Tectonic Plates & Rocks
Tectonic Plates:
A massive piece of the lithosphere (crust and the upper mantle) that floats on top of the mantle (which is partly melted rock).
Because they are on melted rock the plates move.
TTQ! Why do the plates move?
Convection currents from the mantle
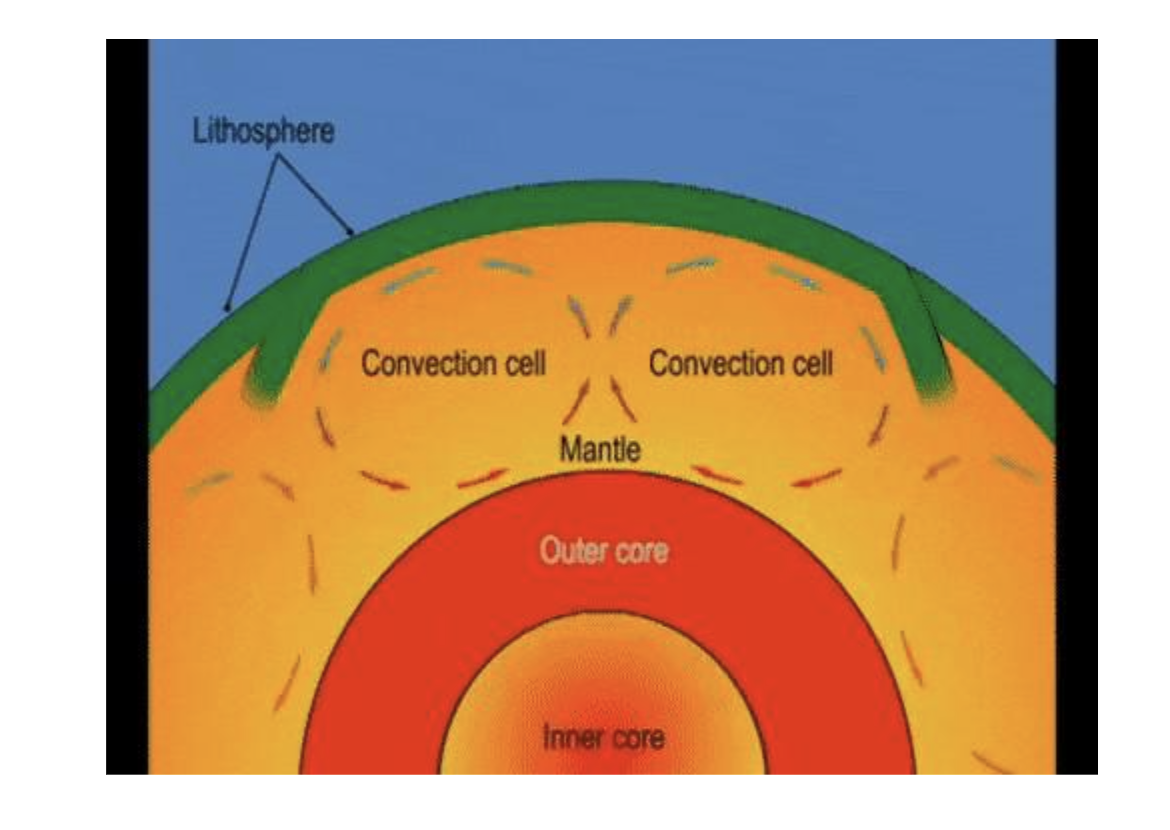
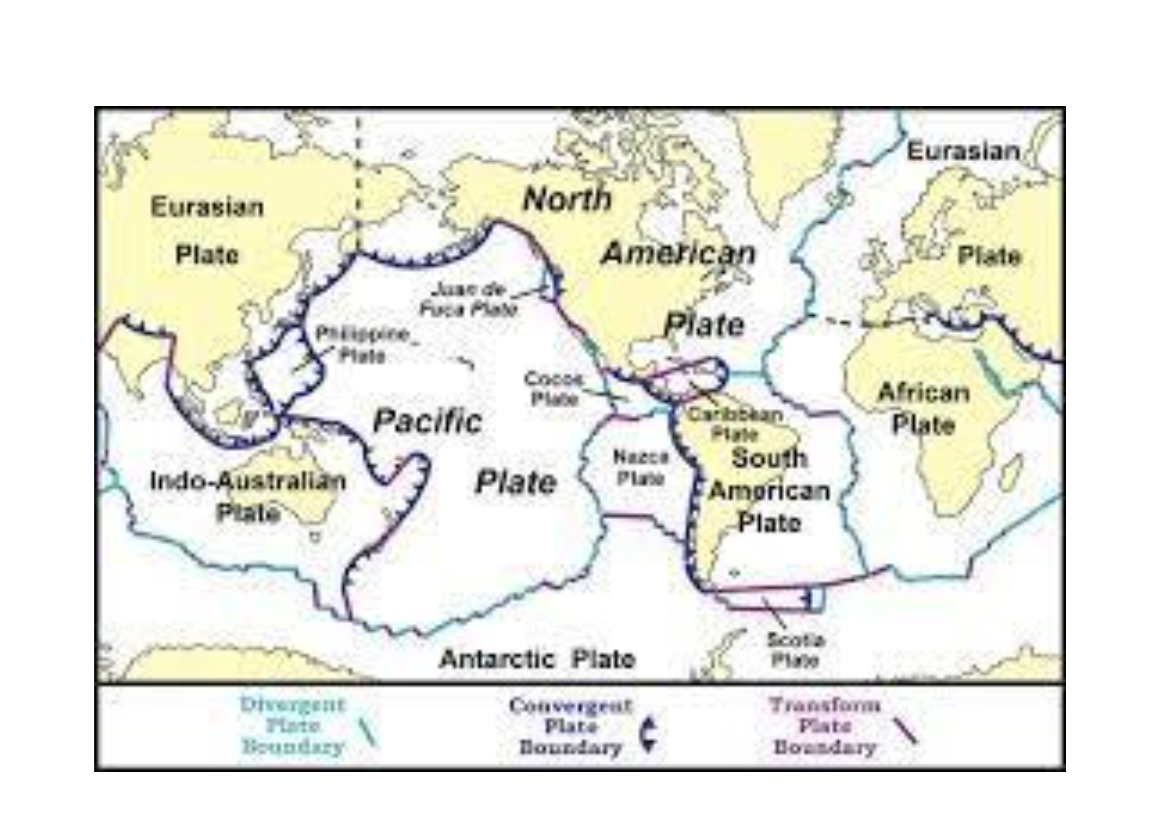
Some of the plates are made of parts of continental crust as well as oceanic crust.
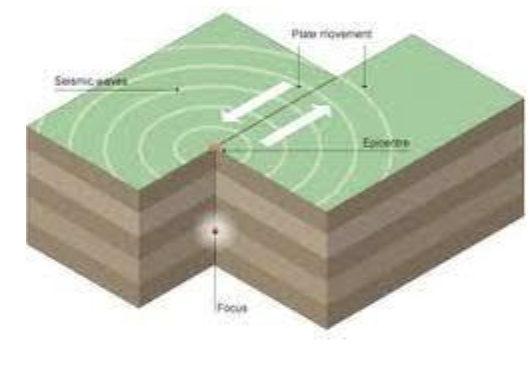
The plates fit together like puzzle pieces. Where they meet are called fault lines.
THE PLATES MOVE BECAUSE THEY ARE FLOATING ON MOLTEN ROCK WHICH MOVES.
The plates can move in three ways:
Collision: collisions can cause the formation of mountains and volcanoes - converging
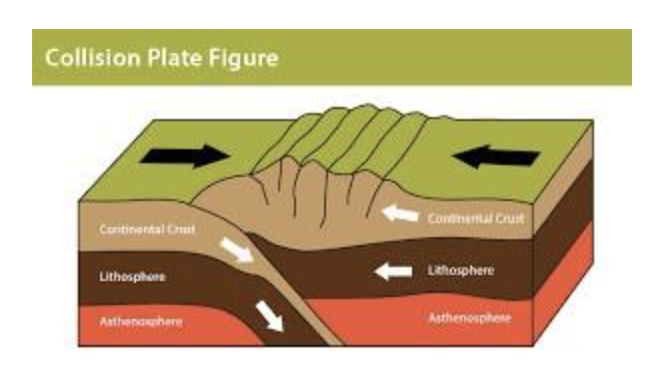
Mountain - when the plates push against each other they fold up
Volcanoes - the oceanic plates subduct (melt) under the continental plates This causes magma to emerge.
