9.1 Female Reproductive System
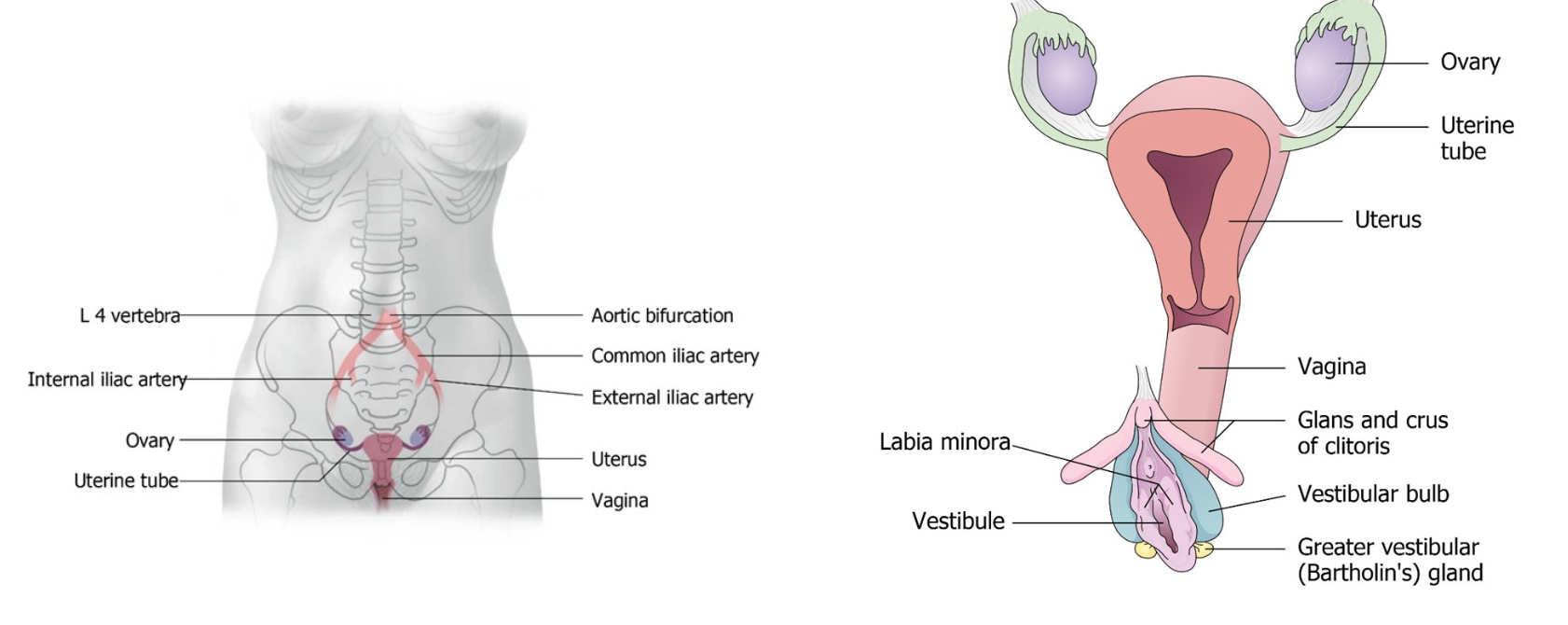
Female Reproductive Organs
Overview of Organs:
Gonads:
Ovaries
Produce ovum (egg cell)
Secrete female sex hormones
Ducts:
Uterine tubes, uterus, vagina
Collect, store and transport ovum and sperm
Accessory Glands:
Serous and mucous glands
Secrete lubricating and transporting fluid
Ovarie
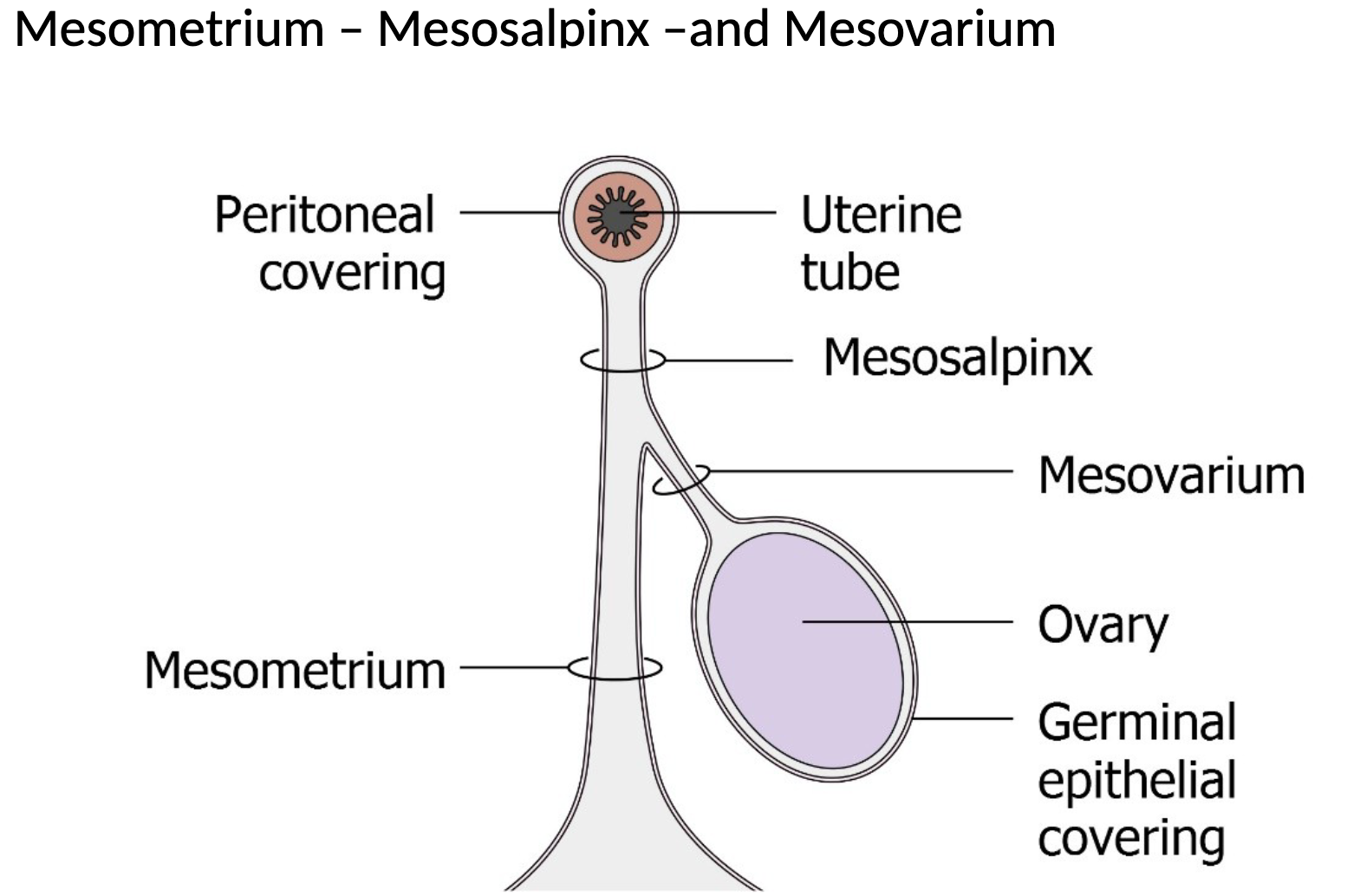
