Science 9 - Unit 1
Defining species
Biological Diversity- Is the # and variety of organisms in an area (differences in characteristics)
The biological species concept is that a species is a group of organisms that can mate and produce viable offspring.
Reproductive isolation: Prevents members of 2 different species from cross breeding.
The only problem with this is that some species are asexual ( do not mate with other members of the same species). Ex: Bacteria
The phylogenetic species concept is when we classify groups of organisms based on their evolution history. Ex: Dinosaurs. Extinct animals use this method because it is good for defining organisms that are in different parts of the world and may look different.
The morphological species concept puts organisms with similar physical characteristics in the same species group.
Niche- Describes what you are. Narrow niche: Highly specialized role. Broad niche: a generalist, is able to withstand many conditions
Speciation- how a new kind of plant or animal species is created
Structural adaptation- Inherited characteristic (helps the organism physically survive)
Behavioral adaptation- Inherited behavioral characteristic (helps the organism survive)
Diversity index- measure of biological diversity in an area Wealth of diversity: When people and animals have many options
A generalist is an organism with generalized requirements, and 8 adaptations that allow them to survive
The Galapagos Finches: many types, live in the equator, small, there are 13 main islands, 13 species, certain kind of bird
Environment: Where a certain organism lives Specialization: Adaptations for surviving in a certain environment
Taxonomy
A species is a group of organisms that share similar genetics and physical characteristics, can inter breed and offspring
Binomial nomenclature is a system that is used to name species. (write the genus and species name in italics and capitalize the 1st letter of the genus) This was made by Carl Linnaeus. (Swedish naturalist who was alive in the 1700s)
There are 8 categories of classification. They are: domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species
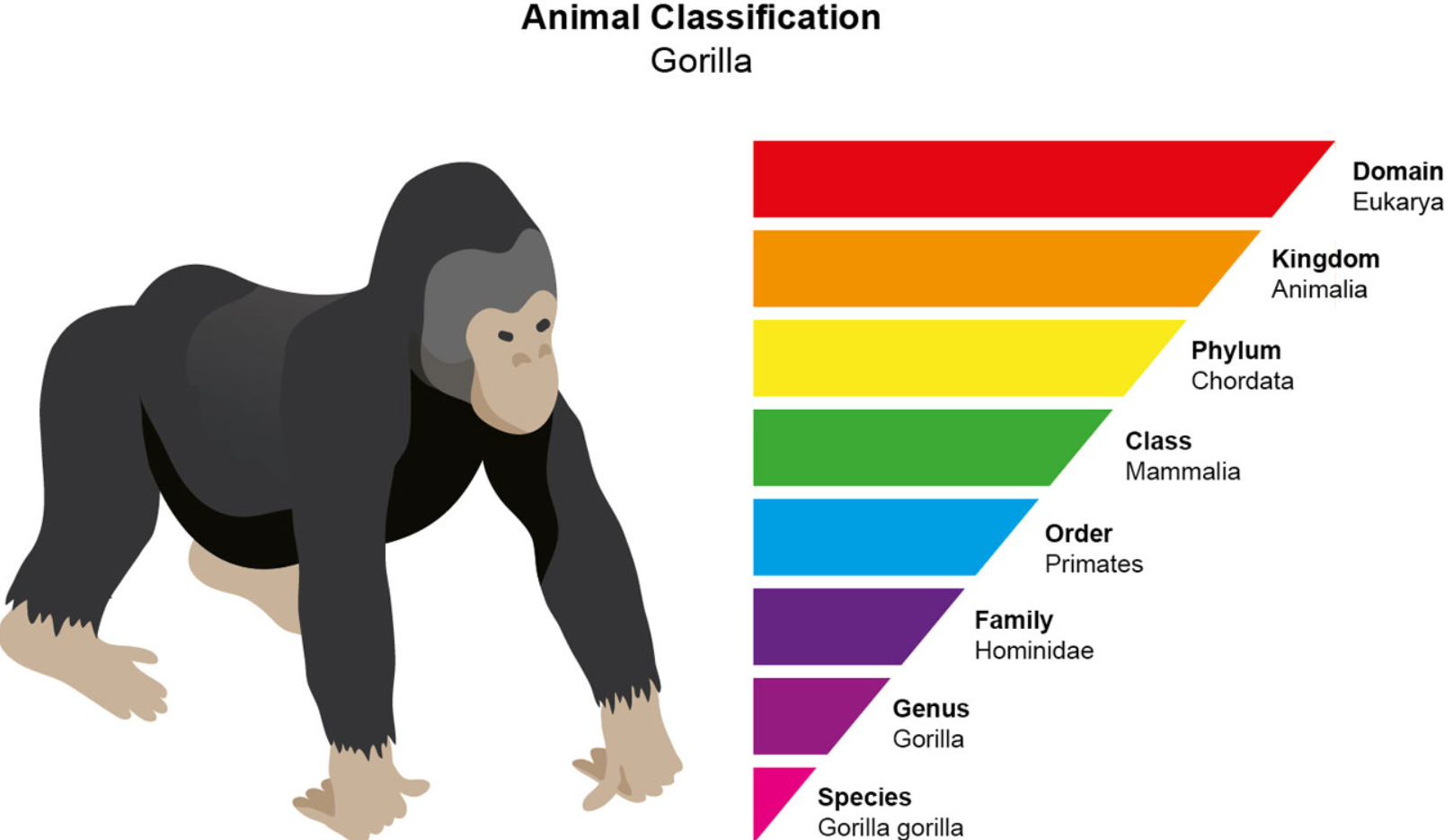
Prokaryotes: No membrane, nucleus, but they do have DNA! Eukaryotes have all 3
Domain= All of life fits! 3 categories: Bacteria, Archaea, (love the extremes, ex: methanogens) and Eukarya (all animals we know!)
