17.1 Energy cycles
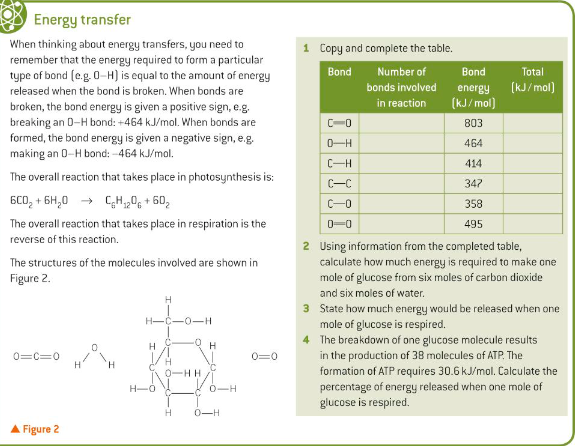
Synoptic links
active transport 5.4
biomass transfer through an ecosystem 23.2
carbohydrates 3.3 and ATP 3.11
respiration chapter 18
The need for energy
Living organisms have to be active to survive, they grow, respond to changes in their environment and deal with threats from other organisms. They need to find, make food and reproduce. This activity that depends on metabolic reactions and processes continually taking place in individuals cells.
Examples of these metabolic activities
Active transport, essential in the uptake of nitrated by root hair cells, loading sucrose into sieve tube cells, selective reabsorption of glucose and amino acids in the kidney and the conduction of nerve impulses.
Anabolic reactions such as the building of polymers like proteins, polysaccharides and nucleic acids essential for growth and repair.
Movement brought about by cilia, flagella or the contractile filaments in muscle cells.
Energy flow through living organisms - energy cannot be created or destroyed. The universe is gradually cooling as it expands because this energy is being dispersed over a larger area.
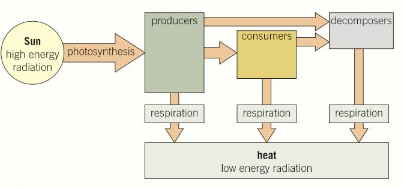
 Radiation from the sun is used to fuel the metabolic reactions and processes necessary to keep organisms alive, before eventually being transferred back to the atmosphere as heat.
Radiation from the sun is used to fuel the metabolic reactions and processes necessary to keep organisms alive, before eventually being transferred back to the atmosphere as heat.
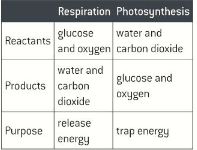
Photosynthesis
Organisms make use of energy in the bonds in organic molecules like glucose, these are formed during photosynthesis. Light is trapped by chlorophyll molecules, this energy is used to drive the synthesis of glucose from carbon dioxide and water.
Respiration
This is the process by which an organic molecule are broken down into smaller inorganic molecules like co2 and water. The energy stored within these bonds of organic molecules is used to synthesis ATP
Photosynthesis is the reaction behind the production of most of the biomass on earth.
Respiration is the process by which organisms break down biomass to provide the ATP needed to drive the metabolic reactions that take place in cells.
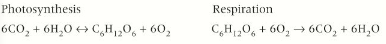
 The importance of C-H bonds
The importance of C-H bonds
In respiration large organic molecules are broken down forming inorganic molecules. The total energy required to break all the bonds in a complex organic molecules is less than the total energy released in the formation of all the bonds in the smaller inorganic molecules. The excess energy released by the formation of the bonds is used to synthesis ATP.
Organic molecules contain large numbers of C-H bonds, particularly lipids. C and H share the electrons almost equally in bonds that form between them. This results in a nonpolar bond and do not require a lot of energy to break. They then form strong bonds with oxygen atoms which results in the release of large quantities of energy. The reverse happens in photosynthesis.