Human Capital
Session 1: Human Capital
Main activities of the human resource management:
- Recruitment and selection
- Provision of contracts
- Ethics and corporate responsibility
- Motivating workers
- talent management
Human resource specialists operating at a higher level will be more focused on strategic planning of the department and linking it to the organisation's objectives. For all the different activities that the department is in charge, many different managers will also be involved.
Line Manager → direct responsibility for employees and their work.
To What Extent We Need Human Resource Managers?
We still need a role for a person skilled in human resource management to establish policies, standards and procedures, so that they are contributing to the organisation's strategic objectives. It is important to differentiate between specialists or generalists HR roles. Different companies will require different things from their HR departments.
Development of the HRM Approach
The major characteristics are:
- Importance of adopting a strategic approach
- Line managers play a dominant role
- Communication plays a vital role and the philosophy must be adopted across the whole company
- Unitarist manager/employee relationship (seeks to eliminate conflict)
- Every employee is important
Focus on Strategy
Competitive advantage was thought to only be achieved through efforts and creativity, hence HRM major focus was the hiring of specialists. HRM specialists will not only need knowledge of people’s strategies and programmes, but also some business acumen.
Role of the Line Manager
Consideration of the people management aspects would be expected in the strategic planning input from managers in all business functions. Activity management of people becomes an integral part of every line manager’s job. What once was performed by specialists, it is now done by line managers. One of the key challenges is to get a line manager to get involved with the management of people.
Integrated Policies and Effective Communication
All policies across the whole HR spectrum must be fully integrated and consistent.
HRM requirements to serve corporate strategy and achieve corporate aims can be seen in two ways:
- HR’s will be acquired, deployed and dispensed as corporate plans. Emphasising quantitative aspects → Hard HRM
- Gaining competitive advantage through the workforce, all potential must be nurtured and developed and programmes about the workers behaviours → Soft HRM
Unitarists and Pluralist Approaches
Unitarists →assumption that all members are dedicated to the achievement of a common goal without the inconvenience of personal interests. The leader decides what the goal is, and so heavily depend on top-down leadership
Pluralism → in a group of people there are different interests and these need to be managed. A motivator of this approach is the fact that employees are just looking to increase their earnings.
Adopting either of these approaches will have an effect on how the workforce will get treated. Unitary employees are more likely to resist unionisation and pluralists are more likely to accept trade unions. Unitarists believe that there are no problems needing solving and so no trade unions are needed.
Partnership, Participation and Employee Involvement
Success of an organisation not only comes by those who have a financial stake in the company, but also by other people who have direct interest in its success. The people affected by the decision are:
- Employees
- Customers
- Suppliers
- Community
Session 2: Organisational Culture
Culture
Set of shared values and norms that control organisational members interactions with each other and with people outside the company.
Values → general criteria that helps determine whats desirable or undesirable.
- terminal : desired and state of outcome that people seek to achieve
- Instrumental: desire mode of behaviour.
Norms → standards or styles of behaviour that are considered acceptable or typical for a group of people.
Organisational Culture Visibility
Visible → Symbols, manifestation….
Partly → norms and standards
Invisible →Values.
Effects of Organisational Culture
Used by people to guide their decisions, especially in situations of uncertainty and ambiguity. It can be a source of competitive advantage and a method to increase effectiveness.
Communication is key in order to manage it as it can be harmful.
Effects of a strong Culture
- Clear orientation
- Efficient communication network
- Fast information processing
- High motivation
Where Does It Come From?
- People's own characteristics → founders bringing their personal values
- Organisational ethics →Code of conduct to clarify behaviour between employees.
- Property Rights →distribution of resources (salaries, stocks…)
- Organisational Structure
Session 3: Interviewing Candidates
Recruitment →provides a pool of candidates for the selectors to choose. Must be done through a fair process and it must be cost efficient and effective
Selection → choose from the pool. Must organise and evaluate candidates information and come to a decision.
The main two questions during the recruitment process are:
- What is needed?
- How do you think the hiring process works from the recruiters POV? Techniques used.
Competencies → set of abilities, attitudes and knowledge that are shown by a candidate. Even skills that lead to the ability to do something successful.