Structure: cortex - ovarian follicle and its derivatives and medulla inner layer
Hormones: production of ovum, secretion of progesterone & oestrogen
Development of Ovarian Follicles
Stages of Follicle Development:
Primordial Follicles:
The earliest stage present at birth
Primary Follicles:
Begin to grow and mature
Preantral Follicles:
Developing stage before antrum formation
Antral Follicles:
Formation of antrum filled with follicular fluid
Mature Follicle:
Ready for ovulation
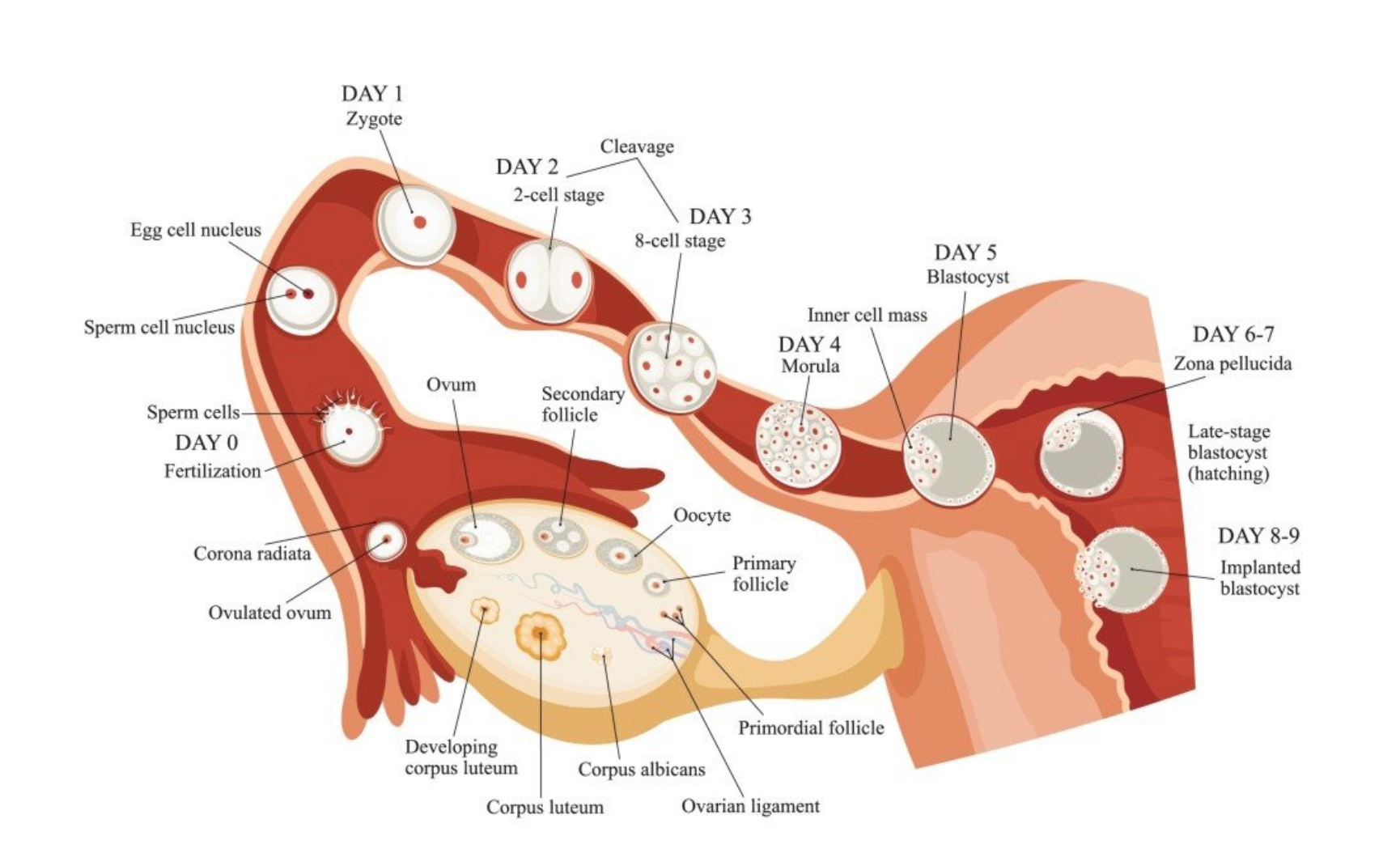
Ovulation and Fertilization
Ovulation Process:
Release of a mature ovum from the ovary
Typically occurs around day 14 of menstrual cycle
Fertilization:
Occurs when sperm meets ovum
Leads to the formation of a zygote
Role of the Corpus Luteum
Corpus Luteum Formation:
Forms after ovulation from the remnants of the mature follicle
Functions:
Secretion of progesterone and estrogen
Important for maintaining the uterine lining for potential implantation
Corpus Albicans:
Degenerated form of the corpus luteum if no fertilization occurs
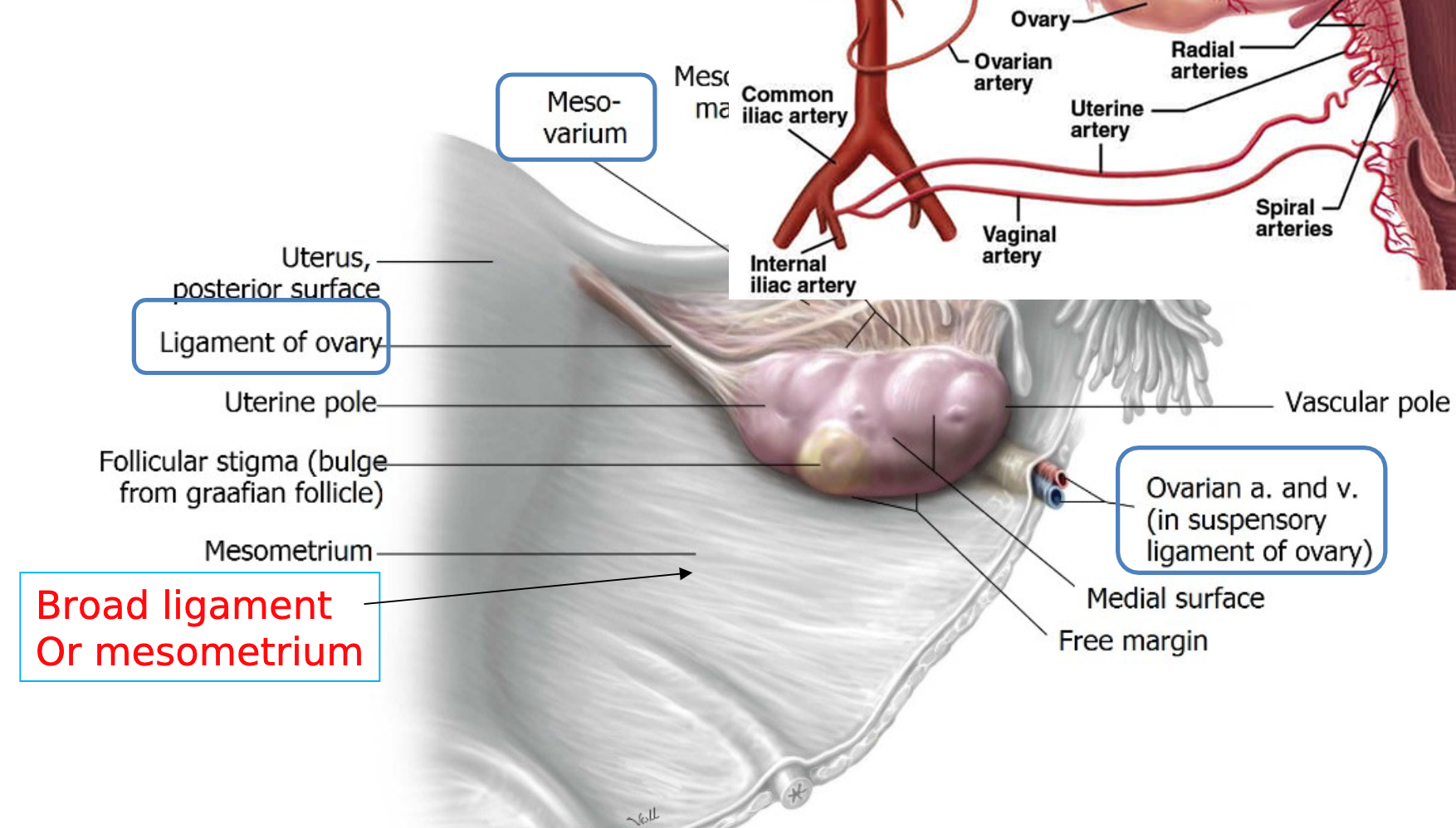
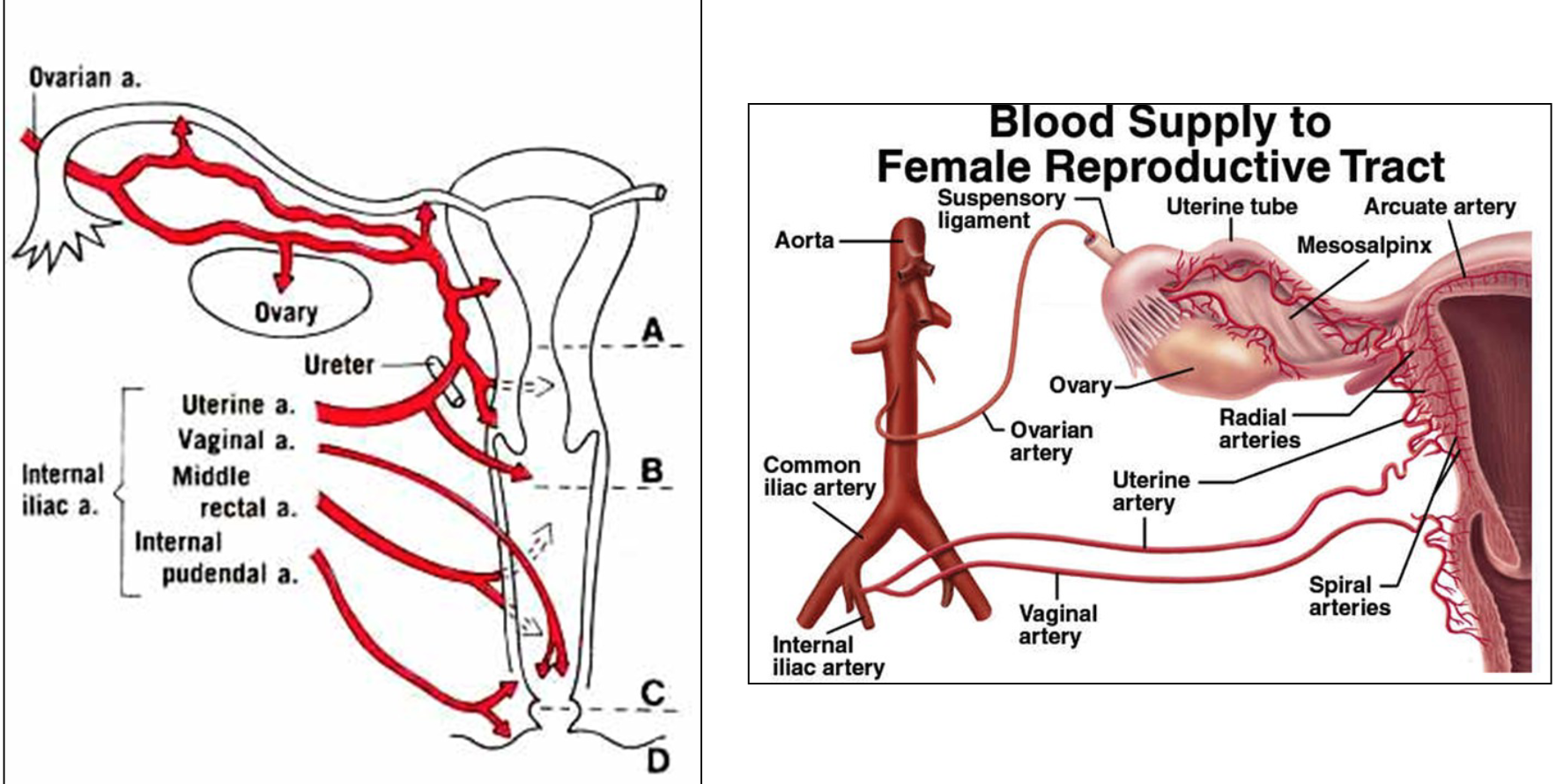
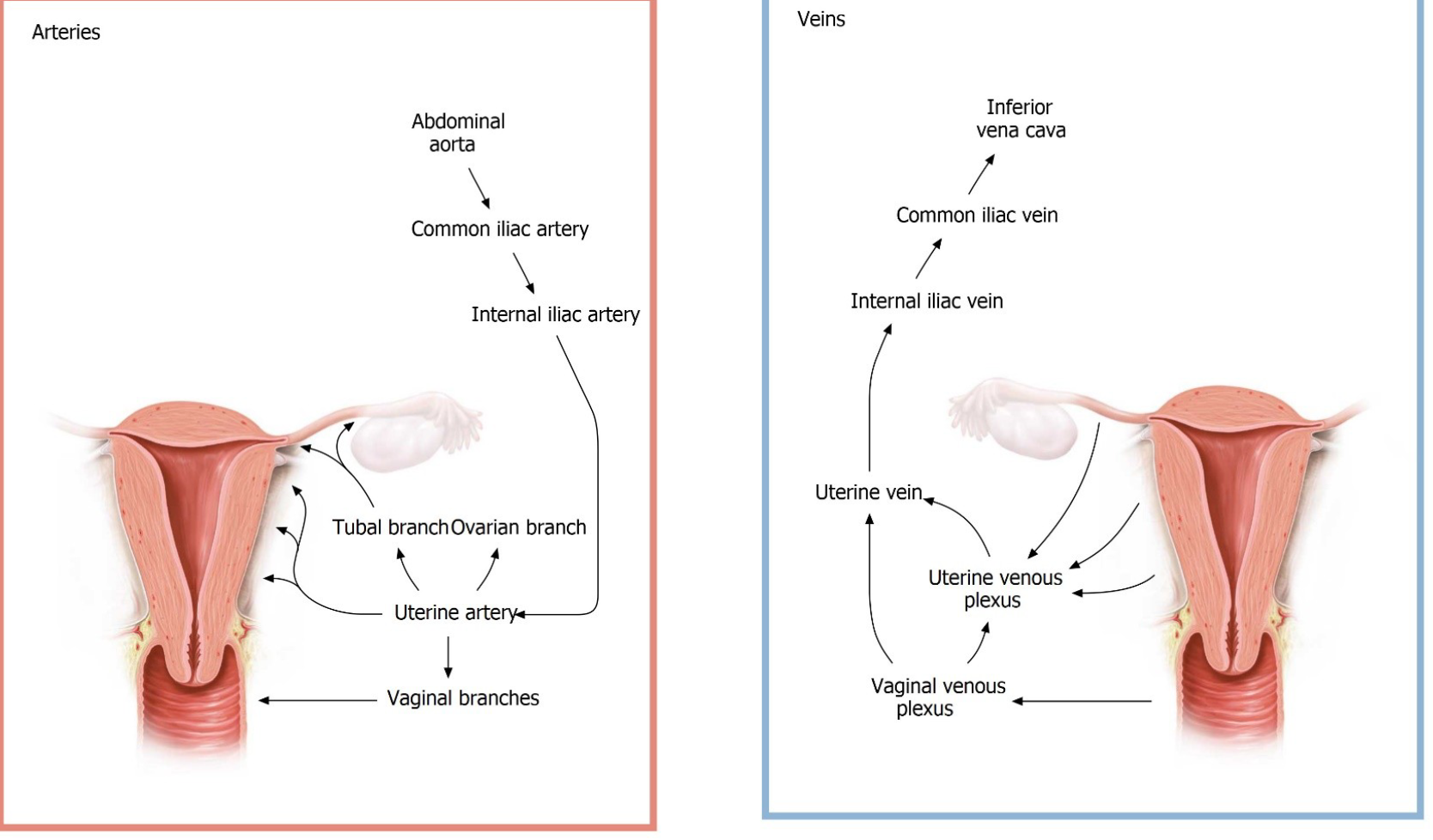
Blood Supply
Ovarian Blood Supply: dual
Gonadal Artery:
Branches from the abdominal aorta
Uterine Artery:
Arises from internal iliac artery
Arterial supply
• ovarian arteries from aorta
• branches of internal iliac (uterine, vaginal & pudendal arteries)
Venous Drainage:
Ovarian Veins:
Right ovarian vein drains into IVC (Inferior Vena Cava)
Left ovarian vein drains into the left renal vein
Nervous System Innervation
Somatic (S2-S4): pudendal nerve to lower vagina – sensory /
motorA. Parasympathetic (S2-S4): vasodilation of erectile tissue, motor to
vagina & uterus.B. Sympathetic (T12-L2): secretory, orgasm
Hormones: oxytocin for uterine contractions
Summary
Understanding of ovarian structure and function is crucial, as well as the process of ovulation and hormonal regulation during the menstrual cycle, blood supply, and nervous system innervation.