Kingdom= Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia
The dichotomous keys are used to identify organisms ( Branching characteristics with 2 possible answers)
Interaction
Species interact with each other for 5 reasons. They interact for food, transportation, protection, reproduction, and health.
Prey, Predator , Competition (a struggle among individual resources in an area) . Symbiotic relationships: Mutualism (++) , Parasitism (+-), and Commensalism, (+0)
Reproduction
Binary fission- when a cell divides into 2 identical cells
Budding - Bud an identical offspring off of themselves. ( offspring just grows and falls of them)
Conjugation- transfer of genetic material between two bacteria of the same species
Gamete= reproductive cells. Each cell has 23 chromosomes
Diversity: Different from one another!
Spores are the way non seed plants reproduce. They can be found in the caps of mushrooms
Pollen tubes are tubes that transport male gamete cells from the pollen grain to the ovules.
Cotyledon- a seed leaf, a structure inside a seed that nourishes the plant embryo
Embryo- a multi cellular organism during early development
Self pollination- pollination of an ovule in a flower with pollen
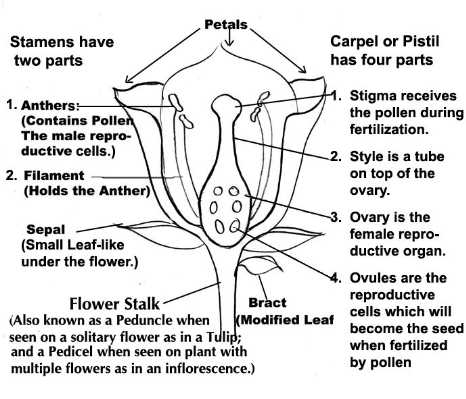
Definitions
Zoospore: A spore capable of swimming by means of flagellum
Zygospore: single celled reproductive structure, in sexual reproduction
Pistil: The seed producing female part of the flower
Pollen Tube: a tube through which sperm from the pollen reaches the egg cell, and fertilizes the plant to form seeds
Vegetative growth: when you take an offspring, put it in water, it grows a root, and you plant it.
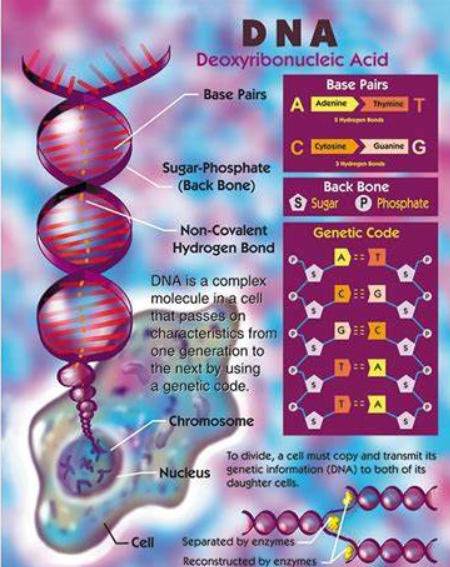
DNA is a molecule that stores genetic information.
Genes are a section of DNA on a chromosome
Cell division occurs twice
DNA
DNA is a molecule that stores genetic information.
Genes are a section of DNA on a chromosome
Interphase is where the cell grows and the chromosomes are duplicated
Traits are certain characteristics that an being has
Genetic engineering- the artificial introduction of genes
Bacterial conjunction- direct transfer of genetic material
DNA contains genes, which are instructions on how to build proteins. Proteins do many functions in cells, they are chemical messengers, they speed up chemical reaction and they fight infections.
Chromosomes are long pieces of DNA that are found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells.
