What to Memorize: Exam 1
Chapter 1
Definitions
Chemistry: the study of the properties and behavior of matter.
Matter: the physical material of the universe; anything that has mass and takes up space.
Property: any characteristic that allows us to recognize a particular type of matter and to distinguish it from other types.
Elements: combine together to create matter.
Atoms: the tiniest particles that are the building blocks of matter and can not be divided further.
Molecules: two or more atoms.
Elements and Symbols
Name | Symbol | Protons | Neutrons | Electrons | Possible Charge |
Antimony | Sb | 51 | 71 | 51 | 3+, 3-, 5+ |
Aluminum | Al | 13 | 14 | 13 | 3+ |
Argon | Ar | 18 | 22 | 18 | 0 |
Arsenic | As | 33 | 42 | 33 | 3- |
Barium | Ba | 56 | 81 | 52 | 2+ |
Beryllium | Be | 4 | 5 | 4 | 2+ |
Bismuth | Bi | 83 | 126 | 83 | 3- |
Boron | B | 5 | 6 | 5 | 1-, +3, |
Bromine | Br | 35 | 45 | 35 | 1- |
Cadmium | Cd | 48 | 64 | 48 | 2+ |
Calcium | Ca | 20 | 20 | 20 | 2+ |
Carbon | C | 6 | 6 | 6 | 0 |
Cesium | Cs | 55 | 78 | 55 | 1+ |
Chlorine | Cl | 17 | 18 | 17 | 1- |
Chromium | Cr | 24 | 28 | 24 | 2+, 3+ |
Cobalt | Co | 27 | 32 | 27 | 2+, 3+ |
Copper | Cu | 29 | 35 | 29 | 1+, 2+ |
Fluorine | F | 9 | 10 | 9 | 1- |
Gallium | Ga | 31 | 39 | 31 | 1+, 3+ |
Germanium | Ge | 32 | 41 | 32 | 2+, 4+ |
Gold | Au | 79 | 118 | 79 | 1+, 3+ |
Helium | He | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
Hydrogen | H | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1+ |
Iodine | I | 53 | 74 | 53 | 1- |
Iron | Fe | 26 | 30 | 26 | 2+, 3+ |
Lead | Pb | 82 | 125 | 82 | 2+, 4+ |
Lithium | Li | 3 | 4 | 3 | 1+ |
Magnesium | Mg | 12 | 12 | 12 | 2+ |
Manganese | Mn | 25 | 31 | 25 | 2+, 3+ |
Mercury | Hg | 80 | 121 | 80 | 0 |
Neon | Ne | 10 | 10 | 10 | 0 |
Nickel | Ni | 28 | 31 | 28 | 2+ |
Nitrogen | N | 7 | 7 | 7 | 3- |
