The Nervous System
Stimulus --> Receptor --> Coordinator --> Effector --> Response
Stimulus - change in the environment/imbalance/evade an opponent
Receptor - specialised receptor cells/eyes and ears
Coordinator - brain or spinal chord
Effector - muscle or glands
Response - movement/skill
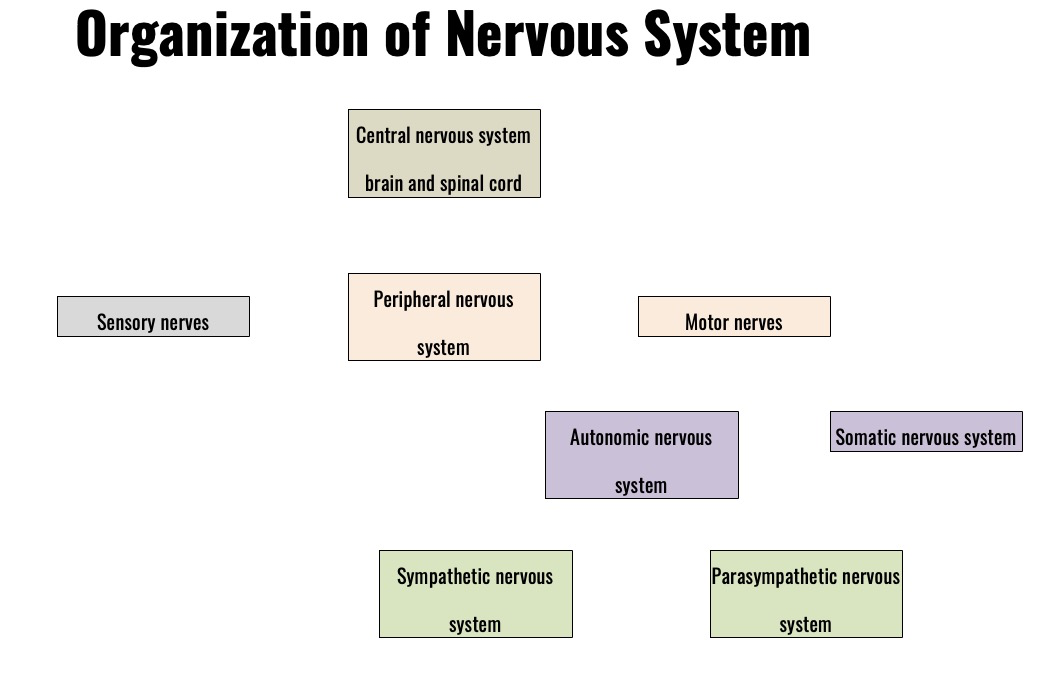
Nervous system is divided into two main parts:
Central Nervous System (CNS): brain and spinal cord
--> processing and integrating information
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): connect the CNS to the rest of the body through nerves
PNS is further divided into efferent pathways
Efferent pathways: carry signals from the CNS to effectors
Motor neurone system
Controls movement
Muscle contraction
Efferent pathways include the somatic system and the autonomic system
Somatic system: controlling voluntary movements (skeletal muscles)
Autonomic system: regulating involuntary functions (heart rate)
The autonomic system is further divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic system
Sympathetic system: activated fight or flight response + stimulate an 'increase' response
Parasympathetic system: promotes rest functions + stimulates a 'decrease' response
Central Nervous System:
Brain
Processes and interprets sensory information
Initiates and coordinates movement
Regulates the body's physiological functions
Spinal Chord
Enables information to travel between the brain and the rest of the body
Peripheral Nervous System
All the nerves outside of the CNS
--> carry messages to and from the brain and spinal cord
Sensory nerves inform CNS about what is going on within and outside the body
--> motor nerves (efferent nervous system) sends information from the CNS to the effectors
