Integrated Marketing Communications
IMC Tools - Digital Media, Advertising, Direct Marketing, Consumer, Personal Selling, Public Relations (PR), Sales Promotion
Advertising - Most visible element of IMC, extremely effective at creating awareness and generating interest, different types of media have pros/cons, skeptical public?
Personal Selling - most expensive method, some products require the help of a salesperson, more expensive than other forms of promotion, good for complex transactions, dialogue is possible, greater customization opportunity
Sales Promotions - good for B2B (business to business) or B2C (business to consumer), can be used for both short-term, and long-term objectives, typically for short-term promotion bump, easy to measure, but be careful about negative long term implications
Direct Marketing - includes online advertising, email and mobile marketing, brand websites, and social media, it is easily personalizable, growth of databases has fueled the growth of direct marketing, new technologies (ex. ads triggered on Facebook based on your profile or where you are/live)
Public Relations (PR) - includes influencers and news channels etc., “free” media attention, importance of PR has grown as cost of other media has increased (social media has enabled execution), consumers becoming more skeptical about marketing, PR becoming more important (consumers informing consumers…. social media and PR are blurring)
An integrated marketing campaign can use social media, PR, search marketing and SEO, events, advertising, direct marketing, email marketing, internal communications, TV/radio, websites
Elements of an integrated marketing communication strategy include..
…personal selling, sales promotions (ex. contests), and direct marketing (ex. telemarketing), which are interactive and offline…