Dominant trait: an inherited trait that shows up if the offspring has it
Recessive trait: an inherited trait that shows up if both parents have it.
Meristem is an area of cell division of an unspecialized cell
Mutation- a change in genetic information or DNA of an organism
Metagen- an agent hat can cause changes in the genetic information of an organism
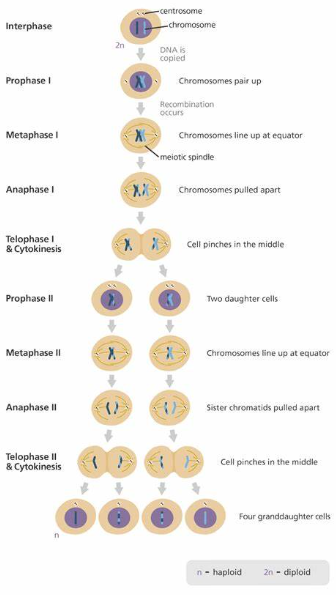
Meiosis (2 rounds)
Meiosis is a type of cell division that produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. It involves two rounds of division resulting in four daughter cells, each genetically distinct. Meiosis is essential for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes.
Before meiosis can happen, interphase happens. This is when the cell is growing, when its DNA replicates, and it begins having cell functions
The purpose of Meiosis is to make gametes
Makes sex cells
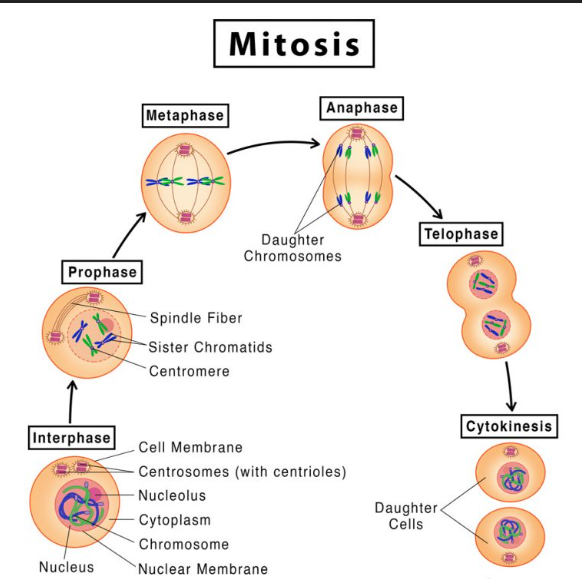
Mitosis
Mitosis is a type of cell division that results in two daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus.
What is the difference between Mitosis and Meiosis? Ans: Mitosis involves the division of body cells, while meiosis involves the division of sex cells and the division of a cell occurs once in mitosis but twice in meiosis
Makes Somatic Cells or Body Cells
Traits and Patterns
Traits are variations of a characteristic. Like short and tall. In this scenario, the height is a characteristic. Traits can be Inheritable, and Acquired.
A gene usually as 2 variations called alleles. If one allele is dominant over the other, it will determine the physical characteristic of the organism, even if the organism has one of the other recessive alleles
A continuous variation is a genetic trait that show a range of possibilities
A discrete variation is an inherited trait that has a limited number of variations
Heritable- a genetic characteristic that can be passed on by a parent to an offspring
Artificial selection
Is when humans decide which organisms reproduce
Natural selection
Is when an organism adapts to its environment
Ex: Kale, Broccoli
Biotechnology- using or modifying living organisms to make marketable products
Transgenic- organism produced by moving DNA from 1 organism to another
Agriculture- fish, Farming
Cloning
Is the process of producing an organism that is genetically identical to another organism
A GMO is an organism that contains a gene from a different organism or species.
Species at risk
Special concern category: Threatened or Endangered
Threatened species: likely to become endangered
Endangered species: Faces extinction in near future
Extirpated species: Gone in some places, found in others
Extinct: no longer exists.
The main reason of habitat loss is because of humans. We have: cleared animals land to build our homes, produced electricity, cut down trees, used the land to farm our own foods, and mining the land for our own treasures
Natural causes contribute to habitat loss as well, such as: flooding, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and climate change
Habitat degradation
Invasive species: thrives in a new environment and takes the niche of another organism
There are 4 ways that invasive species are controlled. They are: Mechanical control (physically killing) Chemical control (using herbicides to remove) Biological control (introducing another species that kills off the invasive species) and Desertification (when the productivity of the ecosystem is reduced)
Pollution
Over the past 100 years, pollutants like Co2 and nitrous oxides have been causing smog. This is very bad for ecosystems because it is toxic
Acid rain is formed when water droplets in the air react with pollutants like sulfur oxides to form acid.
Ph= its acidity