Oxygen | O | 8 | 8 | 8 | 2- |
Phosphorus | P | 15 | 16 | 15 | 3- |
Platinum | Pt | 78 | 117 | 78 | 2+ |
Potassium | K | 19 | 20 | 19 | 1+ |
Radium | Ra | 88 | 138 | 88 | 2+ |
Rubidium | Rb | 37 | 48 | 37 | 1+ |
Silicon | Si | 14 | 14 | 14 | 4+ |
Silver | Ag | 47 | 61 | 47 | 1+ |
Sodium | Na | 11 | 12 | 11 | 1+ |
Strontium | Sr | 38 | 50 | 38 | 2+ |
Sulfur | S | 16 | 16 | 16 | 2- |
Tin | Sn | 50 | 69 | 50 | 2+, 4+ |
Titanium | Ti | 22 | 26 | 22 | 2+, 3+, 4+ |
Uranium | U | 92 | 146 | 92 | 4+, 6+ |
Zinc | Zn | 30 | 35 | 30 | 2+ |
Metric Prefixes and Numerical Values
Prefix | Symbol | Numerical value |
Giga | G | 10^9 |
Mega | M | 10^6 |
kilo | k | 10³ |
centi | c | 10-2 |
milli | m | 10-3 |
micro | \mu | 10-6 |
nano | n | 10-9 |
1 ml = 1 cm3
Density = \dfrac{m}{V}
Fahrenheit: \dfrac{9}{5}\left( °C+32\right)
Celsius: \dfrac{5}{9}\left( °F-32\right)
Kelvin/Celsius conversion
0°C = 273 K
Chapter 2
Metals that have various oxidation states:
V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Au, Hg, Sb, Sn, Pb, U
Metalloids: B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te (stair step on periodic table)
Atomic number is the number of protons (+) and electrons (-)
Mass number is the number of protons plus neutrons
Mass # - Atomic # = number of neutrons
Average Mass: \Sigma [(mass)(% fractional abundance)] for EVERY isotope
Periodic Table Groups
1A = Alkali metals
2A = Alkaline earth metals
3-12 = Transition metals
7A = Halogens
8A = Noble gases
Polyatomic Ions
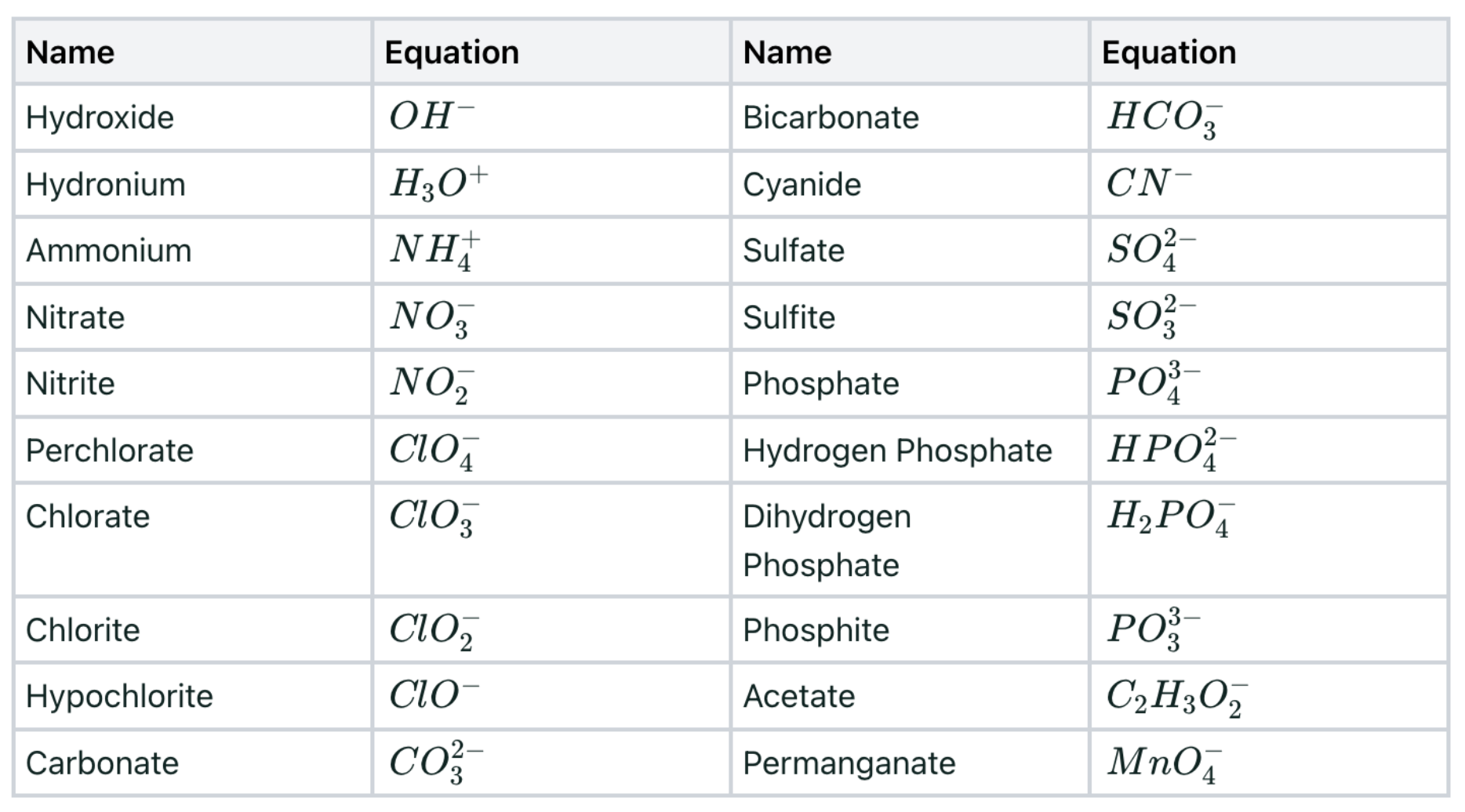
Important molecules
Water (H2O)
Ammonia (NH3)
Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S)
Acids

Organic Molecules (base molecules)
Methane (CH4)
Ethane (CH3-CH3)
Propane (CH3-CH2-CH3) as base molecules
Change ending to –ol for alcohols, using numbering to specify the location when necessary.
