
Science Notes - Sem 2 2024
Feed the World
Focus 1
Undernourished – Having insufficient food or other substances for good health and condition.
Countries in need of food: Zimbabwe, Zambia, Central African Republic, Kenya, Nigeria.
Main causes of hunger and food insecurity:
Conflict
Climate Change
Economy
Gender inequality
Food waste
Extreme weather
Ways to reduce food waste:
Only buy what is needed
Put food waste to use (e.g. compost)
Support local food providers
Store food wisely
Share uneaten food
Focus 2
What Role Source Elemental composition |
Simple Carbohydrates (e.g. Glucose) Primary source of energy
CHO |
Complex carbohydrates (e.g. Starch) More long lasting energy
CHO |
Fats and oils
CHO |
Proteins Regulation of the body’s tissues and organs
CHON |
Vitamins
|
Minerals
|
Common characteristics of metals and non-metals
Metals Non-Metals |
|
Focus 3
What Structure Function |
Roots
|
Stems
|
Leaves
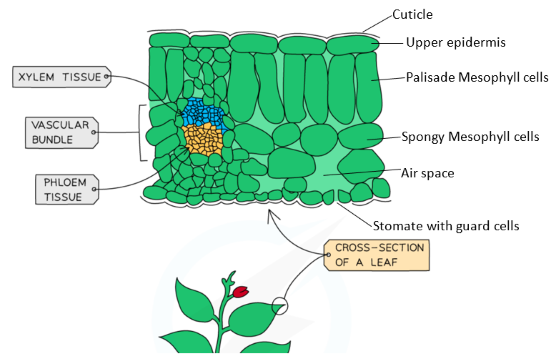
|
Flowers 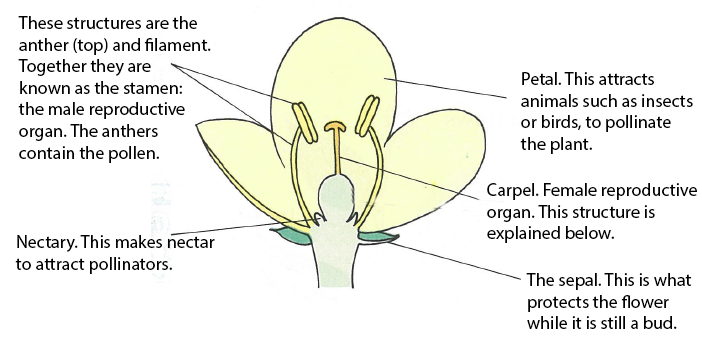
|
Focus 4
What Role Materials needed Word equation |
Photosynthesis To produce glucose 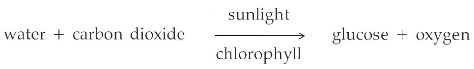 |
Respiration To convert the produced glucose into energy 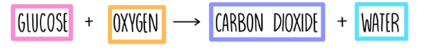 |
Focus 5
How scientific interventions are used to increase food production
Fun Park physics
Focus 1
Type Example |
Light e.g. The lights on the side of a roller coaster |
Heat e.g. Friction |
Mechanical e.g. Using kitchen appliances |
Gravitational e.g. A ball falling when dropped |
Electrical e.g. A battery |
Sound e.g. Whooshing sounds on a roller coaster |
Chemical e.g. A apple |
Kinetic e.g. A moving car |
Types of waves |
Sound waves Sound waves are created through objects vibration and produce waves not visible to the human eye. |
Light waves Light waves are forms of moving energy made of tiny, microscopic particles called photons. |
Focus 2
Conservation of Energy law: The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed.
Roller Coaster Dynamics: Roller coasters convert potential energy (at the top of a hill) into kinetic energy (as they descend).
What How |
Weight Mass x Gravity |
Mass Weight/Gravity For a mass of 4.5 kg: Weight = 4.5 kg×9.8 m/s = 44.1 N |
Ke ½ x mass x velocity squared |
GPE Mass x Gravity (On earth is 9.8) x Height |
Gravity ratios The planet you are calculating/gravity on the other planet e.g., Acceleration due to gravity on earth is 9.8m/s squared. How much would a person weigh on Venus, where the acceleration due to gravity is 8.9m/squared. Ratio= 8.9/9.8=0.9082 = 0.91 Therefore, the gravity on Venus is 91% of the strength of that on Earth. |
Focus 3
A force is a push, pull, or twist applied to one object from another, forces are only measured in Newtons. Forces can start, speed up, change direction, change shape, and stop objects, affecting the object to which it is applied.
