12-04: Trigonometry
Radian Measure
Radian: measure of an angle formed by rotating the radius of the circle through an arc length equal to the radius
It is a unit of measurement - rads for short
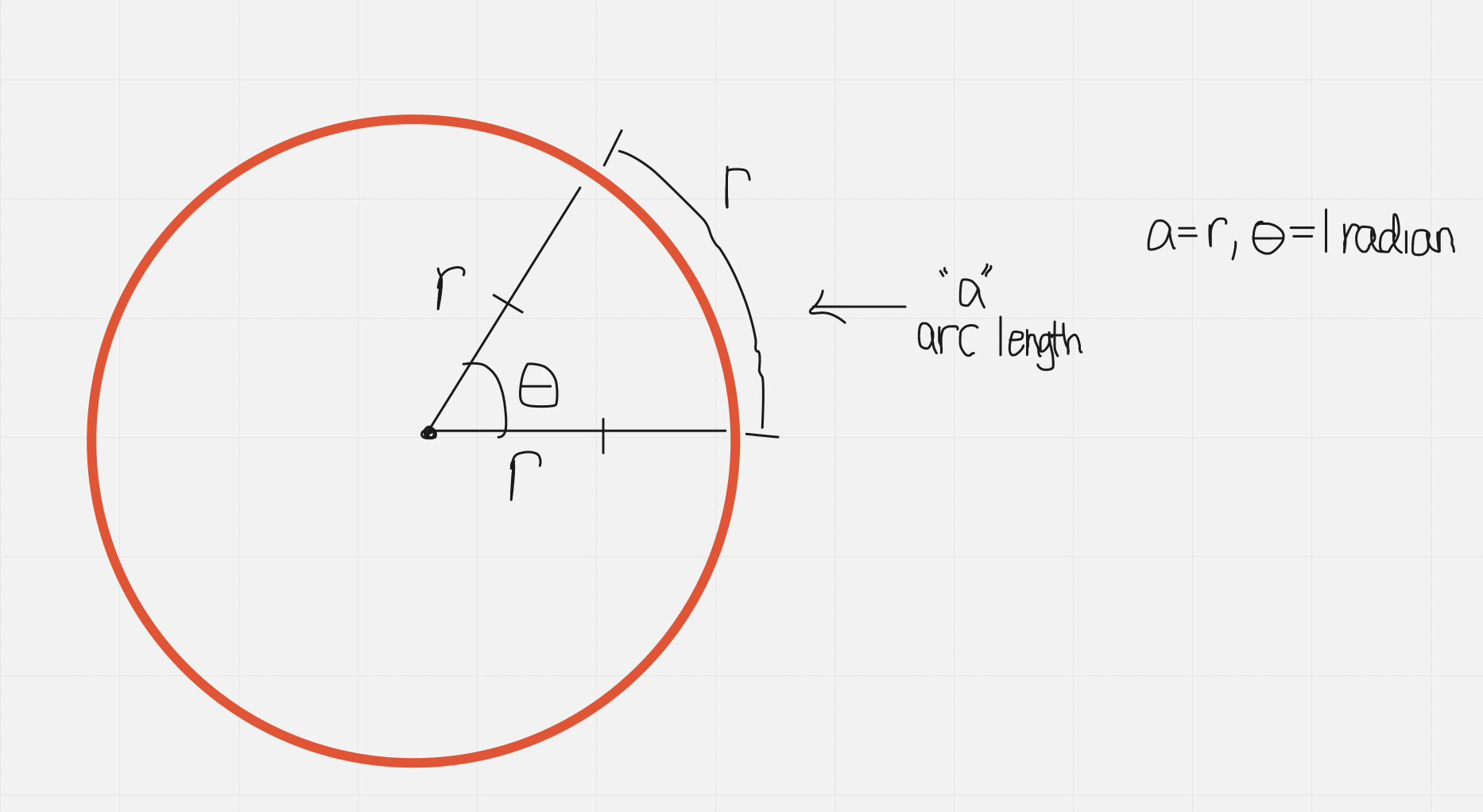
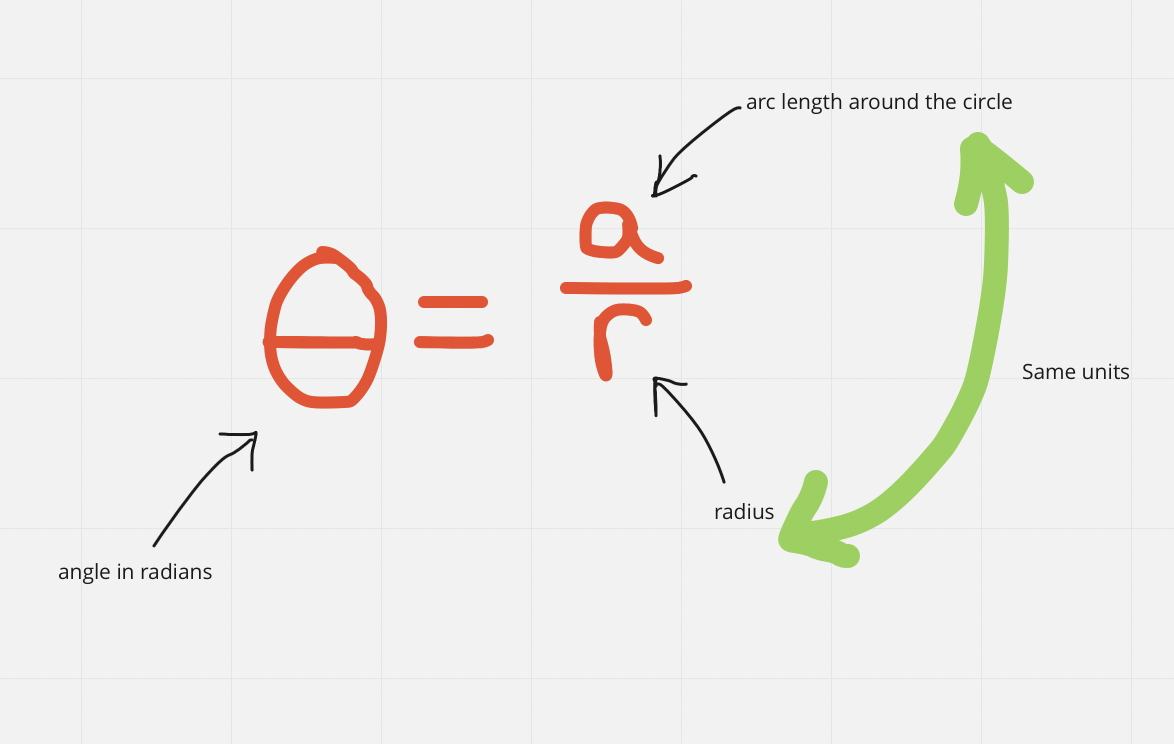
Radian measure of angle ϴ is defined as:
If you complete 1 full revolution then:

- 180º = π rads
- you can use fractions of semi circles to find other values - what you do to one side you must do to the other
Official Conversion Between Degrees and Radians
