
Math/Physics
Class 1:
Units and Dimensions
SI base unit and Derived SI units
Kinematics
Distance vs displacement
distance is the length of a path(total) and it is scalar d
displacement is the change in path and is a vector quantity d
Speed and velocity
Speed is how fast something is going v = d/t and is scalar (m/s)
Velocity is speed and direction - average velocity = s/t
Average acceleration - the rate of change of velocity - a = v/t
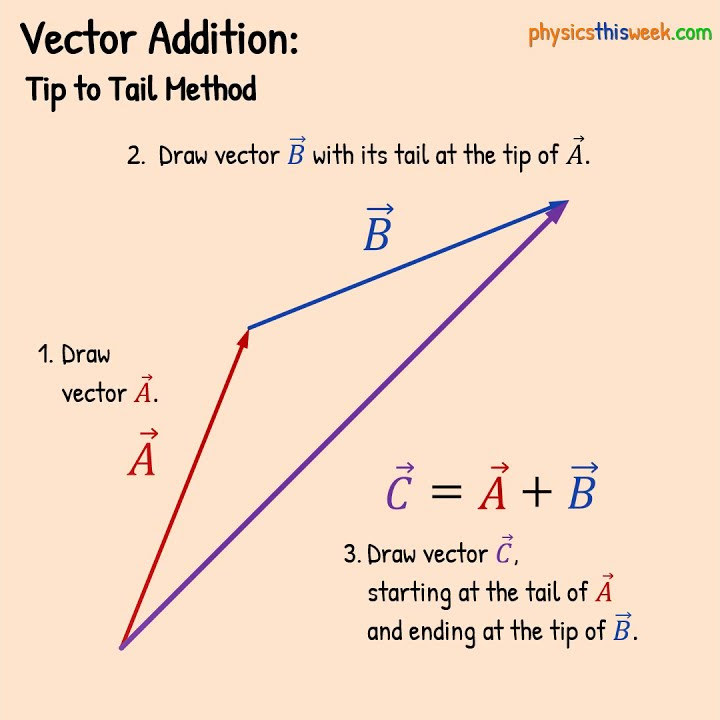
Tail-to-tip method of vectors
The big 5 equations:
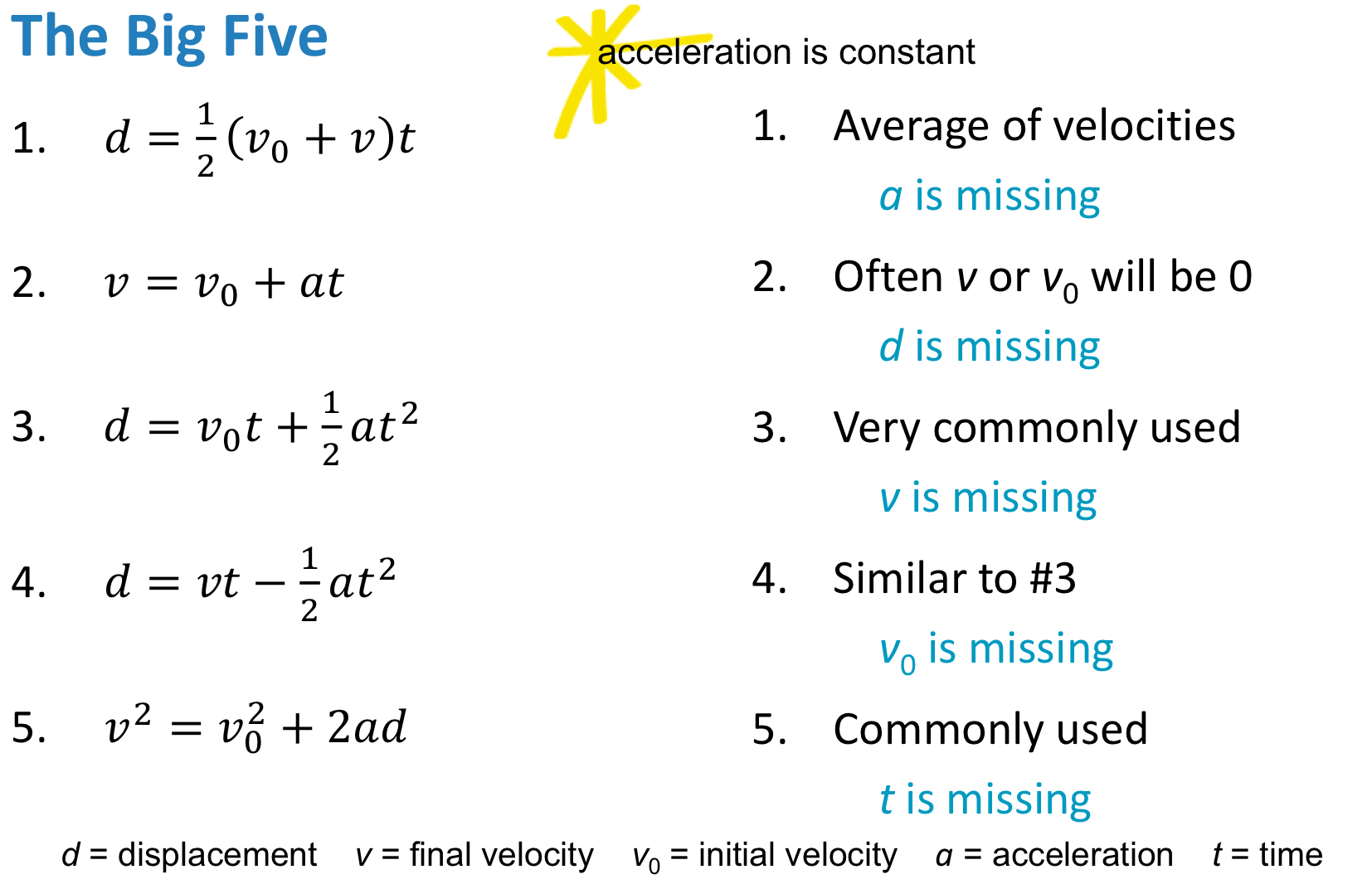
identify known quantities, then the desired quantity, choose the equation with the missing variable you don’t have and solve
Sometimes gravity can be used in place of acceleration → g = 10 m/s²
Using a graph, you can find three quantities → value at a point, slope, area under the curve
For a velocity vs. time graph → slope gives acceleration and area under gives the displacement
Mass: measure of an object’s resistance to acceleration(inertia) = kg scalar
Force
Net force = sum of all applied forces on the object → vector addition
Fnet = ma → mass x acceleration
Components of Fnet can be separated in y and x
Different forces can be = tension, gravity, normal
Know SOH CAH TOA
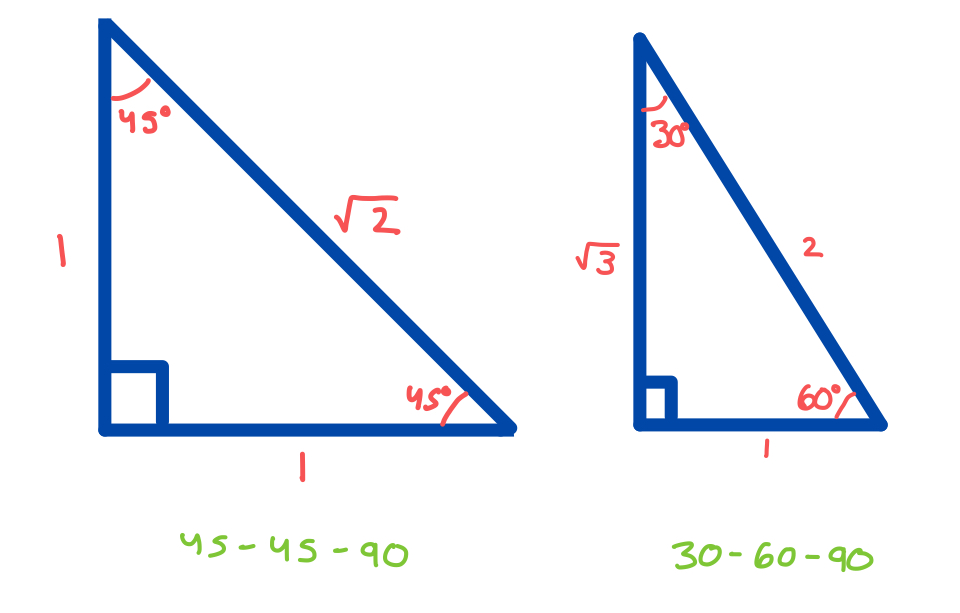
Know your 30-60-90 triangle and 45-45-90 triangle
√2 = 1.4 (valentines day)
√3 = 1.7 (St. Patrick’s day)
Newton’s Laws
1st - Inertia: an object in motion stays in motion at a constant velocity, and an object at rest tends to stay at rest
Fnet = 0 → v is constant
2nd - the acceleration of an object is directly related to its Fnet and inversely related to its mass → F = ma - only one object
3rd - for every action, there is an equally opposite reaction
if forces are equal, they will cancel out - requires 2 objects
Friction force: the force between two slid surfaces that resists slipping motion between them
Kinetic = direction opposes velocity → skidding/slipping
Static friction = direction opposes other forces → No motion relative to the contact surface or rolling without slipping
Class 2 - 22/06/2024:
Uniform circular motion
Torque
Work and Energy
Math/Physics
Class 1:
Units and Dimensions
SI base unit and Derived SI units
Kinematics
Distance vs displacement
distance is the length of a path(total) and it is scalar d
displacement is the change in path and is a vector quantity d
Speed and velocity
Speed is how fast something is going v = d/t and is scalar (m/s)
Velocity is speed and direction - average velocity = s/t
Average acceleration - the rate of change of velocity - a = v/t
Tail-to-tip method of vectors

