Unit 2 Quiz 2 Review Sheet - Study Guide Part 2 - KEY
Unit 2 Quiz 2
Study Guide Part 2
→ Make sure to use a periodic table as you answer the following questions.
Part A - Electrons and Atomic Structure
- The outermost electrons in an atom are found in the __Valence Shell. They are
called ___Valence__ electrons.
- Compared to an electron in the first shell of an atom, an electron in the third shell of the
same atom has ______more_______________ (more / less) energy.
- Identify the following values for a neutral carbon atom:
Total protons: _____6_____
Total electrons: _____6____
Valence electrons: ___4____
e- arrangement: _____2,4________
- Identify the following values for a S2- ion.
Total protons: ___16_______
Total electrons: __16 +2 = __18_____
Valence electrons: ___8____
e- arrangement: _____2, 8,8________
- What do all elements in the final column (group 18) of the periodic table have in common?
They all have eight valence electrons (He is an exception with 2 valence electrons). They all have a complete valence shell.
- Write down the names of the following groups in the periodic table:
- Group 1 _____Alkali Metal______________
- Group 2 __________Alkaline Earth Metal_________
- Group 17 (typo) _______Halogens______________
- Group 18 (typo)_____Noble Gas_________
- What do all elements in the period 2 of the periodic table have in common?
They all have their valence electrons in the second energy level. (Or they have all have 2 shells in total/ 2 energy levels in total)
- Identify the details of the following atoms using your knowledge of atomic structure and the organization of the periodic table.
- How many valence electrons does Sr have? ___2_______
- How many valence electrons does N3- have? ___8___________
- How many electron shells / energy levels does Li have? _____2________
- How many electron shells / energy levels does Ba have? _____6________
- Which of the following elements would have the lewis dot diagram:
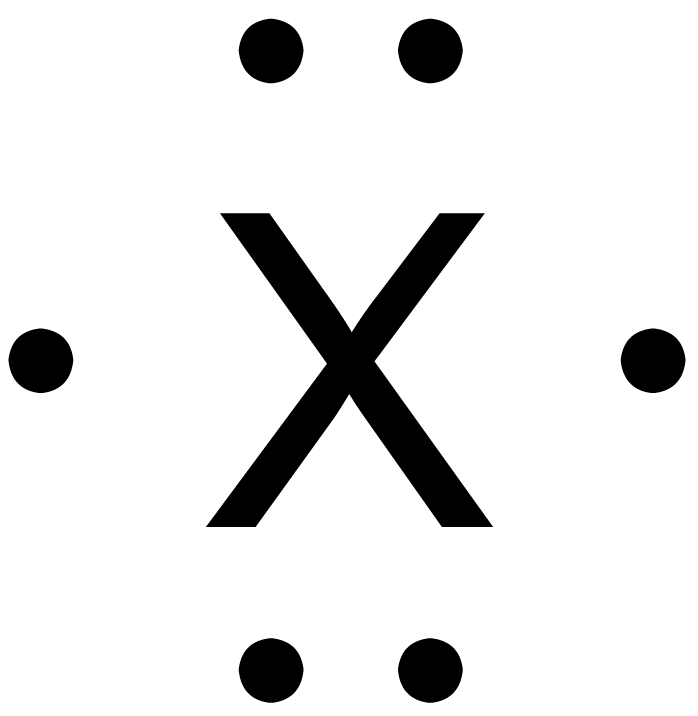
- Neon b) Barium c) Carbon d) Oxygen
Answer: _d) Oxygen__
- The goal of an atom when reacting is to ___fill the valence shell__________________ .
- Metals form __cations_( + ions ) _________ when reacting because they ___lose electrons_____________. Metals are found on the ____left______ side of the periodic table.
- What charge does Magnesium have when it becomes an ion? _____2+________.
Explain why:
Magnesium will lose the two electrons from the third energy level to have eight electrons in its next lower (now valence) shell. |
|---|
- Nonmetals form _____anions_( “-” ions___ when reacting because they _gain electrons__. Nonmetals are found on the ___right__ side of the periodic table.
- What charge does chlorine have when it becomes an ion? ______1- _________.
Explain why:
Chlorine will gain one electron to have eight electrons in its valence shell. |
|---|
- Noble gases do not react because __ they have full valence shells (2 for He, 8 for all others).
Part B - Periodic Table Trends
- Describe the trend in atomic radius as you go from left to right across period 2. Explain using atomic structure and scientific concepts.
The atomic radius will decrease as you go from left to right across a period because of the increase in effective nuclear charge. As you go across a period from left to right, the number of protons increases while the number of shells remains the same, therefore the effective nuclear charge increases. This means that the attraction of the nucleus to the valence shell increases as you move across a period which causes the valence shell to be pulled closer to the nucleus. |
|---|
- Describe the trend in atomic radius as you go down group 17. Explain using atomic structure and scientific concepts.
As you go down group 17, the number of electron shells / electron shielding increases. This results in the atomic radius increasing as you go down a group. |
|---|
- Define ionization energy:
The energy required to remove one electron from an atom. |
|---|
- Describe the ionization energy trend as you go down the alkaline earth metals (group 2). Explain using atomic structure and scientific concepts.
As you move down a group, the ionization energy decreases. This is caused by the increase in atomic radius as you move down a group due to increased shells/ electron shielding. The increased atomic radius results in a decreased attraction between the nucleus and the valence electrons and therefore it is easier to remove the electron. |
|---|
- Which alkali metal is more reactive? Li or Rb? Explain using atomic structure and scientific concepts.
Rb is more reactive. Rb has a lower ionization energy due to its larger size and more shells/electron shielding. The goal of a metal when reacting is to give away electrons in order to achieve full valence. Rb is more reactive since it is able to give away electrons more easily than Li. |
|---|
- Which nonmetal is more reactive? F or O? Explain using atomic structure and scientific concepts.
Fluorine is more reactive. The goal of a nonmetal is to gain electrons to achieve full valence. Even though they have the same number of shells, fluorine is more reactive because it has more protons and therefore can attract electrons to fill the valence shell better than oxygen. |
|---|
 Knowt
Knowt