Ch 10 : Muscle Tissue
Muscle tissue is classified into three types: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth, each of which has unique functions and characteristics that are essential for movement and physiological processes.
Primary function of muscle is to change chemical energy into mechanical energy to produce movement
Three types of muscular tissue (Review Chapter 4)
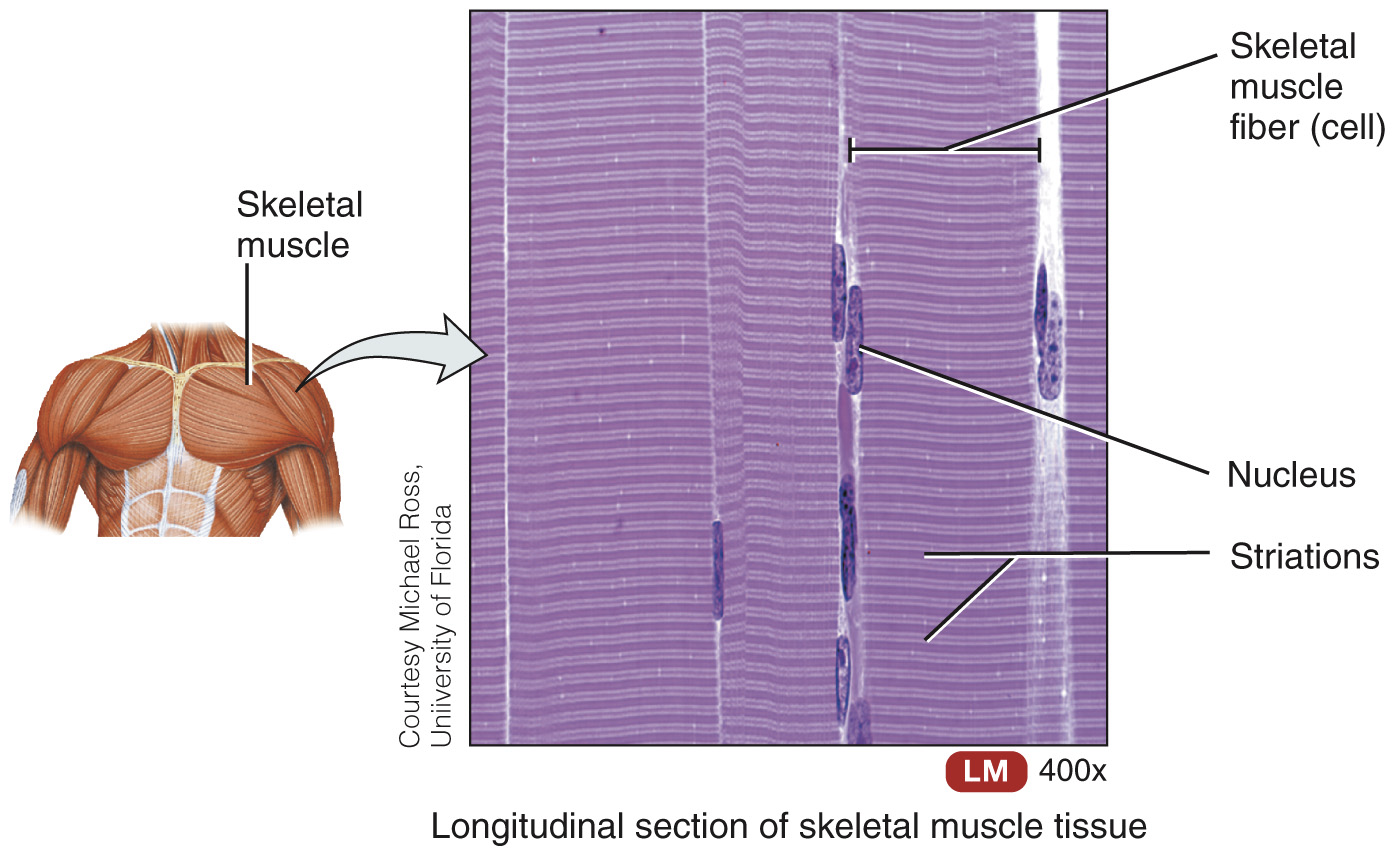
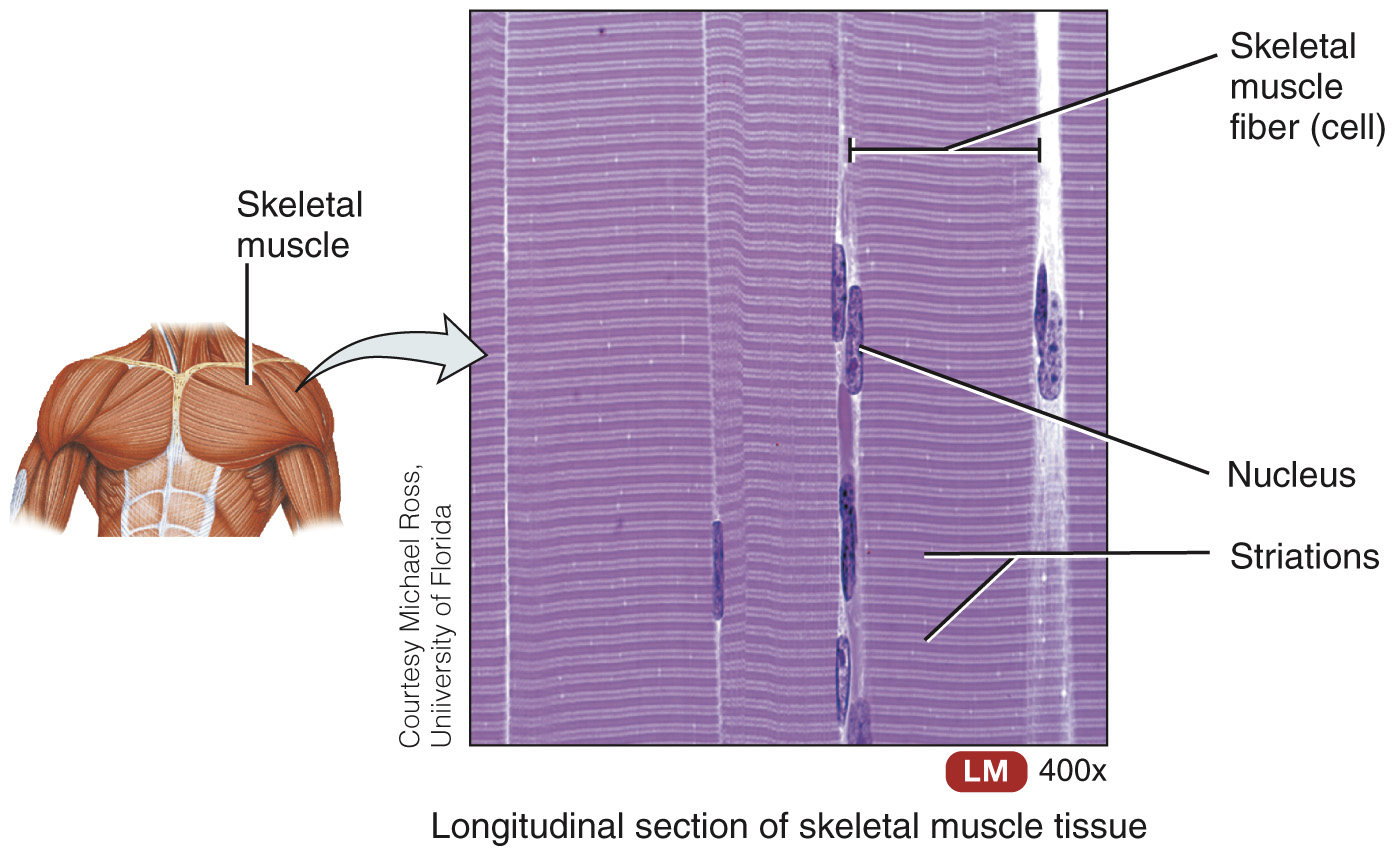
Skeletal muscle tissue – striated, under voluntary control, and moves bones of skeleton
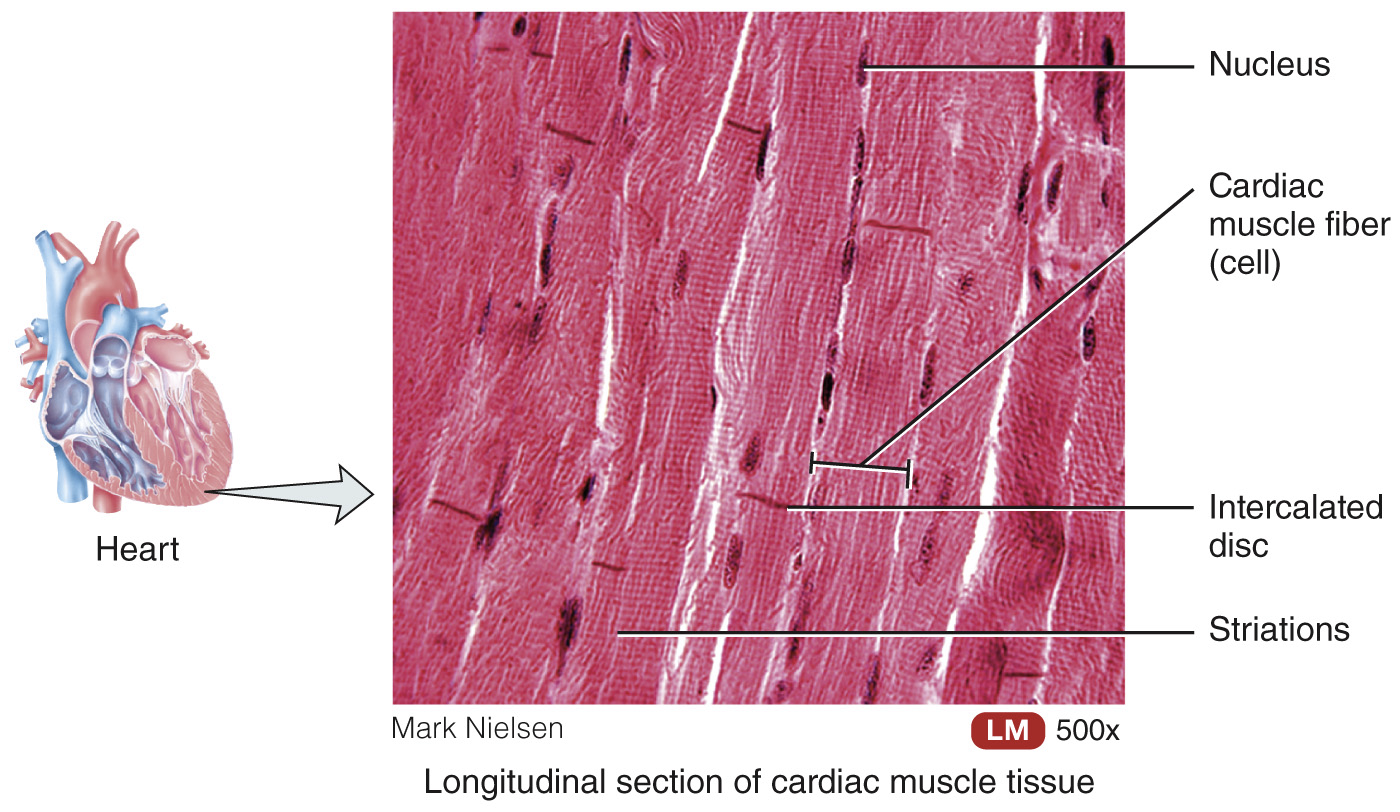
Cardiac muscle tissue – striated, under involuntary control, and pumps blood with auto rhythmicity in heart only