The big 5 equations:

identify known quantities, then the desired quantity, choose the equation with the missing variable you don’t have and solve
Sometimes gravity can be used in place of acceleration → g = 10 m/s²
Using a graph, you can find three quantities → value at a point, slope, area under the curve
For a velocity vs. time graph → slope gives acceleration and area under gives the displacement
Mass: measure of an object’s resistance to acceleration(inertia) = kg scalar
Force
Net force = sum of all applied forces on the object → vector addition
Fnet = ma → mass x acceleration
Components of Fnet can be separated in y and x
Different forces can be = tension, gravity, normal
Know SOH CAH TOA
Know your 30-60-90 triangle and 45-45-90 triangle
√2 = 1.4 (valentines day)
√3 = 1.7 (St. Patrick’s day)

Newton’s Laws
1st - Inertia: an object in motion stays in motion at a constant velocity, and an object at rest tends to stay at rest
Fnet = 0 → v is constant
2nd - the acceleration of an object is directly related to its Fnet and inversely related to its mass → F = ma - only one object
3rd - for every action, there is an equally opposite reaction
if forces are equal, they will cancel out - requires 2 objects
Friction force: the force between two slid surfaces that resists slipping motion between them
Kinetic = direction opposes velocity → skidding/slipping
Static friction = direction opposes other forces → No motion relative to the contact surface or rolling without slipping
Class 2 - 22/06/2024:
Uniform circular motion
Torque
Work and Energy
 Knowt
Knowt