International Competitiveness
If Benin becomes more internationally competitive, it will sell even more cotton exports meaning export revenue will increase. Since exports are a component of AD, this will lead to an increase in AD. An increase in AD should in turn increase output and lead to higher living standards.
If an economy becomes less internationally competitive, it will sell fewer exports meaning export revenue will decrease. Since exports are a component of AD, This will decrease AD. A decrease in AD is likely to decrease output and lead to a decrease in living standards.
MEASURES OF INTERNATIONAL COMPETITIVENESS
Export prices
Unit labour costs
The global competitiveness index
Export Prices
If a country has low export prices foreign consumers are more likely to buy its exports meaning it is more competitive.
The price of oranges exported from Greece (€51) is lower than those from Spain (€62) meaning Greece is more competitive in terms of oranges.
If a country’s export prices are higher than its competitors’ then that country is less competitive.
A decrease in export prices will increase international competitiveness and an increase in export prices will decrease international competitiveness.
Unit Labour Costs
Unit labour cost tells us the average amount spent on wages per unit of output.
Unit labour cost is the cost of labour per unit produced, so:
Unit labour cost = Total wage cost/Total Output
UK’s Unit Labour cost = Total cost of UK labour/Total output in the UK
SRAS only shifts if there is a change in the cost of production. A reduction in the cost of production will mean that firms are willing to supply more for the same price and so SRAS will shift right.
 A decrease in export prices will increase international competitiveness.
A decrease in export prices will increase international competitiveness.
Unit labour cost is the cost of labour per unit produced, so:
Unit labour cost = Total wage cost/Total Output
If workers are really productive, their output will be higher. This means that the cost of producing one unit will be lower.
A higher minimum wage means that the total labour cost will increase which will also increase the unit labour cost. This is likely to make the UK less competitive.
An increase in a country’s unit labour cost means that each unit produced costs more in terms of wages. This increases production costs which leads to a reduction of SRAS and an increase in the price level. This makes exports more expensive and the country less competitive.
The Global Competitiveness Index
An index which attempts to rate the international competitiveness of different countries based on a variety of factors.
The Global Competitiveness Index measures a variety of factors including; infrastructure, health, education and technology.
Measure of international competitiveness annually calculated by the world economic forum
 The high quality of UK pharmaceuticals means that they are more competitive.
The high quality of UK pharmaceuticals means that they are more competitive.
India is more competitive as they have a higher competitiveness rating.
The UK is less competitive as they have a lower competitiveness rating.

Factors Influencing International Competitiveness
Exchange rates
Wage costs
Non-wage costs
Supply-side policies
Exchange Rate (International Competitiveness)
If the exchange rate depreciates, the opposite of SPICEE applies. That is, the price of imports increases and the price of exports decreases.
A depreciation makes exports cheaper meaning they get more competitive.
An appreciation makes exports more expensive meaning they get less competitive.
An exchange rate depreciation will decrease the price of exports and cause an increase in international competitiveness.
An exchange rate appreciation will increase the price of exports and cause a decrease in international competitiveness.
Wage Costs
Variable costs increase as output increases. For example, if a restaurant has a busy shift or wants to expand their output they will need to hire more workers and this will increase their wage costs.
Fixed costs, on the other hand, stay the same as output increases e.g. rent.
An increase in the cost of production will shift SRAS to the left and increase the price level.
A higher price level will make the UK less internationally competitive by making UK exports more expensive.
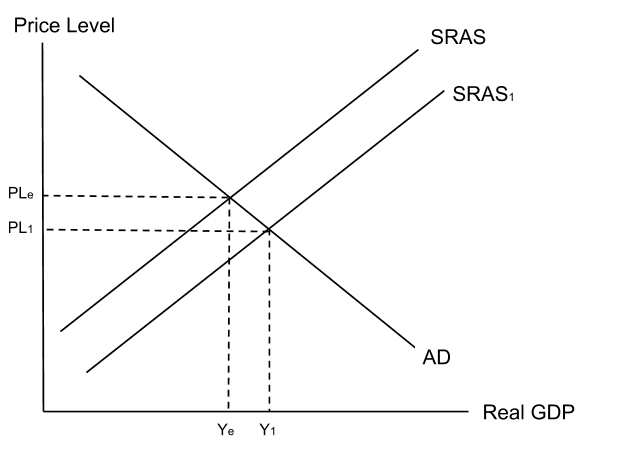
A reduction in the minimum wage will reduce the cost of production. Lower costs will increase SRAS and shift it to the right. This will decrease the price level and make the UK more competitive. This process is shown in the below diagram.
XxxnU.png) An increase in wage costs will increase the cost of production and lead to a left shift of the short-run aggregate supply curve. This will cause the price level to increase and make the country less internationally competitive.
An increase in wage costs will increase the cost of production and lead to a left shift of the short-run aggregate supply curve. This will cause the price level to increase and make the country less internationally competitive.
An decrease in wage costs will decrease the cost of production and lead to a right shift of the short-run aggregate supply curve. This will cause the price level to decrease and make the country more internationally competitive.
Non-Wage Costs
regulations
pensions
tax
China’s loose health and safety regulations lead to lower costs of production. This shifts China’s SRAS to the right and decreases the price level. This makes China more competitive.
Iranian employers do not have to contribute towards pensions. This reduces their labour costs meaning the cost of production is lower in Iran. This shifts Iran’s SRAS to the right and decreases the price level, making Iran more competitive.
Macedonia’s lower corporation tax means that hey have lower non-wage costs. A decrease in non-wage costs shifts SRAS to the right and decreases the price level meaning exports can be sold at lower prices. This makes them more competitive.
Moreover, if corporation tax is lower, companies can keep more of their profits. This can be invested in the factors of production which would reduce long run costs and lead to higher productivity. This would allow them to charge lower prices making them even more competitive.

Supply-Side Policies
Government policies which aim to increase aggregate supply
lowering corporation tax
increasing healthcare spending
A reduction in corporation tax means that firms do not have to pay as much of their profit to the government meaning costs decrease. This will shift SRAS to the right and decrease the price level.
A decrease in spending on healthcare means that there are fewer doctors and nurses available to help fight illnesses. It is therefore likely that there will be more illness in the labour force.
If more workers are unhealthy or ill they will be less productive at work. The productivity of labour will decrease and the LRAS will shift to the left.
An increase in the UK’s price level will make UK goods more expensive which will decrease the international competitiveness of their exports.
Supply-side policies can increase long run aggregate supply and short run aggregate supply. An increase in SRAS, LRAS or both will decrease the price level which will make exports cheaper and increase competitiveness.

 e.g
e.g