Types of Forces:
Contact Forces: Require one object to touch another (e.g., cricket ball and bat).
Non-contact Forces: Act without the objects touching (e.g., gravity).
Non-contact forces |
Gravitational force Keeps you bound to the floor and the surface of the Earth. |
Magnetic force The force of a magnet pulling on some metallic objects; can attract or repel. |
Electrostatic force The force applied between electrically charged objects (e.g., causing hair to stand up when you rub a balloon against it). |
Focus 4
What is friction: Friction is a force that resists or prevents the motion of two surfaces in contact.
Friction's Effects: Heat, wear, and tear on surfaces.
Reducing Friction: Using lubricants like grease and oil, Streamlining objects or vehicles, and using rollers or ball bearings.
Surface Characteristics: Smooth surfaces provide less friction than rough surfaces whereas larger amounts of contact between surfaces result in more friction.
Helpful and Harmful Aspects: Friction can be both beneficial (e.g., allowing for walking) and detrimental (e.g., causing wear).
Focus 5
Unbalanced Forces: When there is a higher force being applied on one side than the other, causing the object or person to move, that means the net force will not be 0 newtons.
Focus 6
Types of charges What it is |
Protons Positive charge, Located in the nucleus of an atom |
Neutrons Neutral charge, Located in the nucleus of a atom |
Electrons Negative charge, Located at the rim of the atom or cell. Electrons can be rubbed of one material and transferred to another, The material gaining electrons becomes negatively charges, and the material that loses electrons is left with a positive charge. |
