Chapter 2 - Movement of Substances
DIFFUSION
- %%Diffusion%% is the net movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration, down a concentration gradient.
- It is a %%passive process%% as energy is not required When the molecules have reached equilibrium between the two regions, the concentrations are the same and there will be no net movement of molecules.
- Diffusion enables living organisms, unicellular or multicellular, to survive by allowing the exchange of nutrients such as glucose, amino acid and fats, gases such as oxygen and waste substances such as carbon dioxide and urea.
FACTORS THAT AFFECT RATE OF DIFFUSION
%%Temperature%%
↑ in temperature, ↑ in kinetic energy of molecules%%Concentration gradient%%
- Concentration gradient is the difference in concentration between two regions.
- The steeper the concentration, the higher rate of diffusion.
Size of molecules
- Heavier molecules move more slowly than lighter molecules.
%%Diffusion distance%%
- Molecules do not have to travel far thus rate of diffusion is faster.
OSMOSIS:
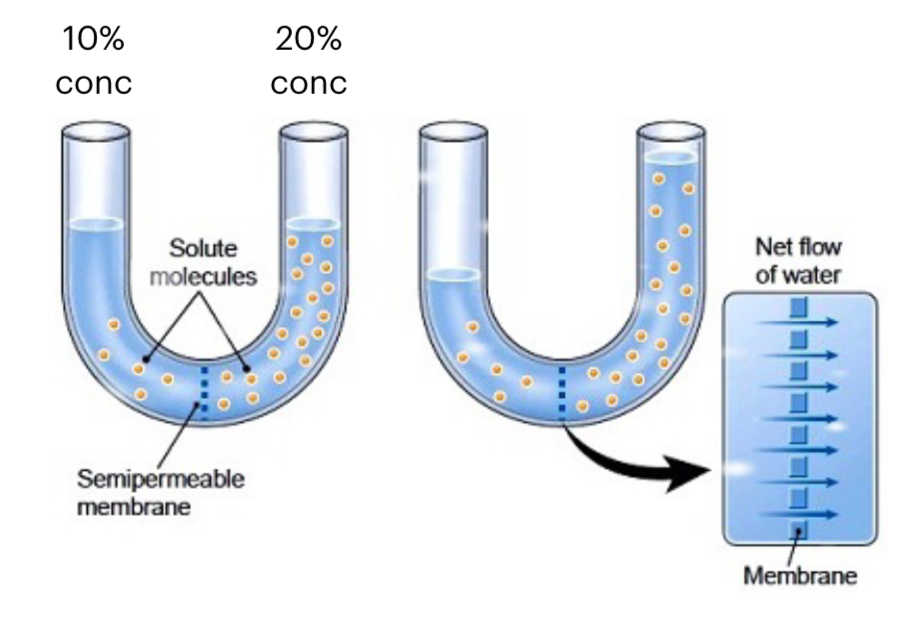
%%Osmosis%% is the net movement of water molecules from a region of higher water potential to a region of lower water potential, through a partially permeable membrane.
Water potential refers to the tendency of water to move from one area to another.
Plasma membrane or visking tubing are examples of %%partially permeable membranes%% that only allow allow some substances such as water, gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass through freely but not some other substances.
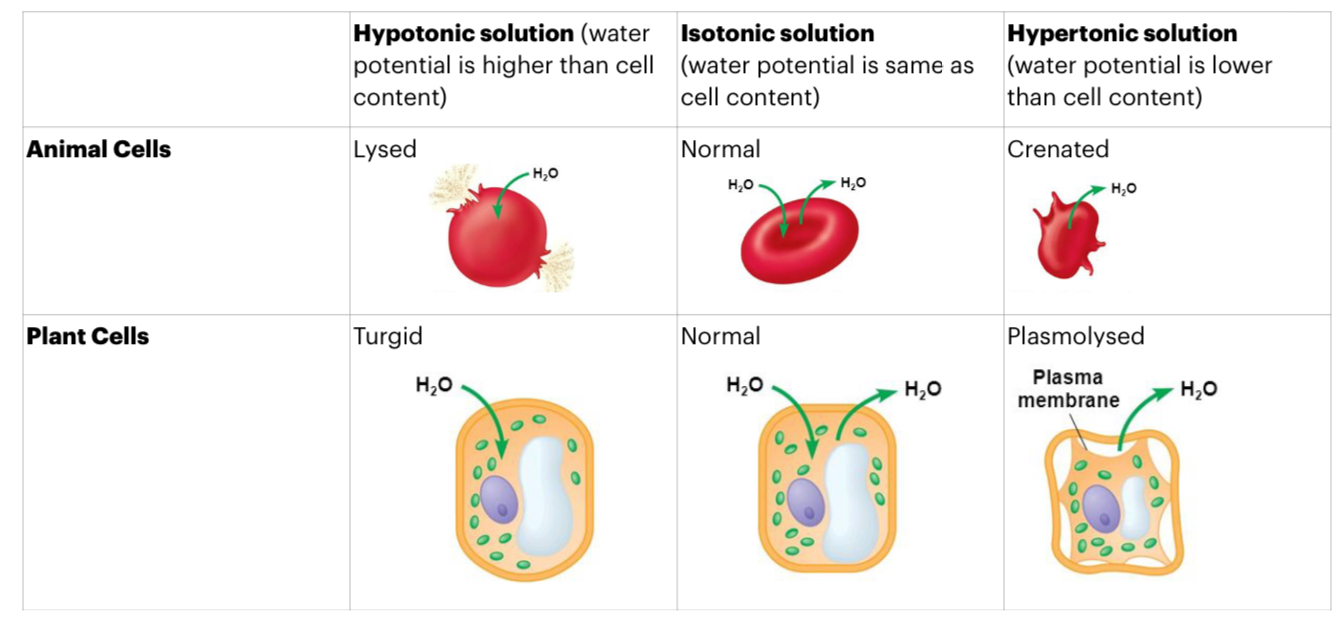
Effects of Osmosis on Plant and Animal Cells:
ACTIVE TRANSPORT:
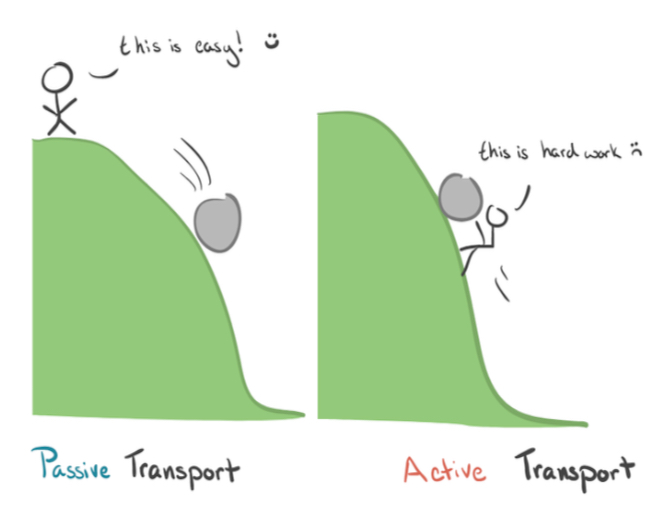
Both diffusion and osmosis is passive transport where energy is not required.
%%Active transport%% is the process where energy is used to move substances, across a cell membrane, from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration, %%against concentration gradient.%%
Since energy is required, amount of mitochondria to carry out aerobic respiration and availability of oxygen is important.
Example: Uptake of dissolved mineral salts by root hair cells and glucose uptake by cells in the villi of the small intestine.
\