Subduction zones - where the oceanic plate melts under the continental plate - volcanoes
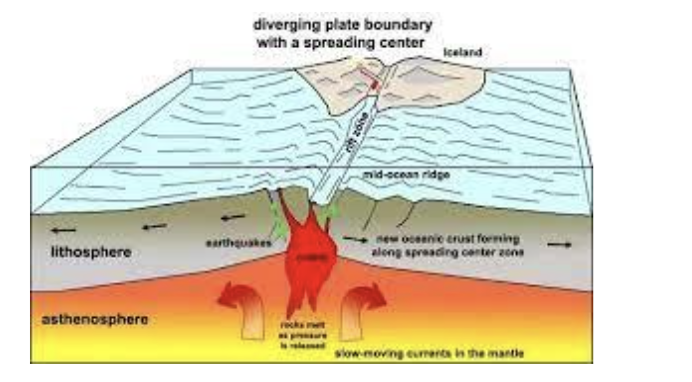
Separate - move apart - diverging
Underwater mountain ranges and volcanoes and underwater earthquakes
Rub together - this causes Earthquakes - slip zone - transform boundaries
The Rock Cycle
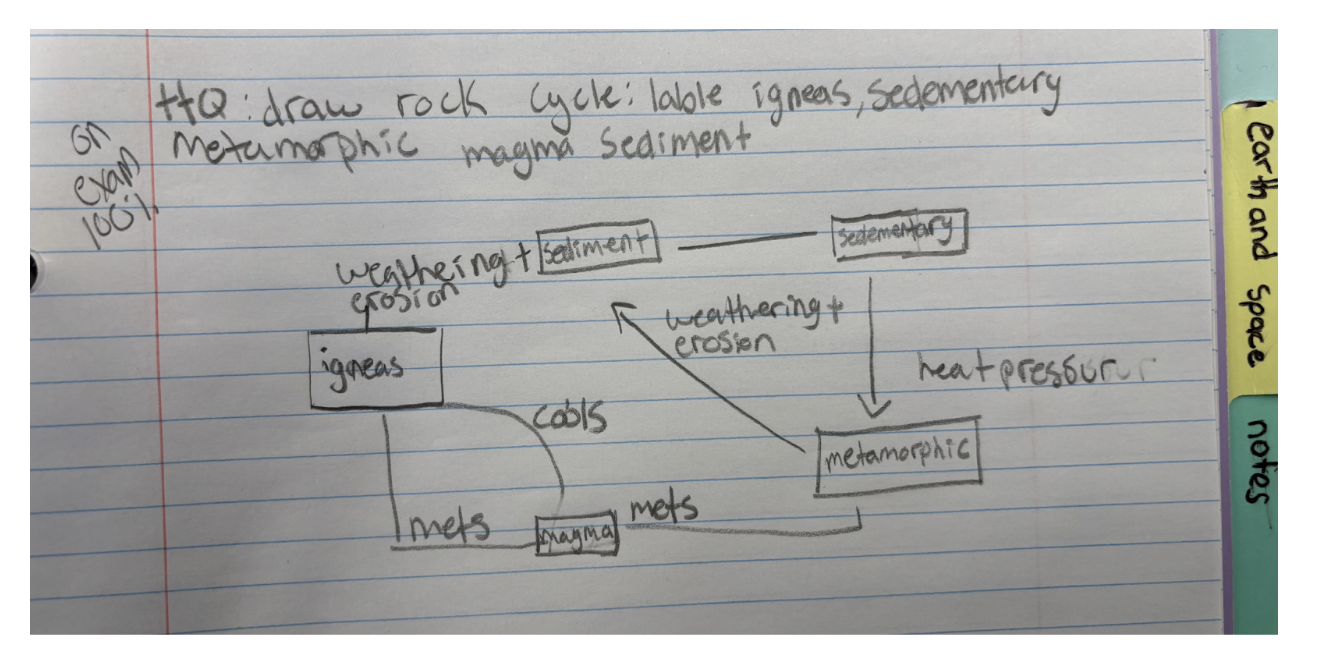
Igneous Rock - forms from cooled off magma from a volcano
Sedimentary Rock - pieces of igneous rock go through weathering (rain, wind, freezing) and break into little pieces called sediment. The sediment gets washed away under oceans where it gets compacted and cemented together.