…direct marketing (ex. mobile marketing), online marketing (ex. blogs, social media), which are interactive and online…
…direct marketing (ex. email marketing), which are online and passive…
…and advertising, sales promotions (ex. coupons), public relations, direct marketing (ex. catalogs), which are offline and passive
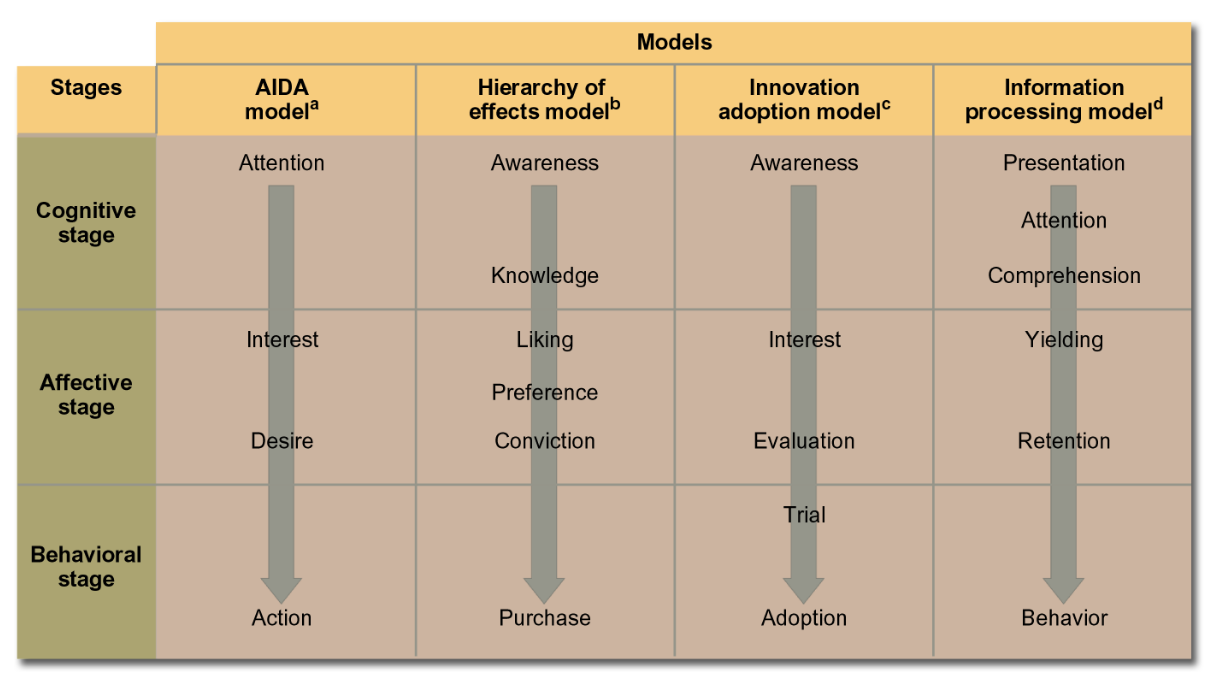
To use the AIDA model to help determine MISSION, goals for reaching customers should include attention (think; cognitive), to interest (feel; affective), to desire (feel; affective), to action (do; behavioral), the end goal being action
To use the Hierarchy of effects model to help determine MISSION, goals for reaching customers should include awareness (think; cognitive), to knowledge (think; cognitive), to liking (feel; affective), to preference (feel; affective), to conviction (feel; affective), to purchase (do; behavioral), the end goal being purchase
To use the Innovation adoption model to help determine MISSION, goals for reaching customers should include awareness (think; cognitive), to interest (feel; affective), to evaluation (feel; affective), to trial (do; behavioral), to adoption (do; behavioral), the end goal being adoption
To use the Information processing model to help determine MISSION, goals for reaching customers should include presentation (think; cognitive), to attention (think; cognitive), comprehension (think; cognitive), to yielding (feel; affective), to retention (feel; affective), to behavior (do; behavioral), the end goal being behavior
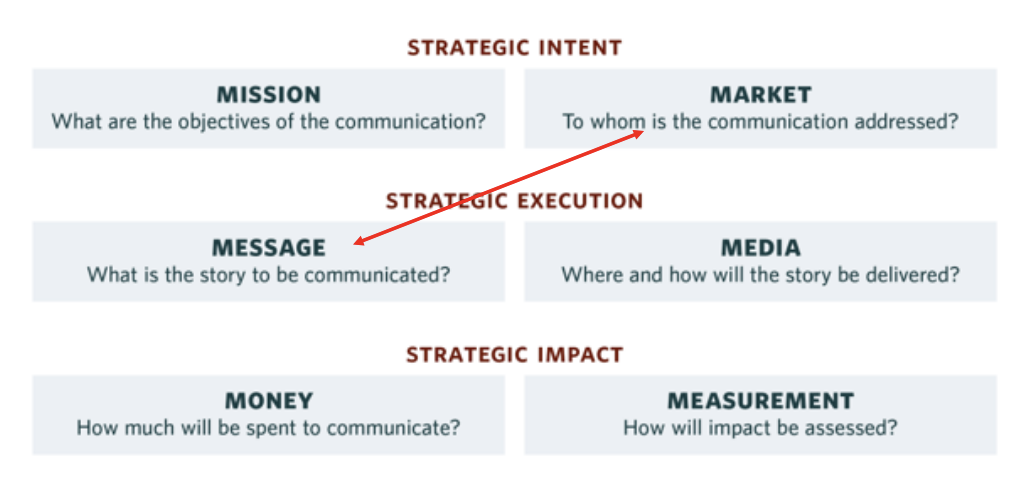
6 Ms of Communication - the first two are strategic intent, which includes mission (what are the objectives of the communication?) and market (to whom is the communication addressed?), the second two are strategic execution, which includes message (what is the story to be communicated?) and