategies - how companies achieve competitive advantage
cost leadership - to gain profit or market share
differentiation - offers unique valued attributes
focus strategy - narrow market segment
cost focus
differentiation focus
MODULE 7 PLC and BCG
Product Life Cycle:
Intro ->
penetration pricing - low price for a new product to attract many buyers
selective distribution - a small number of retail outlets r chosen to distribute the products
skimming pricing - Involves setting a high price for a new product to skim
maximum revenue from the segments willing to pay the high price
Growth stage ->
increase product share
economies of scale - greater quantity, lower per unit fixed cost
internal
external
Economies of scope - cost savings by sharing resources and transferring core competencies
maintained pricing
flanker products - “fighter brands” offer a new product within an existing category to boost market share
maturity->
market is saturated, branding is crucial, products focus on differentiation, distribution intensified
decline stage
intense price cutting, cost cutting to improve profits even when it leads to many product withdrawal
a firm has 3 options
maintain the product
harvest the product
discontinue the product
objectives and strategies of PLC
awareness and trial, maximize market share, maximize profits; defend share, milk the brand
BCG Matrix - prioritize business products and guide resource allocation; x axis - relative market share, y axis - market growth
question marks
stars
cash cows
dogs
market size - number of indivduals who r potential buyers
market share - company’s portion of sales within the entire market it operates
market growth - an increse in the demand of product
most businesses start as a question mark
new ventures in high-growth market. if it doesnt gain market share, it becomes a dog
stars are successful question marks
cash cows have a superior market position but have low costs
dogs - weak market share in low growth markets
SESSION 6
Promotional Mix Methods
traditional marketing - any type of promotion in use by companies for years, proven success rate
Above the line advertising - mass media methods, builds the brand, large audience
ex. when a newspaper asks customers to visit and avail discounts/freebie
below the line advertising - non traditional advertising, drive sales, tangible incentive
ex. when customers finally visit the store, product sample
through the line advertising - involves atl and btl for maximum growth of brand
public relations - positive RS between organization, media, and public
personal selling - firms rep and consumer one2one
sponsorship - org is paid to use our branding
but, what is your message?
promo strategy - reaching your audience
media mix - how to get your message seen
marketing mix
products, price, place, and promotion
off shoring - basing company’s processes overseas
reshoring - moving jobs back home
outsorcing - job functions done outside a company
new people paradigm - people strategy
STEEPLE Analysis - tool for scanning the external environment
socio cultural factors
technological factors
economic factors
environmental factors
political factors
legal factors
ethical
demographic
macroenvironment - conditions in the economy
microenvironment - internal env of a company
political vs legal factors
political - government policy
legal - must be complied with
steeple should assess national and international laws
MODULE 4
place - how and where a company will place its products and services
distribution strategy
marketing channels - Refers to the entire system for getting products (tangible goods and intangible services) from the point of production to the point of
consumption
channel management - process where company develops various marketing techniques and sales strategy to reach customer base
distribution channel - chain of intermediaries through which the
product passed to get from the producer to the consumer.