Chapter 3
Symbols for chemical reactions
(g) = gas
(l) = liquid
(s) = solid
(aq) = dissolve in aqueous (water) solution
(\Delta ) = heat needed for reaction
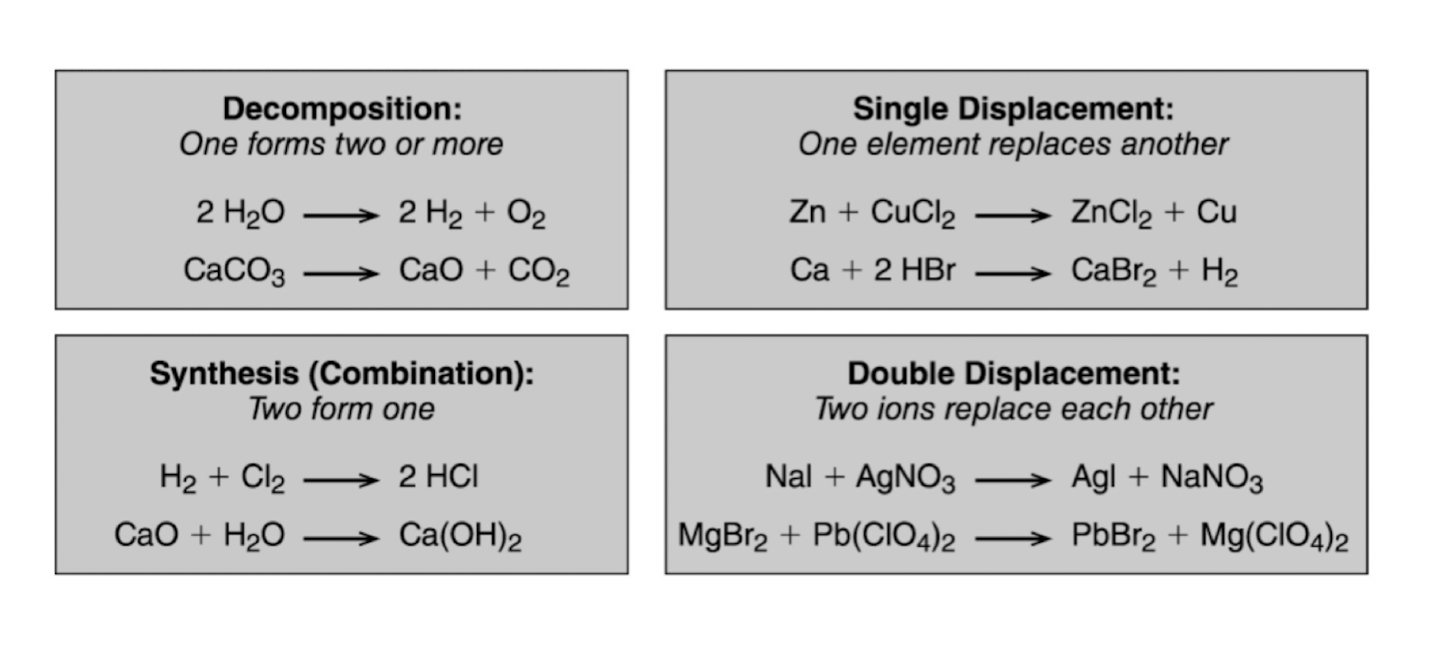
Different reaction types
Percent Composition Formula
% element = [(# of atoms)(molecular weight)/ molar mass of compound] x 100%
Avogadro’s Number: 6.022 × 1023 mol
Percent Yield Formula
(actual yield/theoretical yield) x 100%