media (where and how will the story be delivered?), and the third two are strategic impact, which includes money (how much will be spent to communicate?), and measurement (how will impact be assessed)? … note: market and message typically stem from the positioning statement (point of differentiation and reason to believe affect the message)
Push and Pull Strategies - Pull strategies speak directly to the consumer and attract them (strategies include radio and TV advertising- speak directly to you about benefits), push goes through outbound communication and pushes messages to the audience through marketing channels
Considerations for budgeting in advertising: Importance of advertising within the overall IMC plan, complexity of message, reachability of target, level of involvement, nature of the product and market, competitive activity, state of your brand/product; methods include Objective-and-Task method or Rule-of-Thumb methods
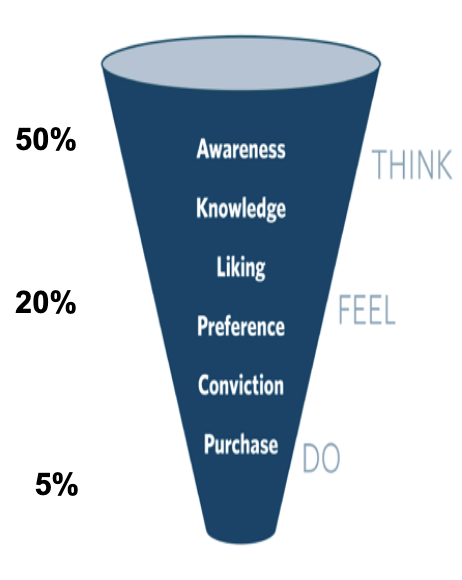
Objective and Task Method - Reflect back on AIDA model, what would it take to get 50% of your target aware? frequency required? Targeted (Gross) Rating Points = Reach x Avg. Frequency (50% reach x 6 =300, Note that could also be 60% reach x 5 = 300), Trade off between reach and frequency
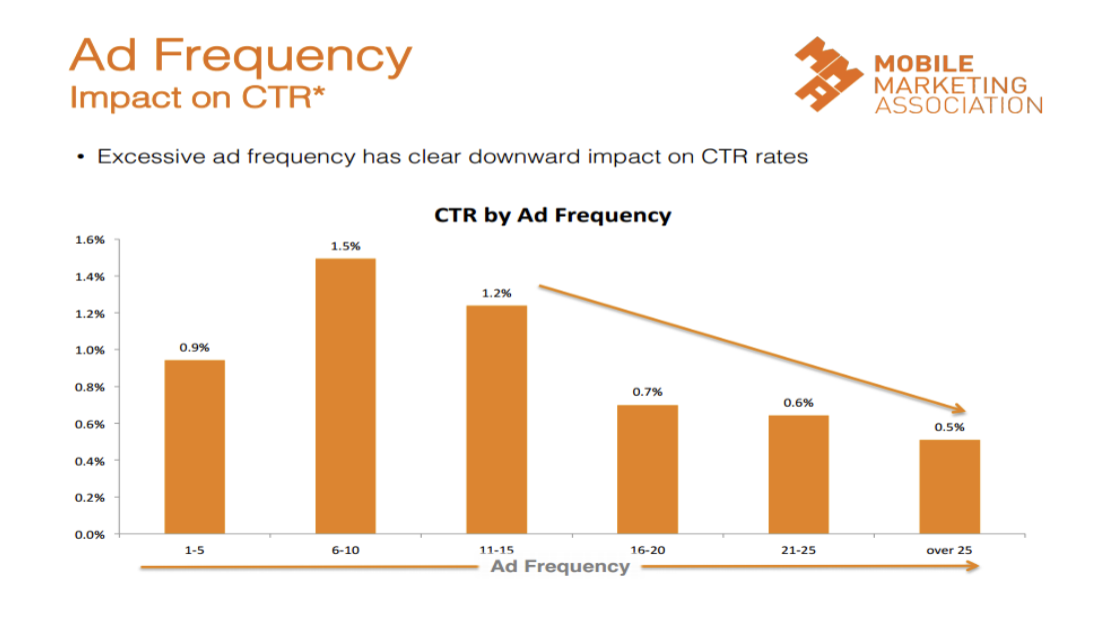
Within this method, watch out for… insufficient frequency, excessive frequency, agency will have to have some both in order to meet goals (not each and every person will be at correct frequency)
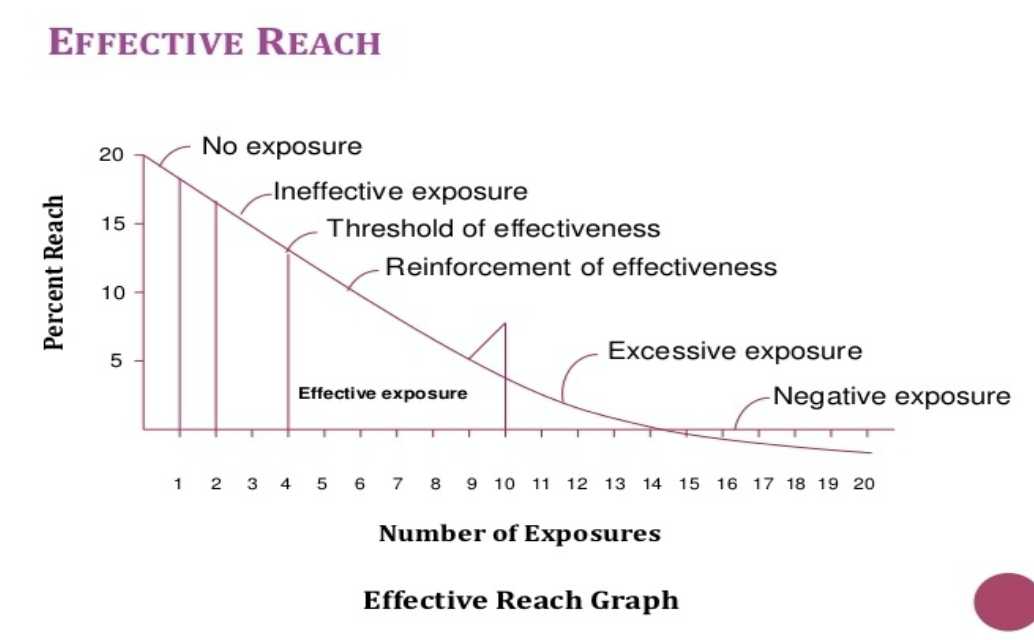
Effective advertising reach is within 4-10 promotion repetitions throughout around 6 months to a year according to studies
Lagged Effect - advertising does not always have an immediate impact, multiple exposures are often necessary, it is difficult to determine which exposure led to purchase