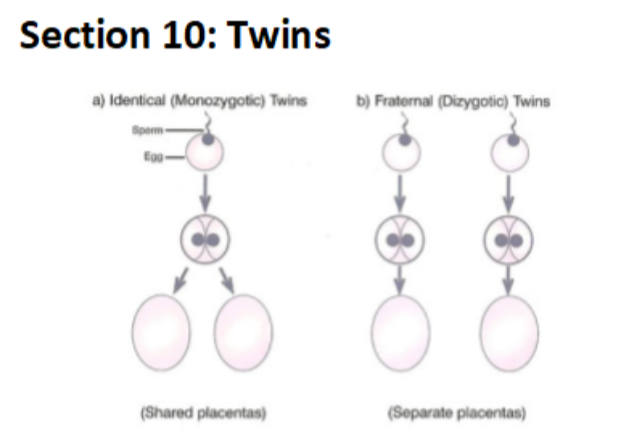
KEY WORDS AND DEFINITIONS - Penis is The organ in the male reproductive system that carries urine and semen to the outside of the body. Vagina is A muscular tube that leads from the cervix to the outside of a woman's body. Reproductive system are The organs and tissues involved in producing offspring. Testicle is The male reproductive organ the produces sperm in animals Ovary is A pair of organs in the female reproductive system where ova (eggs) and hormones are produced. Ova is The female gametes produced by ovaries in animals (singular: ovum) Sperm is The male sex cell or gamete Foetus is An unborn baby. Usually eight weeks from conception. Gamete is The sex cell of an organism, in humans they are sperm (male) and ovum (female) Uterus is Also known as a womb. This is where the fertilised egg (ovum) develops. Oviduct is Also called a Fallopian tube or egg tube, this tube leads from an ovary to the uterus. Ovulation is The process of releasing an egg from an ovary. Umbilical cord is The cord that connects the foetus to the placenta. It contains blood vessels. Placenta is The organ in the uterus of pregnant mammals that allows the transfer of nutrients and waste products between the mother and the foetus through the umbilical cord. Fertilisation is the joining of the nucleus of two gametes Embryo is An organism in the early stages of development Gestation is The time during which a fertilised egg develops into a baby ready to be born. Amniotic fluid is Liquid that protects the foetus in the uterus. Menstruation is The loss of blood and tissue from the lining of the uterus through the vagina during the menstrual cycle. Implantation is When embryo embeds itself in the uterus wall Zygote Cell is formed when two gametes combine
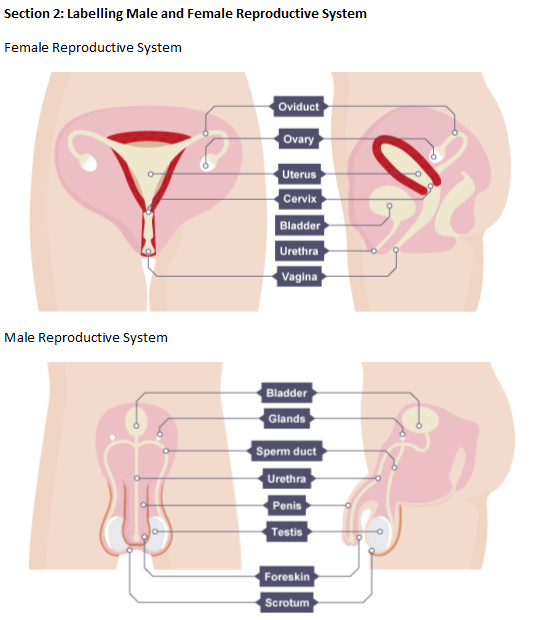
Ovary To produce eggs is Female
Vagina Receives the penis during sexual intercourse and allows menstrual flow to leave the woman female
Uterus Place where fertilised ovum (egg) develops into an embryo (unborn baby) Female
Cervix Helps in controlling the flow of menstrual blood and directs the sperm into the uterus Female
Oviduct/Fallopian tube To carry the eggs from the ovary to the uterus Female
Penis Allows semen (containing sperm) to be ejaculated into the woman (also serve as an excretory organ for men) Male
Scrotum To protect the testes Male
Urethra To carry sperm out of the male body (also carries urine out in men and women) Male and female
Testis To produce sperm Male
Sperm duct To carry sperm from the testes to the penis Male
Glands To add fluid to the sperm Male
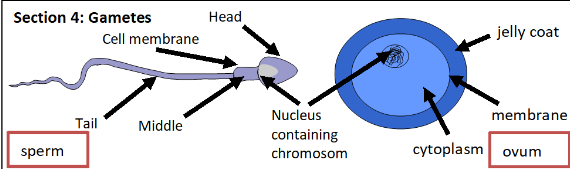
Section 5: Adaptations of Gametes
Has a cell membrane sperm and ovum
Contains genetic information in the nucleus ovum
Specially strengthened head sperm
Unable to move ovum
Small and streamline sperm
Large ovum
Millions produced sperm
Contains large food store ovum
Contains enzymes to digest the membrane of the cell sperm
Only a few produced ovum
Swims with a tail sperm
Section 6: Menstrual Cycle
Days 1-4 Lining breaks down and menstruation (bleeding) occurs
Days 4-14 Lining of the uterus builds up
Days 14 Ovulation (egg released)
Days 14-28 Lining maintained
Progesterone Maintains the lining of uterus during days 14-28
Oestrogen Controls release of the egg
Section 7: Ovulation and Fertilisation In the female one of the ovaries produces an egg every 28 days. This is called ovulation. During sexual intercourse sperm is ejaculated into the vagina. The sperm have to pass through the cervix and into the uterus. The uterus is acidic to help kill microbes and prevent infection. The journey is very far – the sperm will eventually reach the fallopian tube where they will meet the egg. If the sperm and egg meet the chemicals in the sperm will digest the outside of the egg and two nuclei will join. This is called fertilisation. Only one sperm will successfully fertilise an egg
Section 8: Pregnancy
Day 0 Fertilization: sperm has joined with ovum in the oviduct
Day 1 Fertilised egg divides into two cells
Day 3 Four cells divide into eight cells
Day 5-6 The embryo has developed a fluid filled space
Day 28 The embryo is 3mm long. As small heart pumps blood along an umbilical cord to the placenta
8 weeks The embryo develops into a foetus. It has eyelids and small fingers and toes
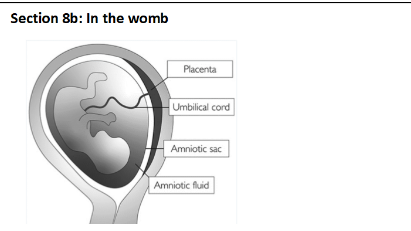 Section 9: The placenta
Section 9: The placenta
Substance is Oxygen direction Mother to foetus
Substance Glucose direction Mother to foetus
Substance Carbon dioxide direction Foetus to mother
Substance Urea direction Foetus to mother