Cell Divison
Chromatid: each strand of a duplicated chromosome
Centromere: the area where each pair of chromatids is joined
Centrioles: tiny structures located in the cytoplasm
Spindle: a fanlike microtubule structure that helps separate the chromatids
Chromatin: DNA + histone proteins unraveled into DNA soup
Chromosomes: how we organize DNA
Mitosis: Asexual reproduction
Interphase: G1, S, G2
M phase: Mitosis, Cytokinesis
Mitosis: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase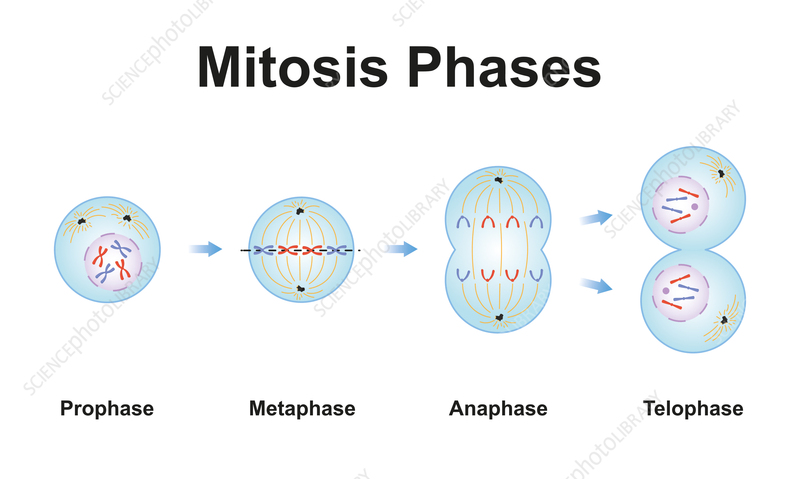
Prophase: duplicated chromosome condenses/becomes visible/ centrioles move to opposite sides of nucleus to help organize the spindle
Metaphase: chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell/spindle fibers connect the centromere to the two centrioles
Anaphase: centromeres are pulled apart + the chromatids separate to become individual chromosomes
Telophase: chromosomes spread out in a tangle of chromatin/nuclease re-forms around each cluster of chromosomes/spindle breaks apart, and nucleus becomes visible in each daughter cell
Cytokinesis: membrane is drawn in until cytoplasm is pinched into 2 = parts/ each part contains own nucleus/organelles
Meiosis: Mitosis for gametes
Steps in Meiosis: Meiosis 1, Meiosis 2, Fertilization
Meiosis 1: Homologous chromosomes are separated in 2 cells/there will be 2 cells but each cell was half ½ as many chromosomes
Prophase 1: crossing over segments of non sister chromatids/ break and reattach to the other chromatid
Metaphase 1: chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell/spindle fibers connect the centromere to the two centrioles
Anaphase 1: centromeres are pulled apart + the chromatids separate to become individual chromosomes
Telophase 1: chromosomes spread out in a tangle of chromatin/nuclease re-forms around each cluster of chromosomes/spindle breaks apart, and nucleus becomes visible in each daughter cell
Meiosis 2: similar process to mitosis
Prophase 2: duplicated chromosome condenses/becomes visible/ centrioles move to opposite sides of nucleus to help organize the spindle
Metaphase 2: chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell/spindle fibers connect the centromere to the two centrioles
Anaphase 2: centromeres are pulled apart + the chromatids separate to become individual chromosomes
Telophase 2: chromosomes spread out in a tangle of chromatin/nuclease re-forms around each cluster of chromosomes/spindle breaks apart, and nucleus becomes visible in each daughter cell/now there are 4 haploid (n) daughter cells
Fertilization: fusion of sperm and egg to form a zygote
Spermatogenesis: Process of using meiosis to make sperm— each sperm has 23 chromosomes
Oogenesis: Process of using meiosis to make egg— the result is 3 small polar bodies which gave all of its nutrients to the ovum
***Each Gamete can only have half of the chromosome by the end of the process
Regulating the Cell Cycle
Cyclins: a family of proteins that regulate the timing of the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells
Regulatory Proteins—
Internal regulators: respond to events inside the cell
External regulators: respond to events outside the cell
Growth factors: external regulators that stimulate the growth/division of cells
Apoptosis: process of programmed cell death/plays a role in development by shaping the structure of tissues, organs in plant, animals.
Cancer: body cells lose the ability to control all growth/ cancer cells divide uncontrollably to form a mass of cells (tumor)
Benign tumor: non cancerous
Malignant tumor: Cancerous/ spreads easily (metastasis)
Treatments: chemotherapy/radiation/surgery