Skills → learned and applied abilities. Strengths gained through experience and training. They are applied to achieve results.
Steps Once you Have a Vacancy
- Writing a job advertisement → include enough information to interest those that could fit, and discourage those that won’t. Must include:
- COmpetencies required
- Salary and benefits
- Opps and challenges
- Job tittle
- How to apply
- Internal Search → network, database, promotion
- Advantages → deep knowledge of its strengths and weaknesses, commitment to the company and it requires less training.
- Disadvantages → if you are not chosen you might become less motivated.
- External Search → Press, Internet, Head Hunters…
- Targeted Recruitment → encouraging previously disadvantaged groups to apply. However the decisions that follow must be merit based. How to draw them:
- Statement encouraging under-represented groups
- Photos and text showing people in non-traditional roles
- Different mix of people.
- Selection Process → Shortlist, Telephone interview (screening), assessment centre (groupwork, tests)
- Interviews
What's an Assessment Centre?
It is a group selection activity, allowing for evaluation on different competencies amongst candidates. Candidates are assessed for graduate programs, summer internships…
Advantages
Comparison between several candidates. Observe group work. Increase validity of selection decisions.
Disadvantages
Needs to be well designed. Costly. Training is needed. Acceptance
Some examples are:
- Interviews
- Role plays
- Pitch
- Case study
- Job Interview →Selection interview is the procedure to predict job performance based on the responses provided.
Types of interview
Structured → prepared ahead of time and possibility to change questions
Unstructured → there is no set format
The content can be:
- Situational → behaviour in a certain situation
- Job related
- Behavioural → past reactions. They follow the STAR model:
- Situation / Tasks → Background
- Action → How you solved it
- Result → Outcome
- Learning → takeaways
Administration
- 1-to-1
- Panel → group of interviewees questioning together.
- Mass →panel and various candidates.
- Sequential → several interviewers, one candidate
How to avoid errors?
Plan and prepare for the interview, follow a structure and ask relevant questions. Make sure you are encouraging a conversation and clarify what the job requires.
What should be avoided?
Only positive halo and horn effects. First impressions are very important and avoid stereotyping.
The reasons to leave an interview can be:
- Voluntary → another job
- Involuntary → dismissal and redundancy.
Understanding the reasons and putting in practice a good recruitment and retention plan is key.
Session 6: Learning, training and development
Before we were used to training employees to perform specific tasks, however as the market and society evolved, people are encouraged to learn how to learn. To stay competitive talent must be retained and the search for more cannot stop.
Benefits of inhouse training → tailored to the company and it is less expensive
Benefits of external training → fresh knowledge and leaves opportunity for benchmarking
On vs Off the Job Training (training requiring absence from work)
Adv → Cheap and tailored.
Disadv → Learning faults, training is necessary for on the job trainers.
In house development programs are put in place in order to train employees without spending too much money.
E-learning → computer based and its used as part of distance training. Easily accessible and flexible.
Blended Learning → combines different approaches like: coaching, workshops and self-assessments.
Learning Logs → learn from experience.
Mentoring and Coaching
Mentoring → traditionally people with experience leading the new ones. They guide and suggest learnings and they learn from their mentees. Their main aim is encouraging individual learning.
Coaching → they help indv or groups perform better. They might be internal or external and there are three types:
- Traditional → experts in specific fields and helps with skills and knowledge
- Transitional →large changes in the future of the organisation and teaches how to proceed.
- Transformational → targeted at sr management, guides towards new ways of working and it is more used when change is involved.
There are some trend at the moment:
- Development of abilities
- Talent management
- Engagement
- Retention
- Career path
Session 7: Performance Management
Main goal is to motivate and make sure everyone is working towards the same goal. It is a shared goal and process, everyone should feel part of the project and some kind of ownership. The main tool normally used is Performance Appraisal.
This is the formalised way of giving employees feedback about their performance at work. They are normally written reports and discussed in a meeting. The philosophy behind is that people work better when achieving expected results. They are collaborative, know their expectations and determine how they are doing.
Main uses
- Performance review
- Review of development needs → see if training is needed
- Assesing potential → Promotion?
