The Carbon Cycle
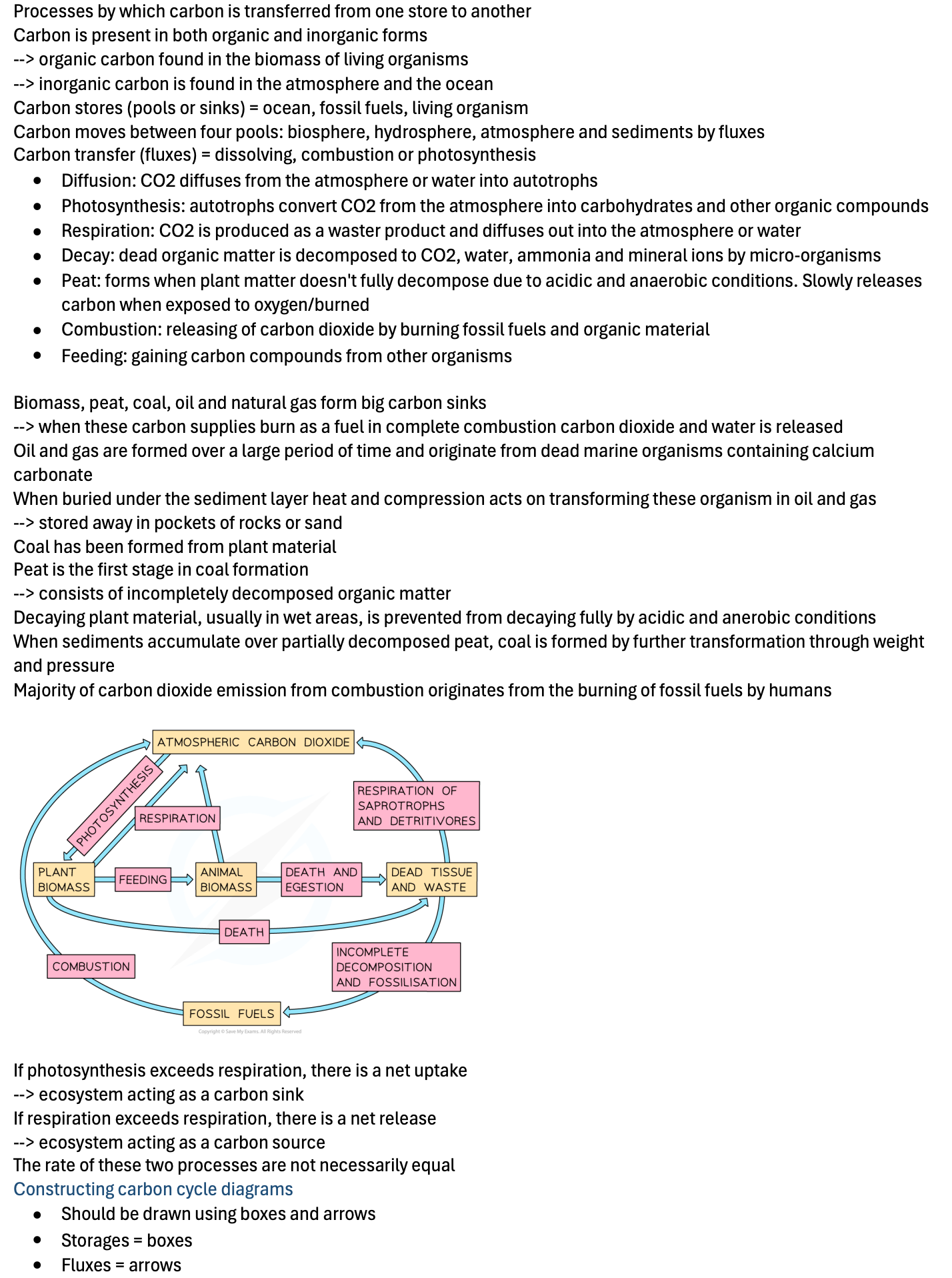
Processes by which carbon is transferred from one store to another
Carbon is present in both organic and inorganic forms
--> organic carbon found in the biomass of living organisms
--> inorganic carbon is found in the atmosphere and the ocean
Carbon stores (pools or sinks) = ocean, fossil fuels, living organism
Carbon moves between four pools: biosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere and sediments by fluxes
Carbon transfer (fluxes) = dissolving, combustion or photosynthesis
Diffusion: CO2 diffuses from the atmosphere or water into autotrophs
Photosynthesis: autotrophs convert CO2 from the atmosphere into carbohydrates and other organic compounds
Respiration: CO2 is produced as a waster product and diffuses out into the atmosphere or water
Decay: dead organic matter is decomposed to CO2, water, ammonia and mineral ions by micro-organisms
Peat: forms when plant matter doesn't fully decompose due to acidic and anaerobic conditions. Slowly releases carbon when exposed to oxygen/burned
Combustion: releasing of carbon dioxide by burning fossil fuels and organic material
Feeding: gaining carbon compounds from other organisms
Biomass, peat, coal, oil and natural gas form big carbon sinks
--> when these carbon supplies burn as a fuel in complete combustion carbon dioxide and water is released
Oil and gas are formed over a large period of time and originate from dead marine organisms containing calcium carbonate
When buried under the sediment layer heat and compression acts on transforming these organism in oil and gas
--> stored away in pockets of rocks or sand
Coal has been formed from plant material
Peat is the first stage in coal formation
--> consists of incompletely decomposed organic matter
Decaying plant material, usually in wet areas, is prevented from decaying fully by acidic and anerobic conditions
When sediments accumulate over partially decomposed peat, coal is formed by further transformation through weight and pressure
Majority of carbon dioxide emission from combustion originates from the burning of fossil fuels by humans
If photosynthesis exceeds respiration, there is a net uptake
--> ecosystem acting as a carbon sink
If respiration exceeds respiration, there is a net release
--> ecosystem acting as a carbon source
The rate of these two processes are not necessarily equal
Constructing carbon cycle diagrams
Should be drawn using boxes and arrows
Storages = boxes
Fluxes = arrows