Week 2 Demand, supply and market equilibrium
Chapter Overview
Essentials of Economics, Fifth Edition
Authors: R. Glenn Hubbard, Anne M. Garnett, Anthony O'Brien, Philip Lewis
Focus: Interaction of Demand and Supply
Learning Objectives
3.1 Demand Influencing Variables
Discuss various factors that influence the demand for goods and services.
3.2 Supply Influencing Variables
Discuss various factors that influence the supply of goods and services.
3.3 Market Equilibrium
Explain reaching equilibrium in the market using graphical illustrations.
3.4 Price and Quantity Changes
Predict changes in prices and quantities using demand and supply graphs.
The Tablet Computer Revolution
Introduction of iPad by Apple's CEO, Steve Jobs, in 2010 resulted in immediate success.
Competition emerged rapidly, impacting market dynamics positively for consumers (more choices, lower prices).
Ceteris Paribus Condition
Definition: Requirement that when analyzing the relationship between two variables, other variables must remain constant.
The Demand Side of the Market
Key Terms
Quantity Demanded: Amount of a good consumers are willing to buy at a certain price.
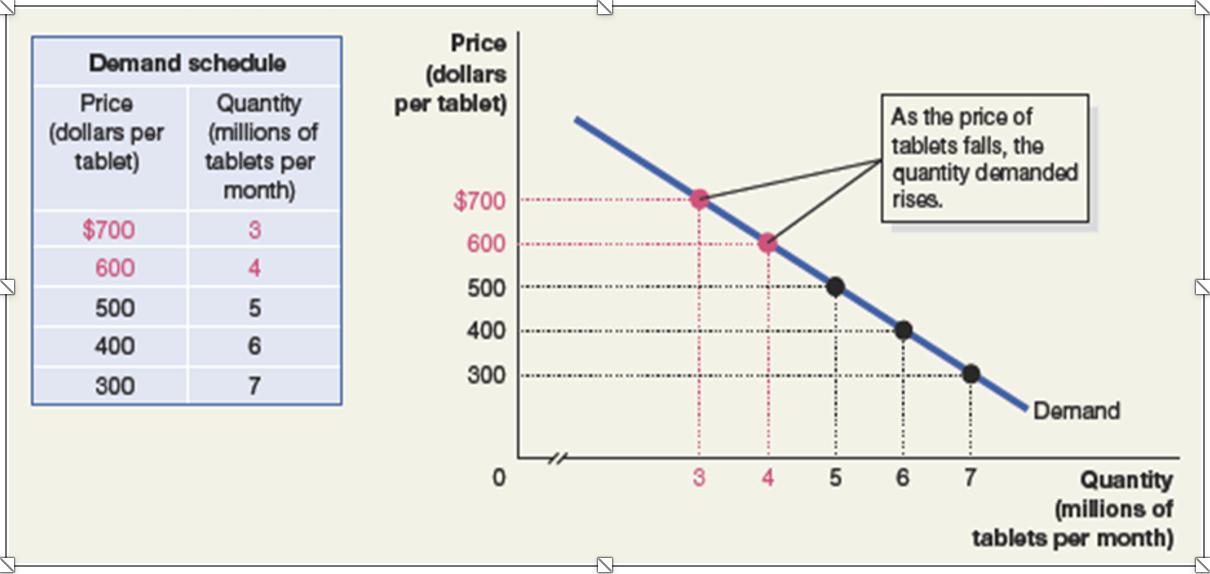
Demand Schedule: Table displaying the relationship between product price and quantity demanded.
Demand Curve: Graph showing the relationship between price and quantity demanded.
Market Demand: Total demand from all consumers for a good or service.
Law of Demand
Principle: The law states that, ceteris paribus, as the price of a product falls, the quantity demanded increases; conversely, when the price rises, the quantity demanded decreases, reflecting the inverse relationship between price and demand.
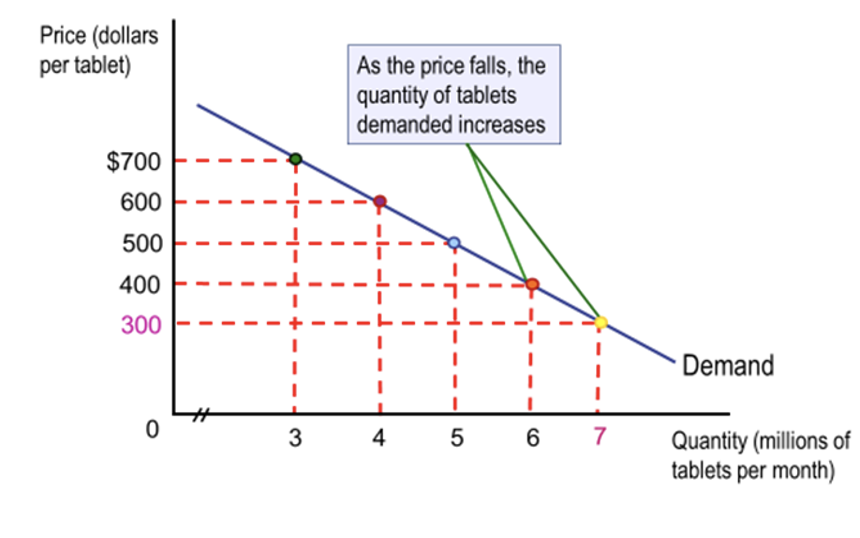
Changes in Demand
Quantity Demanded vs. Change in Demand
Change in Quantity Demanded: Movement along the demand curve due to a price change.
