Chapter 14: Coordination and Response: II Animal Receptor Organs
The Mammalian Eye
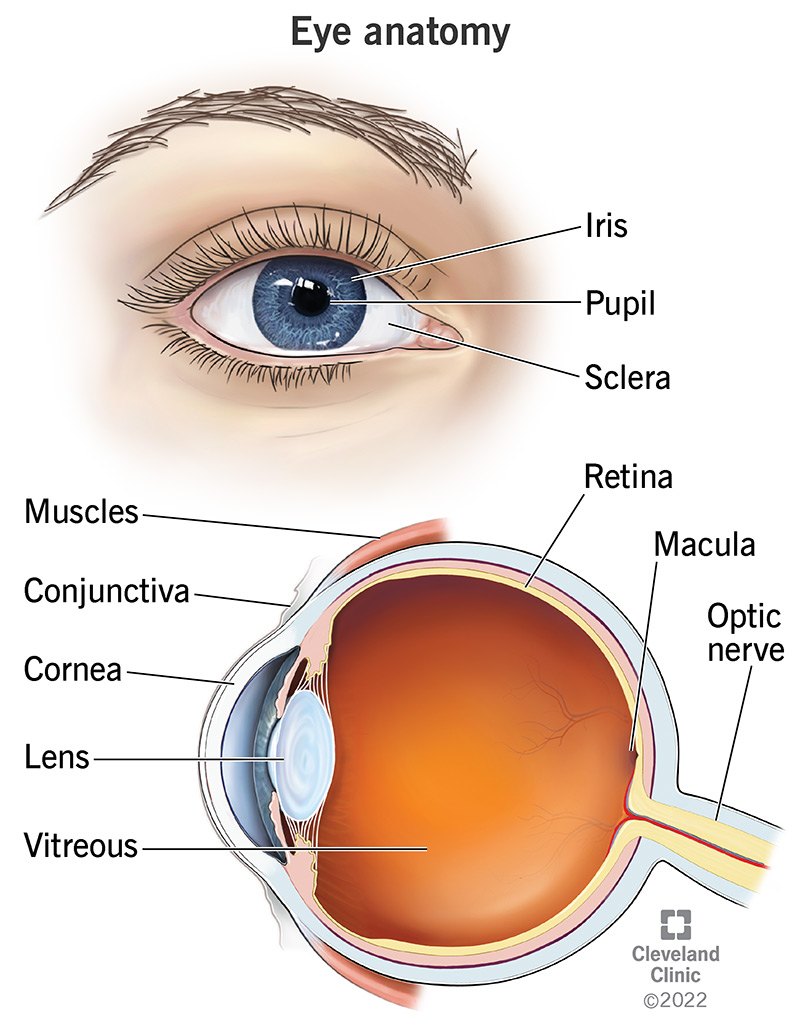
- %%Cornea%%
- A clear layer coating iris.
- Refracts light in the eye.
- %%Iris%%
- Colored section of eye.
- Controls amount of light entering by contracting and dilating pupil.
- %%Pupil%%
- Allows entrance of light.
- %%Lens%%
- Behind iris.
- Focuses image on retina.
- %%Retina%%
- Contain photoreceptors; rods and cons.
- %%Optic Nerve%%
- Each photoreceptor cell is attached to neuron.
- Carries nerve impulses to brain.
- %%Fovea%%
- Section in middle of retina.
- Provides clear images.
- %%Ciliary Muscles%%
- Alters the thickness of muscles.
- %%Choroid Coat%%
- Contains number of blood capillaries which nourish eye.
- Painted black (due to supply of blood vessels) to prevent internal reflection of light.
- %%Aqueous Humor%%
- Watery fluid.
- %%Vitreous Humor%%
- Transparent jelly like fluid.
NOTE: both aqueous humor and vitreous humor serve to keep eyeball form and refract light.
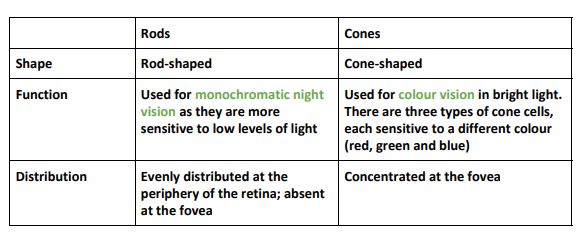
Rods and Cons
Controlling the entry of light in eye
- Achieved by altering diameter of pupil.
- Size of pupil controlled by iris muscles - circular and radial muscles.
- When circular muscle contract, radial muscles relax, and pupil becomes smaller.
- When radial contract, circular muscle relax , and pupil enlarges (diltes).
- Pupil enlarges when surrounding light intensity is low, and smaller when the light intensity is high.
Vision
Focusing (Accomodation)
It is the ^^adjustment of lens^^ of the eye so that ^^clear images^^ of objects at different distances are formed on ^^retina.^^
- @@Focusing on distant object@@
- Circular ciliary muscles relax.
- Suspensory ligaments are pulled tight - lens become flatter and less convex.
- @@Focusing on nearer object@@
- Circular ciliary muscles contract.
- Suspensory ligaments are released loosely - lens becomes thicker and more convex.