Focus 7
Measuring Force:
The instrument used to measure force is a force meter or spring balance.
Force is measured in newtons (N).
Net Force:
The net force is the result of subtracting opposing forces; add forces only when they are in the same direction.
*Forces always occur in pairs.
Balanced Forces:
Forces that cancel each other out (e.g., tug of war with equal teams).
The net force is 0 newtons.
Unbalanced Forces:
One side applies more force than the other, causing movement (e.g., tug of war where one team has more players).
The net force is not 0 newtons.
Air Resistance:
As an object's speed increases, air resistance (a form of friction) also increases due to contact with more air particles.
Terminal Velocity:
The constant speed reached when the weight force and air resistance are balanced
Emergency
Focus 1
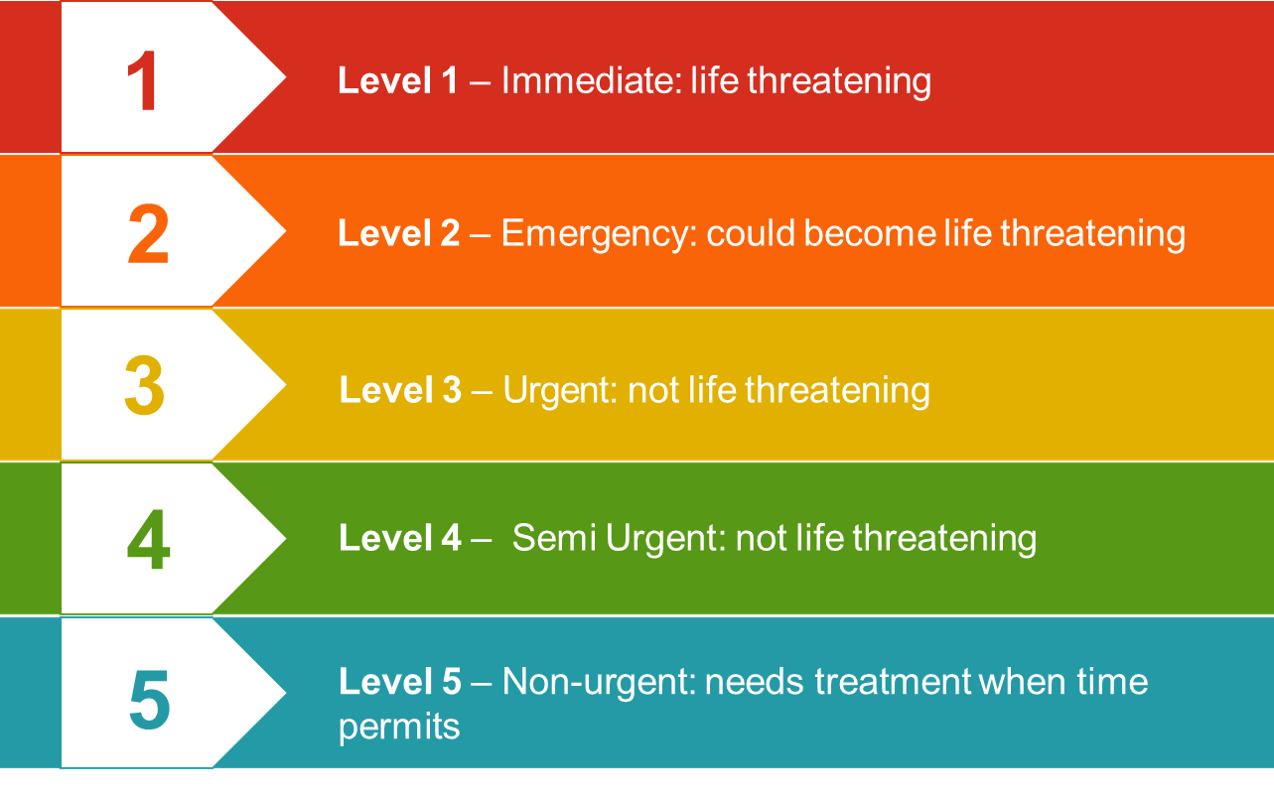
Role of triage: The role of triage is to assess the severity of an injury/incident to allow doctors to decide the treatment order.
Unicellular organisms: Are organisms only consisting of one type of cell, mitosis will produce an identical copy of the parent cell
Multicellular organisms: Are organisms consisting of more than one type of cell, mitosis helps the organism grow and quickly repair tissue
The Requirements of cells (MEWWIN):
M – Matter
E – Energy source
W – Water
W – Waste removal
I – Irons
N – Nutrients
Focus 2
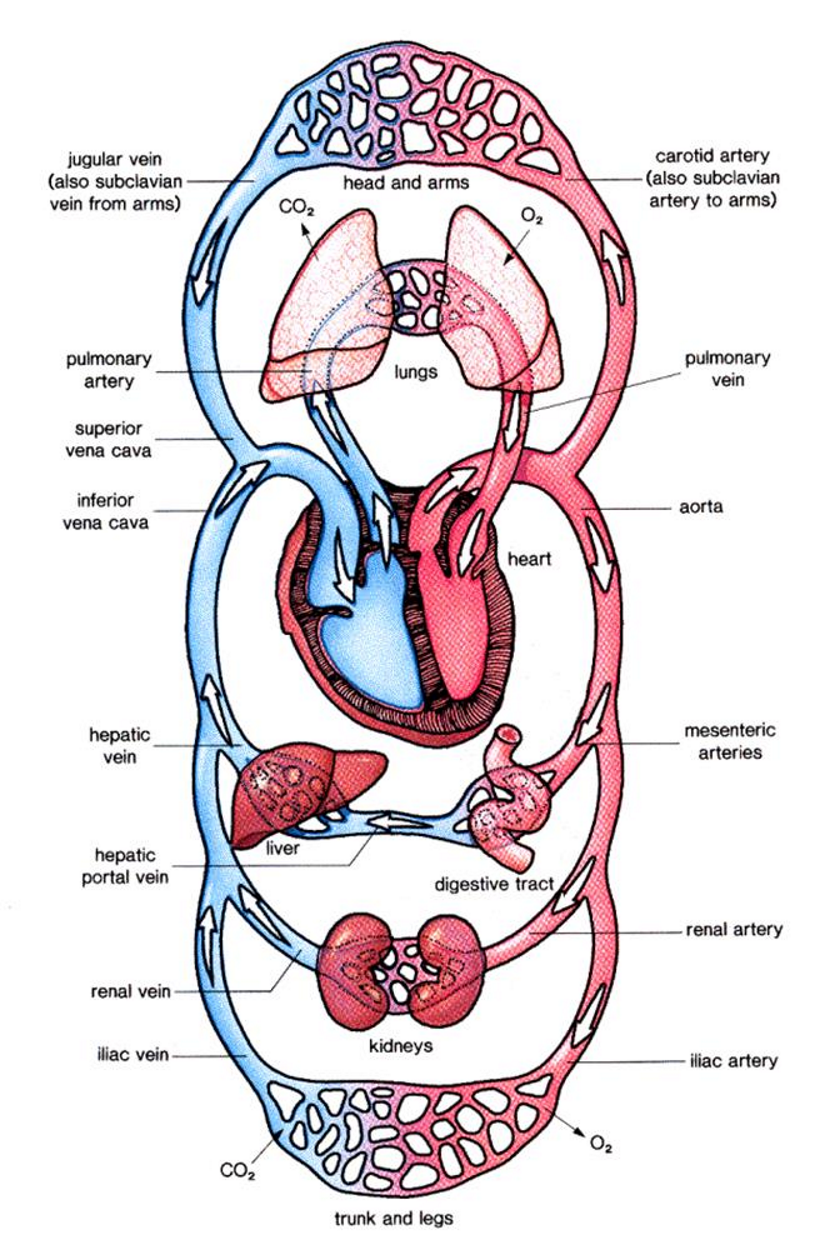
Components of the circulatory system |
Heart
|
Blood vessels
|
Blood
|
Function of the heart:
The heart is essential; it keeps our blood mobile and provides our cells with oxygen and nutrients to survive.