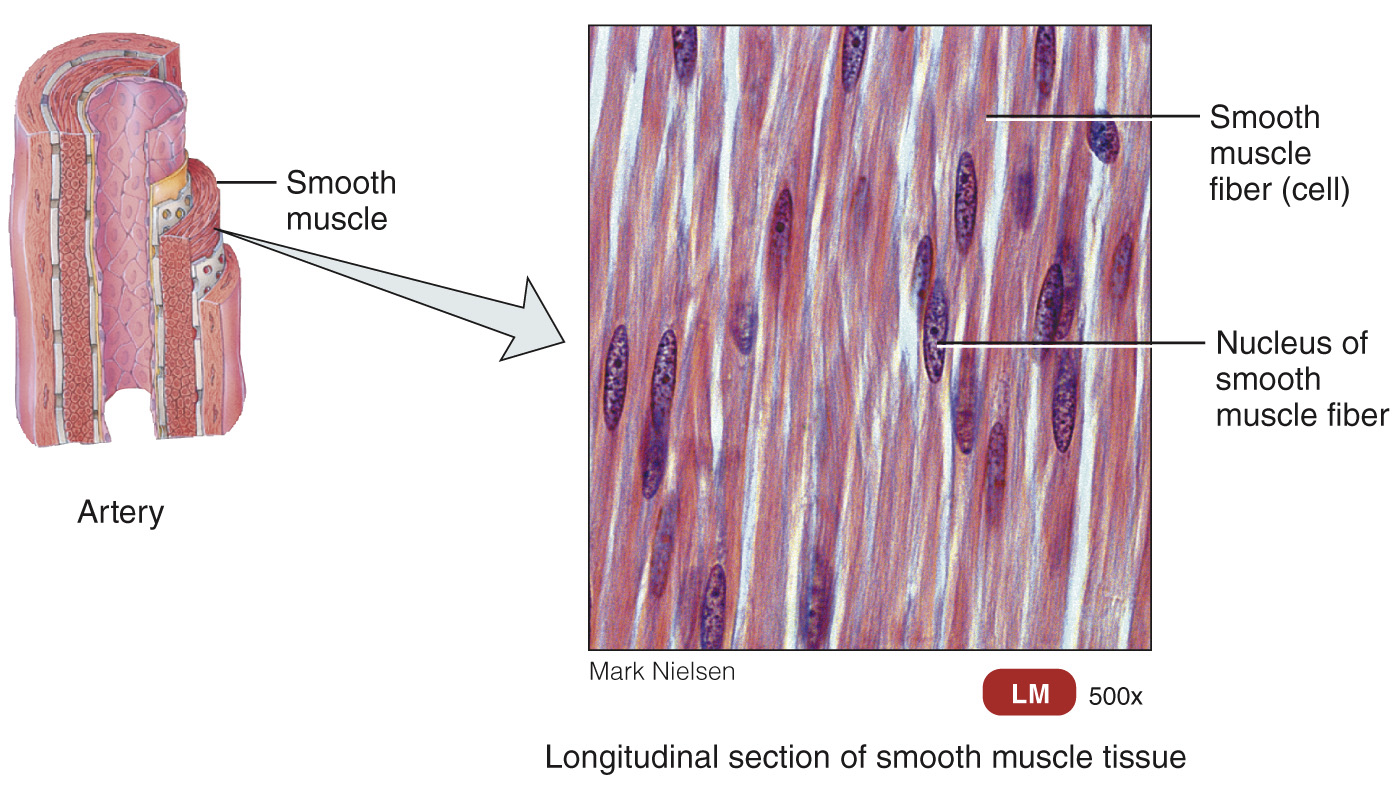
Smooth muscle tissue – non-striated, under involuntary control, and moves substances in hollow internal organs
Functions of Muscle Tissue
Produces body movements (walking, running etc.)
Integrated function of skeletal muscles with bones and joints
Stabilizes body positions (Standing up right, sitting etc.)
Skeletal muscle contractions without movement
Moves substances within the body
All three kinds of muscles as part of different organ systems
Generates heat
Involuntary shivering of skeletal muscle helps maintain temperature homeostasis
Special Properties of Muscle Tissue
Electrical excitability
Produce electrical action potentials (impulses) in response to certain stimuli
a property of both neurons and muscle cells
Contractility
Ability to shorten forcefully when stimulated (by AP), generating tension (ex. Lifting a book off a table)
Extensibility
Ability to stretch within limits without being damaged
Ex. (Stomach filling with food)
Elasticity
Ability to return to original length after contraction or extension
Skeletal Muscle as an Organ
Organ level of organization
Different types of tissues function together
Skeletal muscle tissue
Individual cells are called muscle fibers
Each skeletal muscle organ composed of hundreds to thousands of muscle fibers
Connective tissue
Surrounds and protects skeletal muscle tissue
Nerve and blood supply
Organ is well supplied with nerves and blood vessels
Connective Tissue of Organ
Hypodermis
Areolar and adipose tissue
Separates muscle from skin, insulates and protects
Fascia
Dense connective tissue sheet
Unites muscles with similar functions, carries nerves and vessels, and fills spaces between muscles
Three layers of connective tissue in organ (Epimysium, Perimysium, Endomysium)
Protect and strengthen skeletal muscle fibers
Tendon or aponeurosis
Rope-like or broad flat extension of connective tissue beyond muscle fibers for attachment of muscle organ