- Deciding on rewards
- Presents the opportunity to plan future objectives
Main Problems
- Lack of clear purpose
- Links with pay and rewards → keep reward considerations and development separate.
- Information kept secret from employee
- Appraiser attacking appraisee → personality traits are hard to change
- Lack of criteria, being too subjective.
Role of the LM
Judge → judging worth, quality or values. Needs to be fair.
Helper → helps improve. Suggests training
It is an important thing to do because it helps assess competencies, improve current performance, identify potential and many others.
Assessing performance
360 degree feedback → appraisal in the centre of feedback. Gathered by whom the employee is in contact with.
Personal development review → 1-to-1 sessions. Normally done with the line manager, which provides support and coaching.
Approaches when assessing performance
Objectives
- SMART objectives
COmpetencies → Inputs employee makes to the org
- Determines their level a¡that they have to achieve
Rating Scales
They seek to encourage objectivity and they are graded statements to be rated linked to the job description.
Evaluating Behaviours seeks to understand and evaluate how employees use their personal traits and competencies to the performance of work, and how it can be improved.
Typical scales are:
- Behaviour-Observation scales (BOS)
- frequency of job related observed and uses a number scale
- Behaviour-anchor rating scales (BARS)
- Group of raters suggests descriptions for behaviours for each aspect of main duties (scale from excellent to unacceptable)
The main risks of performance appraisal is that we tend to focus on negative aspects, put a lot of emphasis on past performance, focus too much on rates, expect only monetary rewards and judge with subjectivity (extreme trends).
Trends
Many companies nowadays are eliminating ratings. They believe in quality conversations, which tend to have a greater impact on the employee. The idea is to let the employee know their status at all times.
Session 9: Equal Opportunities and Diversity
Pay and REwards Systems
Every company needs one. This payment and rewards system must have:
- Objectives aligned with the organisation's strategy.
- Orderly way for pay increases and progression in the company to be clear.
- Pay basis is fair.
The main objectives are:
- Attract the most employees.
- Retain employees
- Stimulate company growth and employee performance.
Payment schemes are done after determining the importance of different jobs, these are job evaluations. There are three factors to look for:
- Company’s ability to pay → pay is viewed as a cost
- Competitors rate of payment
- Movement in market rates
The decisive factors in order to declare a job more important than the other are:
- Importance of the role
- Strategic plan, is the employee a crucial piece
- Results of the performance appraisal systems.
- Characteristics of the employment market involved.
Jobs must be evaluated and ranked. Comparison must be done in order to find similarities and finally decide on the pay.
There are two critical factors that will finalise the process and that is comparing it to similar jobs ( External competition ) and finding the balance with the level of job ( Internal equity )
There are different types of payment systems, all offering pay in different ways. It is very important to choose the correct one as you will be indirectly sending a message to the employees. This message needs to support strategic objectives. SOme examples are:
- Time rates → pay based on fixed hourly pay
- Indv pay by results
- Group incentives
- Profit sharing → percentage of company’s earnings
- Performance-related pay
- Non-monetary rewards → maybe company car, but NO money.
- Flexible pay
Diversity
Each of us is unique. We are different in visible and non-visible ways.
These things can be protected or not by anti discrimination legislation.
Equality Act 2010 (UK)
- Age → protects the young and the old
- Disability
- Gender reassignment → person trying to undergo procedures to change sex.
- Religion or belief → belief is how a person decides to live their life
- Race
- Sex and sexual orientation.
There are three different types of discrimination
Direct Discrimination
Treated less favourably for something directly related to: sex, gender, age,race…whether this person has this characteristic or not does not matter.
Indirect Discrimination
Treated unfavourably due to some provision, criterion or practice that would disadvantage the group to which she/him/they belong.
For example: hiring truck drivers that are 1.8m tall at least, it cannot be objectively justified.
Harassment
Unwanted conduct that violates the dignity of the person. The behaviour can be verbal or physical.
There are different approaches in order to try and treat everyone equally, the fist one is:
The Equal Opportunities Approach
- Based on sameness → supports legislative actions, providing a level playing field where all can compete in equal terms. They hope that equal opportunities lead to equality of outcome.