The heart is the motor of the circulatory system. The heart muscle contracts and pumps deoxygenated blood directly into the lungs, where it becomes oxygenated.
Muscle that acts like a pump, size of your fist, located in the left/middle of your chest.
It is a natural pacemaker called the sinoatrial node, located in the right atrium.
Sinoatrial node controls the heart by sending electrical signals, making the heart contract and pump blood.
Arteries, veins and capillaries |
Arteries Arteries have thick muscular walls, to allow for strong pumps of oxygenated blood away from the heart. |
Veins Veins are similar in size to arteries but have less muscle in their walls, veins contain one-way valves preventing any blood going backwards, the veins pump blood towards and into the heart. |
Capillaries Capillaries have the thinnest walls of all the blood vessels, their walls are 1 cell thick allowing substances to easily pass through, the capillaries connect the arteries and veins. |
Feed the World
Focus 1
Undernourished – Having insufficient food or other substances for good health and condition.
Countries in need of food: Zimbabwe, Zambia, Central African Republic, Kenya, Nigeria.
Main causes of hunger and food insecurity:
Conflict
Climate Change
Economy
Gender inequality
Food waste
Extreme weather
Ways to reduce food waste:
Only buy what is needed
Put food waste to use (e.g. compost)
Support local food providers
Store food wisely
Share uneaten food

Focus 2
What Role Source Elemental composition |
Simple Carbohydrates (e.g. Glucose) Primary source of energy
CHO |
Complex carbohydrates (e.g. Starch) More long lasting energy
CHO |
Fats and oils
CHO |
Proteins Regulation of the body’s tissues and organs
CHON |
Vitamins
|
Minerals
|
Common characteristics of metals and non-metals
Metals Non-Metals |
|
Focus 3
What Structure Function |
Roots
|
Stems
|
Leaves

|
Flowers 
|
Focus 4
What Role Materials needed Word equation |
Photosynthesis To produce glucose 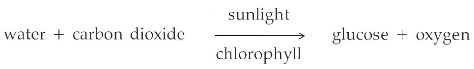 |
Respiration To convert the produced glucose into energy  |
Focus 5
How scientific interventions are used to increase food production
Fun Park physics
Focus 1
Type Example |
Light e.g. The lights on the side of a roller coaster |
Heat e.g. Friction |
Mechanical e.g. Using kitchen appliances |
Gravitational e.g. A ball falling when dropped |
Electrical e.g. A battery |
Sound e.g. Whooshing sounds on a roller coaster |
Chemical e.g. A apple |
Kinetic e.g. A moving car |
Types of waves |
Sound waves Sound waves are created through objects vibration and produce waves not visible to the human eye. |
Light waves Light waves are forms of moving energy made of tiny, microscopic particles called photons. |

Focus 2
Conservation of Energy law: The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed.
Roller Coaster Dynamics: Roller coasters convert potential energy (at the top of a hill) into kinetic energy (as they descend).