direct: producer to consumer
indirect: uses intermediary
manufacturers - produces finished goods from raw materials
wholsalers - buy large quantities from suppliers, B2B
retailers - sells to consumers
direct channel marketing
B2B or B2C
common distribution outlets
intensive distribution - low priced products
exclusive distribution - single outlet, high prices
selective - small num of outlets. large geo spread
MODULE 9
marketing strategies r built on:
segmentation
targeting
positioning
shift from mass marketing to target marketing
STP process:
segmentation - identify bases
targeting - measure segment attractiveness
positioning - develop a value proposition and marketing mix
market segmentation - very important part of the market planning process
diving market into segments of common consumer that have common characteristics
divide consumers into categories
find right subset of ppl
we segment bc its a misconception that anyone can be a customer, and that there’s a considerable cost to reach everyone
4 methods u can group consumers into common cgaracteristics
demographic, psychographic (activities), behavioral, geographic
geodemographics - neighborhoods, nearby residents share similar demog and lfiestyles
requirements for effecitve segmenation
mesurable
accessible
substantial
differentiable
actionable
decision roles:
initiator
influencer
decider
buyer
use
MODULE 11
4 types of stratefies
SO strategies - use a firm’s internal strengths to take advantage of external oppirunities
ST strategies - Using a firm's strengths to avoid or reduce the impact of external threats
WO strategies - improves internal weaknesses by taking advantage of external opportunities
WT - defensive tactic
MODULE 12
Market segmentation - divide market into segments that have common characteristics
identify segments na sutiable target markets
target market - most potential customers
potential amrket - interested but not purchased
ideal customer - people with shared traits who are most interested in a product
customer segment - group of customers with similar characteristics
main purpose of targeting - define primary target market
PTM - core market
STM - we dont pursue directly, future primary buyers
TTM - wait and see group, will wait for product to be popular
MODULE 13
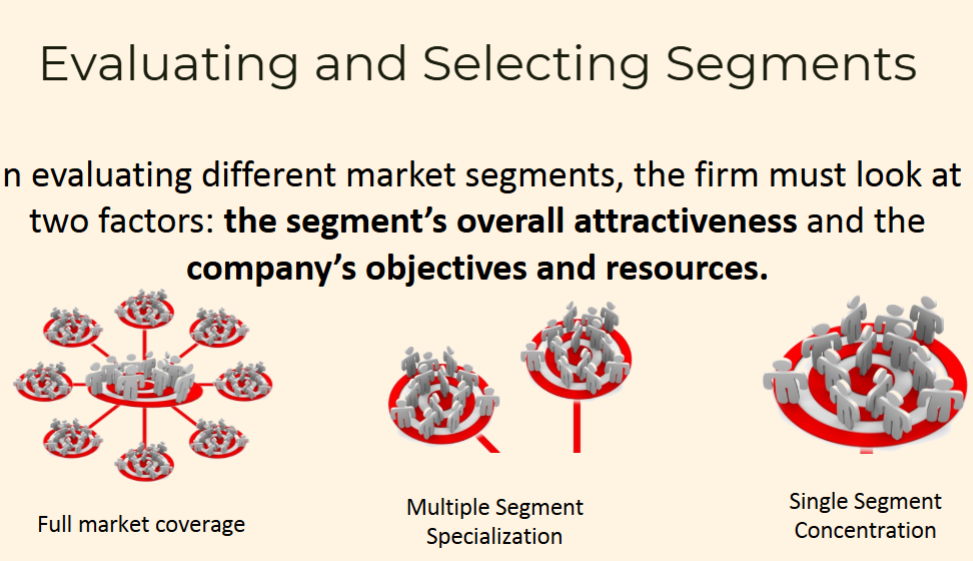
1. Mass Market (No Segmentation)
Everyone gets the same product and message.
Example: Toothpaste that says “for all ages” — no specific group is targeted.
2. Full Market Coverage
The brand tries to cover the whole market but with different messages or products for different groups.
Example: A car company selling economy cars, SUVs, and luxury cars to appeal to every kind of buyer.
3. Multiple Segments
The brand chooses several groups to target, each with its own marketing approach.
Example: A clothing brand with separate lines for teens, adults, and seniors.
4. Single Segment
The brand focuses on just one group and tailors everything for them.
Example: A vegan snack brand that only targets health-conscious millennials.
5. Individuals as Segments (Customization)
The brand customizes products or marketing for each person.
Example: Nike By You (custom shoes), Spotify playlists tailored to you.
positioning - creates a brand or product identity in target customers’ minds, where we want our product perceived
expensive and service
perceptual map - interpreted, customers brand perceptions
quality, value fo rmoney, service
In conclusion, perceptual mapping measures customer perception while positioning maps compare the actual traits of a company and its offerings.
Customer perception might be right or wrong.. But positioning maps only capture and compare reality