- Promoting the rights of all society members → company representation as i is in society
- Influence behaviour through legislation → this prevents discrimination from occurring when hiring and HR managers must control conformity with laws.
However there are some problems with this approach. It is not easy to formalise everything in the organisation and fair procedures not necessarily lead to equal outcomes. It is simplistic to treat the symptoms rather than the cause of discrimination.
The second one is:
The Management of Diversity Approach
- Based on difference → focus on individuals and not jus minorities, legislation is not effective, change in how these groups are seen is needed. The main objective is to look for individual improvement.
- Organisational culture must change → diversity must be implemented strategically and it is not just HR’s job
- Benefits for the organisation → enhanced customer relations, reduced labour costs and financial benefit from retaining staff and improvement of workforce quality.
However there are some problems. Benefits to the organisation are sometimes hard to materialise and valuing group base differences might reinforce stereotypes.
THIS TABLE SUMMARISES ALL
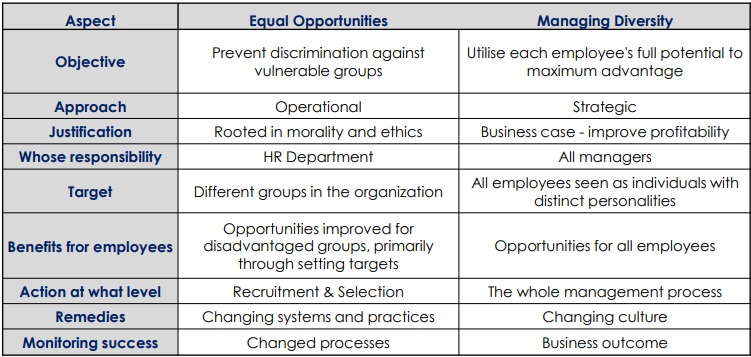
In order to achieve diversity in companies, they tend to combine both approaches
Senior management and line managers must be committed to these approaches as diversity needs to be inscribed in the organisations culture. Managers that achieve diversity need to be rewarded.
Diversity is something that people need to be aware. Through programs or simply oral communication people can become aware of it. Also it is very important but flexibility is key in order to comply with the different members of the company.
All of this is implemented through a plan model:
- Support from lñeaders
- Integrate diversity in goals and selection processes
- Involve all stakeholders through clear and open communication
- Challenge negative behaviours
- Monitor and evaluate progress.
Session 10: The Future of HCM
The use of AI for job interviews
How s AI changing Recruitment?
- Ensuring best fit → online presence allows to assess overall fit more accurately. People are able to find the job that best fit themselves.
- Faster Initial selection process → automated processes
- AI-led interview processes → social and visual signals no longer beneficial
- Skills to engage with recruitment platforms → body language and microgestures
AI is taught different accents by processing data from lots and lots of voices. However, this can create a bit of bias as there are some that are harder to understand.
This bias is created through algorithms that introduce it
Some of the reasons are:
- Poor data collection as some groups may not be equally represented
- Training of the algorithms strictly depends on the data used.
- Is the process of data collection ethical? Is it private, monitoring…
Algorithmic control is a set of technological tools to remotely manage workforces, something like the uber app is a clear example as it controls everything regarding the drivers location.
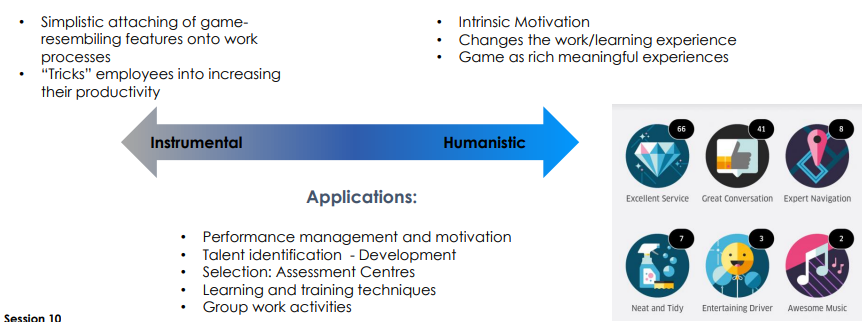
Gamification → using game-like elements to make nongame tasks more interesting