Chapter 18: Metals
Metals
- Metals are found in group 1, group II and the Transition Block of the periodic table.
- As we go down the group there is an increase in metallic character.
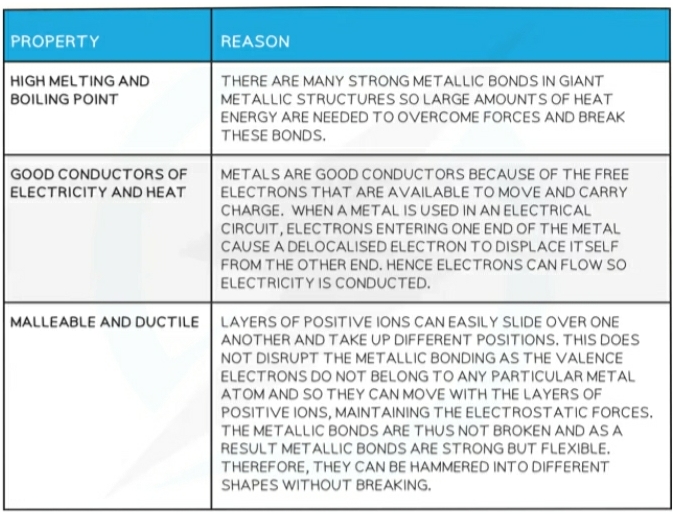
Properties of Metals
Reactivity with water
Metals react with cold water and form a metal hydroxide and hydrogen gas
[ ] metal + water → metal hydroxide + hydrogen
[ ] For example calcium: Ca (s) + 2H2O (l) → Ca(OH)2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Reactivity with acids
metal + acid → salt + hydrogen
[ ] Fe (s) + 2HCl (aq) → FeCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Reactivity with oxygen
- metal + oxygen → metal oxide
- [ ] 2Cu (s) + O2 (g) → 2CuO (s)
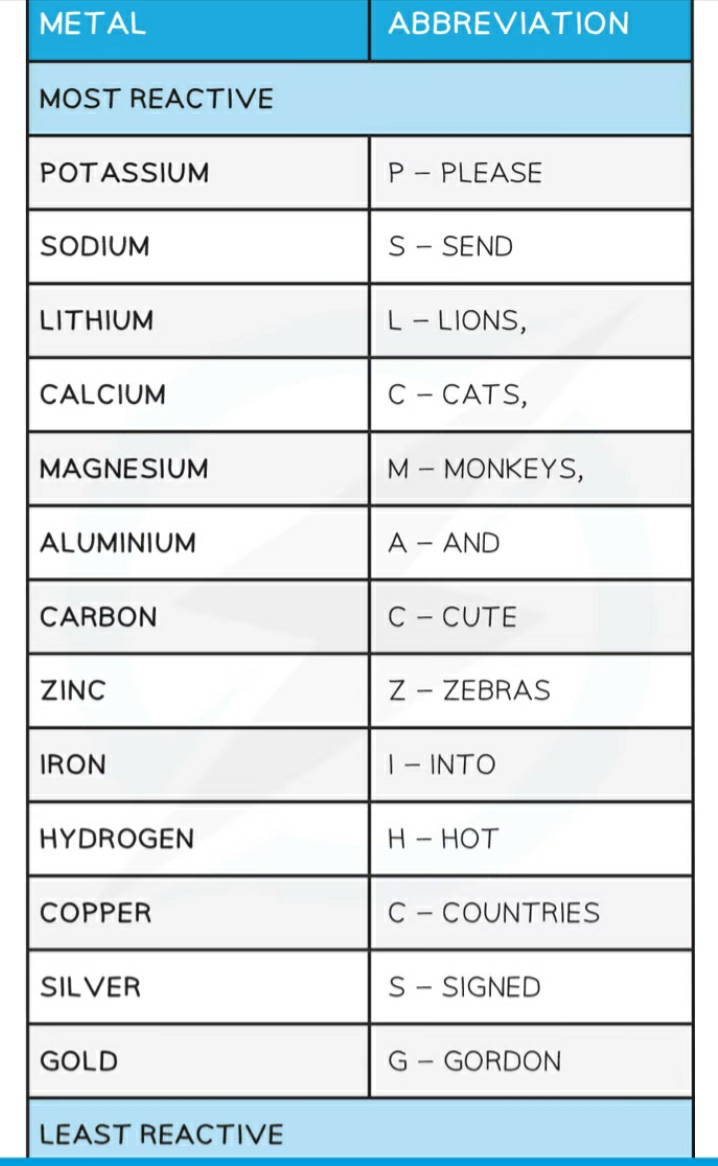
Reactivity series
Reactions with Aqueous Ions & Oxides
Example> COPPER (II) OXIDE
[ ] Magnesium is above copper in the reactivity series,
[ ] magnesium is more reactive so can displace copper from its oxide
[ ] Copper is reduced
[ ] The reducing agent in the reaction is magnesium: copper oxide + magnesium → copper + magnesium oxide
[ ] CuO (s) + Mg (s) → Cu (s) + MgO (s)
Displacement reactions
Displacement reactions between metals and aqueous solutions of metal salts
[ ] Any metal will displace another metal that is below it in the reactivity series from a solution of one of its salts
[ ] Magnesium + copper sulfate
[ ] Magnesium is a reactive metal and can displace copper from a copper sulfate solution
, more reactive metal slowly disappears from the solution, displacing the less reactive metal.
Decomposition reactions
Thermal decomposition reactions: Some compounds decompose or breakdown when they are heated to sufficiently high temperatures
These reactions are called thermal decomposition reactions.
metal hydroxide → metal oxide + water
[ ] Zn(OH)2 (s) → ZnO (s) + H2O (l)
metal carbonate → metal oxide + carbon dioxide
[ ] MgCO3 (s) → MgO (s) + CO2 (g)
metal nitrate → metal nitrite + oxygen
[ ] 2NaNO3 (s) → 2NaNO2 (s) + O2 (g)
metal nitrate → metal oxide + nitrogen dioxide + oxygen
[ ] 2Cu(NO3)2 (s) → 2CuO (s) + 4NO2 (g) + O2 (g)