Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) & Ribosomes
- The endoplasmic reticulum is sometimes known as the ER and the ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis.
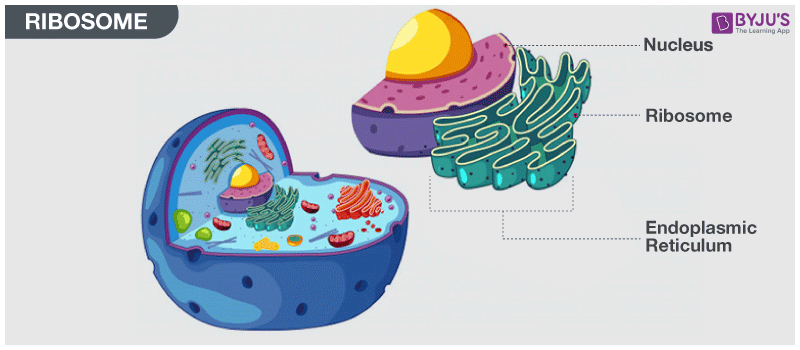
Ribosomes
- Ribosomes are found in all cells, regardless of whether or not they have a nucleus.
- Ribosomes receive the instructions from DNA via the messenger RNA (mRNA) because DNA cannot leave the nucleus. When a protein is needed, DNA will transmit a small snippet of the DNA to the mRNA and the mRNA will take the instructions out of the nucleus to the ribosomes, which are usually freely floating in the cytoplasm of the cell. We call these small snippets of DNA mRNA transcripts, which code for a specific protein. The ribosome creates the protein from the instructions on the mRNA.
- Sometimes, there can be an error transcribing the DNA to mRNA. When this happens, neither the DNA nor the mRNA know. They are not “smart” enough to recognize this change. The same is true for the ribosome. The ribosome is just like a copy machine – it translates whatever code it receives from the mRNA into protein. If an incorrect code is brought to the ribosome, the ribosome will simply copy whatever it can, even if it produces the incorrect protein.
- Ribosomes are found in every cell, but they are most plentiful in cells that produce a lot of proteins.
- For example, cells in the pancreas have a lot of free ribosomes because they produce a lot of digestive enzymes, which are proteins.
- Ribosomes can also be found attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). When ribosomes are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum, they specifically create proteins that are going to be transported because the endoplasmic reticulum is a network that moves proteins throughout the cell.
Endoplasmic Recticulum
- The endoplasmic reticulum is a network used to move proteins throughout the cell. There are two types of ER: smooth and rough. The endoplasmic reticulum usually surrounds the nucleus of the cell.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Smooth ER does not have ribosomes attached to it, so it looks smooth under a microscope.
- This type of ER synthesizes – or makes – lipids, steroids, and hormones (another type of lipid).
- The smooth ER also works to detoxify the cell from drugs and other toxins. Cells that do a lot of detoxing have a lot of smooth ER.
- For example, the liver, which is used to detoxify the body from drugs and alcohol, has a lot of smooth ER in it. Because the liver is so involved in detoxification, people that abuse drugs and alcohol can wear out their livers because they are constantly forcing their livers to detoxify those substances.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Rough ER has ribosomes attached to it, making it look rough under a microscope.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum makes proteins for transport and more endoplasmic reticulum.
 Edited: 05 October 2022
Edited: 05 October 2022