Change in Demand: Shift of the entire demand curve due to factors other than price.
Factors Influencing Demand Shifts
Income:
Normal Good: Demand increases with an increase in income.
Inferior Good: Demand decreases with an increase in income.
Prices of Related Goods:
Substitutes: Increase in the price of one good increases demand for another.
Complements: Decrease in price of one good increases demand for its complement.
Tastes and Preferences: Changes can shift demand based on new information or trends.
Population and Demographics: More buyers generally increase demand.
Expected Future Prices: Expectations about future price changes can influence current demand.
The Supply Side of the Market
Key Terms
Quantity Supplied: Amount of a good suppliers are willing to produce at a specific price.
Supply Schedule: Relationship between product price and quantity supplied presented in table form.
Supply Curve: Graph showing the relationship between price and quantity supplied.
Market Supply: Total supply from all firms producing a good or service.
Law of Supply
Principle: An increase in product price leads to an increase in quantity supplied; a decrease in price leads to a decrease in quantity supplied.
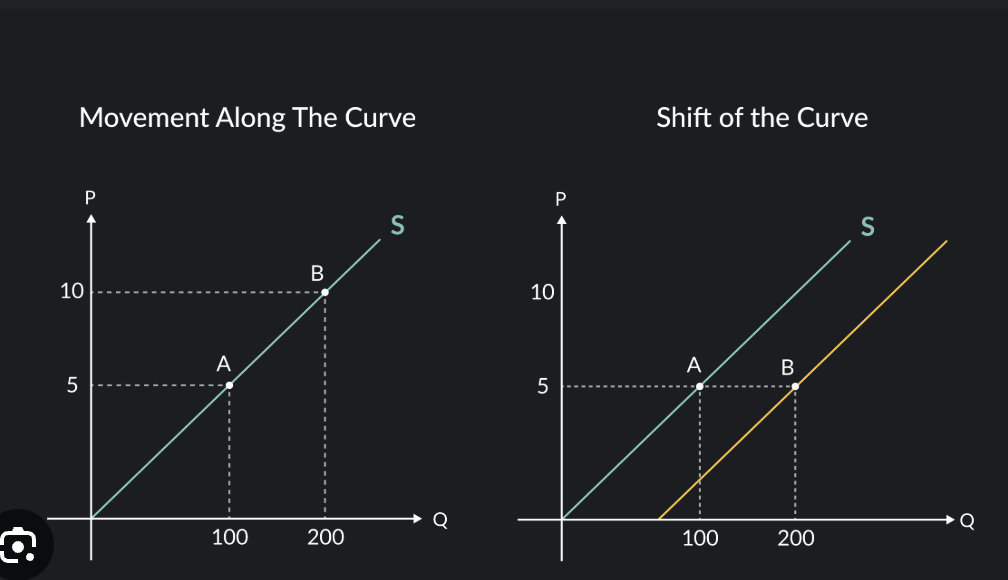
Changes in Supply
Quantity Supplied vs. Change in Supply
Change in Quantity Supplied: Movement along the supply curve due to a price change.
Change in Supply: Shift of supply curve due to factors other than price, creating new supply schedules.
Factors Influencing Supply Shifts
Prices of Inputs: Higher production costs reduce supply; lower costs increase supply.
Technological Change: Advances can lower costs and increase supply.
Productivity: Output per unit of input; higher productivity yields more supply.
Prices of Related Goods (Substitutes in Production): Price changes in alternative goods can affect supply.
Number of Sellers: More sellers in the market increase supply; fewer sellers reduce supply.
Expected Future Prices: Expectations of future prices affect current supply decisions.
Market Equilibrium
Definitions
Competitive Market Equilibrium: Many buyers and sellers interact, achieving a balance.
Market Equilibrium: Condition where quantity demanded equals quantity supplied at a certain price.
Equilibrium Price and Quantity: Price at which demand equals supply, and the quantity bought and sold at that price.
Effects on Market Equilibrium
Surplus: Occurs when the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded, resulting in downward pressure on prices as producers look to clear excess stock.
Shortage: Takes place when the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied, creating upward pressure on prices as consumers compete for limited goods.
Changes in Market Equilibrium
Increase in Demand:
Rightward shift in demand curve leads to higher equilibrium price and quantity.
Increase in Supply:
Rightward shift in supply curve leads to lower equilibrium price and higher quantity.
Simultaneous Shifts: Both demand and supply can shift simultaneously, affecting quantity but leading to ambiguous price changes.
Summary Tables
Shifts in Demand and Supply: Table detailing how shifts affect equilibrium price and quantity.
Check Your Knowledge Questions
Movement along the demand curve caused by price changes.
Factors that lead to shifts in supply curves.
Assessing surplus or shortage scenarios at given price levels.