1.11 - CompTIA A+ Core 2
1.11 - Cloud Productivity Tools: Professor Messer
Email systems
Email systems: Mission-critical cloud email service (primary method of communication. Migrating email servers/systems to the cloud offers better connectivity, faster communication, integrated redundancy/backups, and centralized security services.
Examples: Outlook (Microsoft Cloud), Gmail (Google Workspace)
Storage
Storage: Cloud storage allows scalable, near-unlimited storage for organizations. Also allows data/files to be synchronized between different devices.
Sync/folder settings
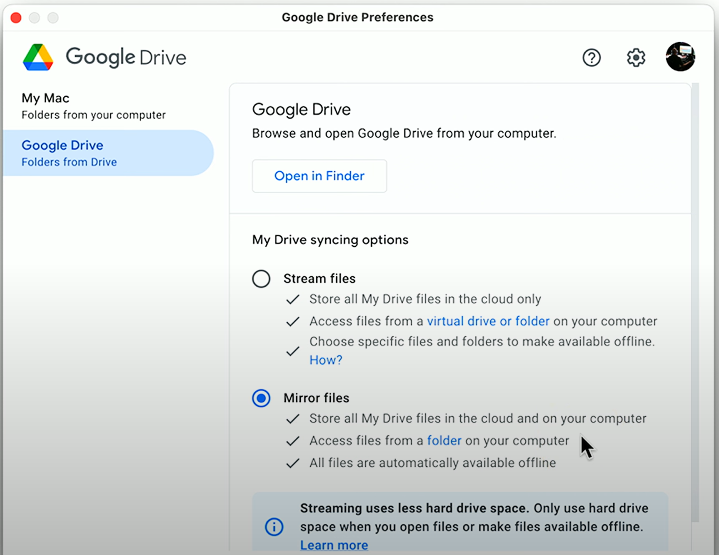
Sync/folder settings: Cloud storage services allow users to select which folders can receive cloud synchronization
Collaboration tools
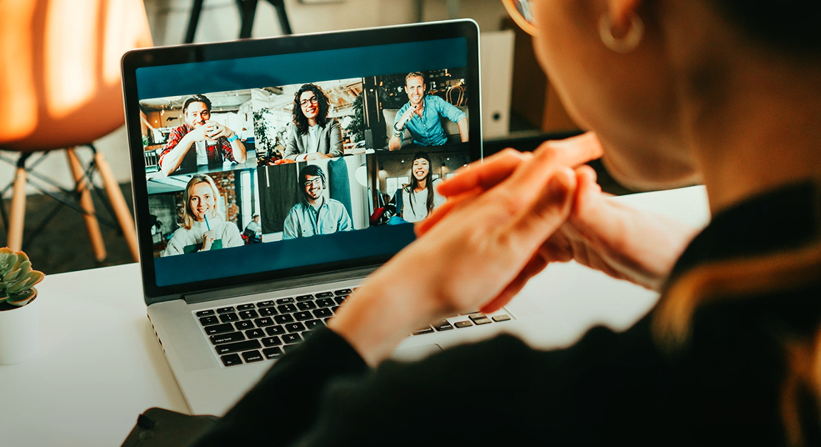

Collaboration tools: Cloud-based tools that allow you to work with other people in real-time.
Spreadsheets
Spreadsheets/spreadsheet software: Software that allows editing of documents in which data is arranged in the rows and columns of a table and can be used to perform calculations. Examples: Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets
Video conferencing
Video conferencing: Software that enables real-time communication between two or more participants in different locations using video and audio over the internet. Used to simulate face-to-face meetings/remote work. Examples: Zoom, Microsoft Teams
Word processing tools
Word processing tools: Software that allows the creation, formatting, and editing of documents. Examples: Google Docs, Microsoft Word
Instant messaging
Instant messaging: Software that allows text-based, real-time communication over the internet. Examples: Microsoft Teams, Signal, Telegram.
Identity synchronization
Identity synchronization: A process that ensures user identity data is consistent across multiple platforms and devices. Examples: Azure Active Directory, Microsoft Active Directory.
Licensing assignment
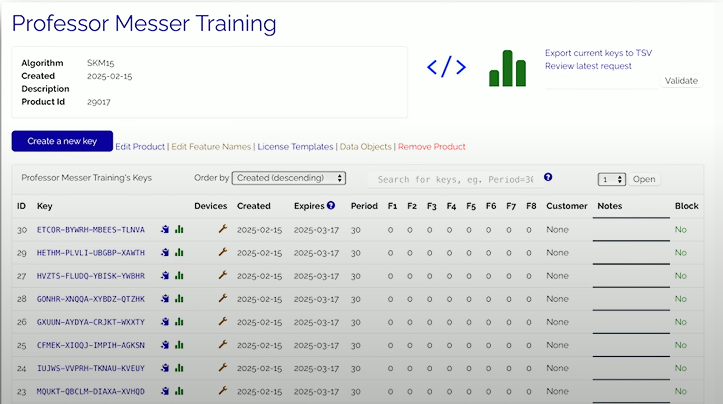
Licensing assignment: Allows distribution of digital license keys via the cloud. You can see every license owned for a particular software, and move licenses between users.