What How |
Weight Mass x Gravity |
Mass Weight/Gravity For a mass of 4.5 kg: Weight = 4.5 kg×9.8 m/s = 44.1 N |
Ke ½ x mass x velocity squared |
GPE Mass x Gravity (On earth is 9.8) x Height |
Gravity ratios The planet you are calculating/gravity on the other planet e.g., Acceleration due to gravity on earth is 9.8m/s squared. How much would a person weigh on Venus, where the acceleration due to gravity is 8.9m/squared. Ratio= 8.9/9.8=0.9082 = 0.91 Therefore, the gravity on Venus is 91% of the strength of that on Earth. |
Focus 3
A force is a push, pull, or twist applied to one object from another, forces are only measured in Newtons. Forces can start, speed up, change direction, change shape, and stop objects, affecting the object to which it is applied.
Types of Forces:
Contact Forces: Require one object to touch another (e.g., cricket ball and bat).
Non-contact Forces: Act without the objects touching (e.g., gravity).
Non-contact forces |
Gravitational force Keeps you bound to the floor and the surface of the Earth. |
Magnetic force The force of a magnet pulling on some metallic objects; can attract or repel. |
Electrostatic force The force applied between electrically charged objects (e.g., causing hair to stand up when you rub a balloon against it). |
Focus 4
What is friction: Friction is a force that resists or prevents the motion of two surfaces in contact.
Friction's Effects: Heat, wear, and tear on surfaces.
Reducing Friction: Using lubricants like grease and oil, Streamlining objects or vehicles, and using rollers or ball bearings.
Surface Characteristics: Smooth surfaces provide less friction than rough surfaces whereas larger amounts of contact between surfaces result in more friction.
Helpful and Harmful Aspects: Friction can be both beneficial (e.g., allowing for walking) and detrimental (e.g., causing wear).
Focus 5
Unbalanced Forces: When there is a higher force being applied on one side than the other, causing the object or person to move, that means the net force will not be 0 newtons.
Focus 6
Types of charges What it is |
Protons Positive charge, Located in the nucleus of an atom |
Neutrons Neutral charge, Located in the nucleus of a atom |
Electrons Negative charge, Located at the rim of the atom or cell. Electrons can be rubbed of one material and transferred to another, The material gaining electrons becomes negatively charges, and the material that loses electrons is left with a positive charge. |
Focus 7
Measuring Force:
The instrument used to measure force is a force meter or spring balance.
Force is measured in newtons (N).
Net Force:
The net force is the result of subtracting opposing forces; add forces only when they are in the same direction.
*Forces always occur in pairs.
Balanced Forces:
Forces that cancel each other out (e.g., tug of war with equal teams).
The net force is 0 newtons.
Unbalanced Forces:
One side applies more force than the other, causing movement (e.g., tug of war where one team has more players).
The net force is not 0 newtons.
Air Resistance:
As an object's speed increases, air resistance (a form of friction) also increases due to contact with more air particles.
Terminal Velocity:
The constant speed reached when the weight force and air resistance are balanced
Emergency
Focus 1
Role of triage: The role of triage is to assess the severity of an injury/incident to allow doctors to decide the treatment order.

Unicellular organisms: Are organisms only consisting of one type of cell, mitosis will produce an identical copy of the parent cell
Multicellular organisms: Are organisms consisting of more than one type of cell, mitosis helps the organism grow and quickly repair tissue
The Requirements of cells (MEWWIN):
M – Matter
E – Energy source
W – Water
W – Waste removal
I – Irons
N – Nutrients
Focus 2
Components of the circulatory system |
Heart
|
Blood vessels
|
Blood
|
Function of the heart:
The heart is essential; it keeps our blood mobile and provides our cells with oxygen and nutrients to survive.
The heart is the motor of the circulatory system. The heart muscle contracts and pumps deoxygenated blood directly into the lungs, where it becomes oxygenated.
Muscle that acts like a pump, size of your fist, located in the left/middle of your chest.
It is a natural pacemaker called the sinoatrial node, located in the right atrium.
Sinoatrial node controls the heart by sending electrical signals, making the heart contract and pump blood.
Arteries, veins and capillaries |
Arteries Arteries have thick muscular walls, to allow for strong pumps of oxygenated blood away from the heart. |
Veins Veins are similar in size to arteries but have less muscle in their walls, veins contain one-way valves preventing any blood going backwards, the veins pump blood towards and into the heart. |
Capillaries Capillaries have the thinnest walls of all the blood vessels, their walls are 1 cell thick allowing substances to easily pass through, the capillaries connect the arteries and veins. |
