The Periodic Table
The Periodic table is a method of classifying elements.
- Elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number (each proceeding element has one more proton)
- Made up of rows called periods and columns called groups; the position of an element helps determine its electronic configuration
- Period number: number of electron shells
- Group number: number of valency electrons (outer shell electrons)
- ^^Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties^^
Periodic Trends
- Table moves from metals on the left to non-metals on the right.
- Down a group of metals, elements become more reactive
- With non-metals, going down a group, reactivity decreases
^^Alkali Metals^^
- Group I metals: Lithium, sodium and potassium
| Chemical Properties | Physical Properties |
|---|---|
| Readily react with oxygen and water; stored in oil | Good conductors of heat and electricity |
| React violently with chlorine | Soft and easy to cut |
| Burst into flames when heated with oxygen[red flame for lithium; yellow flame for sodium; lilac flame for potassium] | Shiny when freshly cut |
| Produce soluble white compounds. | Low melting and boiling points compared to most metals. |
| React with water to form alkaline metal and hydrogen gas | Low densities for metals |
Reactivity increases down the group
Density Increases
Softness increases
Melting point decreases
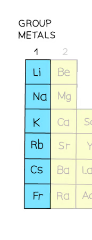
^^Halogens^^
| Properties | Patterns |
|---|---|
| States and Colors, at RTP: \n Fluorine- Yellow gas \n Chlorine- Green gas \n Bromine- Red liquid \n Iodine- Black solid | Down the group; size, mass and density increase |
| Poisonous | Down the group, color darkens |
| Diatomic; form halide ions in displacement reaction | Reactivity decreases down the group, \n because it has to gain an electron, \n so the closer the electron is to the positive nucleus the more easily it will be gained, \n so atoms with fewer shells will react more easily. |
| Do not conduct electricity | melting point increases down the group |
| Brittle and crumbly when solid |
^^Transition Metals^^
High melting points (except mercury)
Malleable and ductile
Good conductors of heat & electricity (silver is the best)
High density
Have no trend in reactivity
Used as catalysts
Form colored compounds
Can form complex ions as they have variable valences
^^Noble Gases^^
| Properties | Uses |
|---|---|
| Density increases down the group | Helium- filling balloons and aircrafts because it is lighter than air and will not catch fire. |
| Monoatomic and colorless | Argon – filling (tungsten) light bulbs to stop the filament reacting with oxygen. |
| M.P. and B.P. increases down the group | Neon – is used in advertising signs because it glows red. |
| Don’t conduct electricity | |
| Inert due to full outer shell electrons |