These rocks often layered in different colors and can have fossils in them
Metamorphic Rock - sedimentary rocks that are deep in the ocean are exposed to heat and pressure from the mantle and they chemically change into new types of rock. They metamorphosize (change).
The Water Cycle.
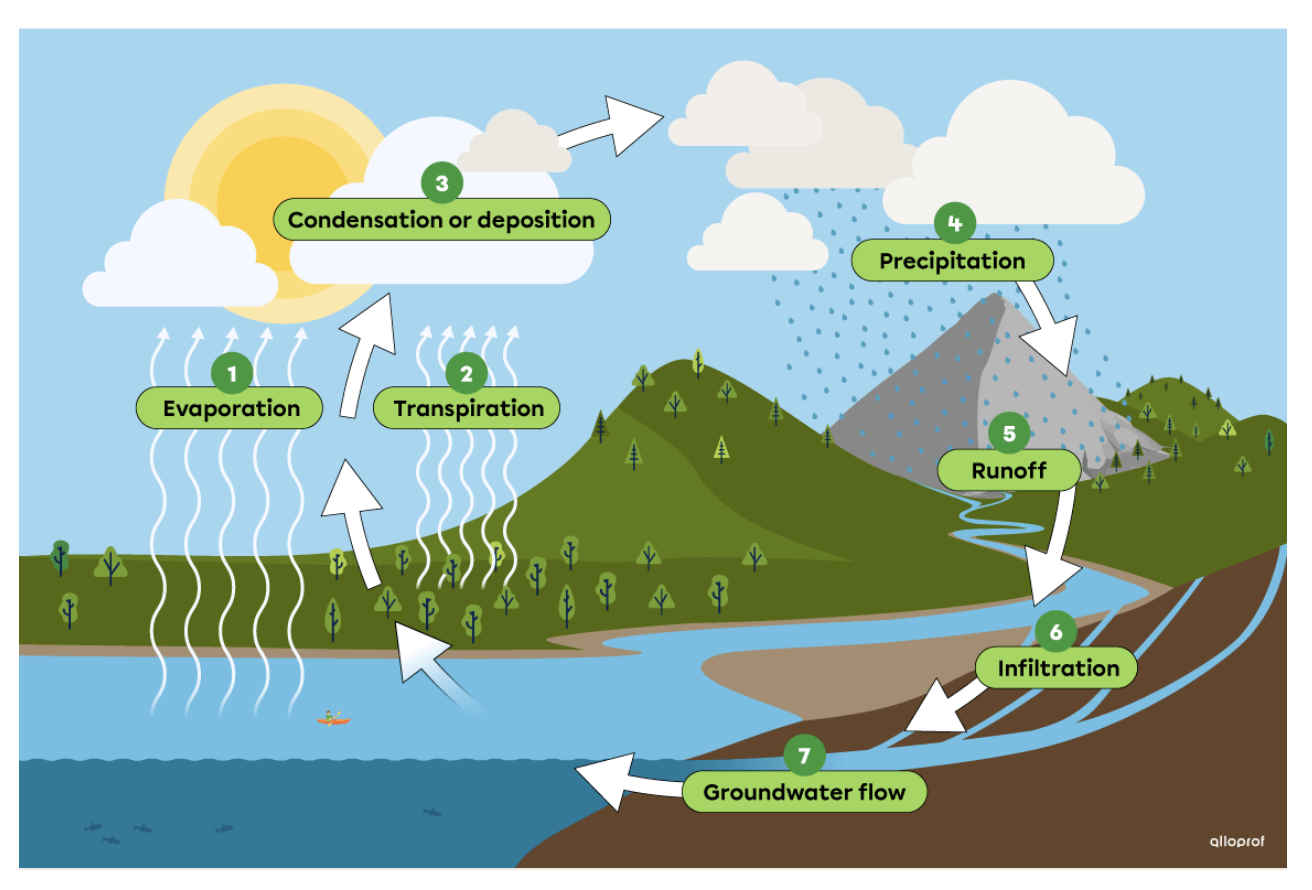
Evaporation - water evaporates from bodies of water because of the heat of the sun
Transpiration - water evaporates from the trees because of the heat of the sun
Infiltration - water permeates the soil - how water gets into a well
Runoff - water runs down mountains
Condensation - evaporated water forms clouds
Precipitation - when the clouds become heavy rain will fall