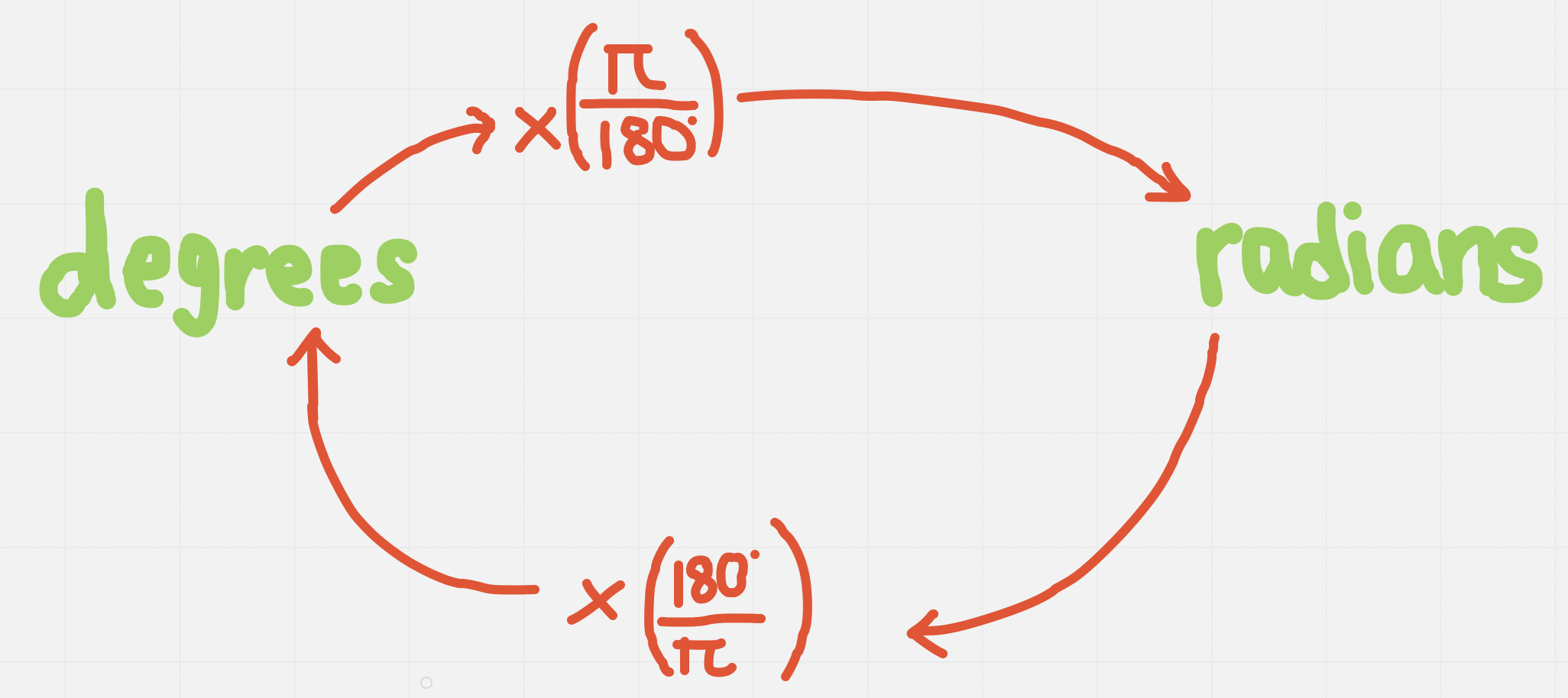
- Exact: leave π and fractions
- Approximate: decimal value
Angular Velocity
The angular velocity of a rotating object us the rate at which the central angle changes with respect to time
It is a rate of change → about how much the angle changes
RPM: Revolutions per minute → revolutions divided by minutes
- “Per” means division
Use Factor Label Method Process
e.g. The hard disk of a personal computer rotates at 7200 RPM. Determine the angular velocity in degrees per second.
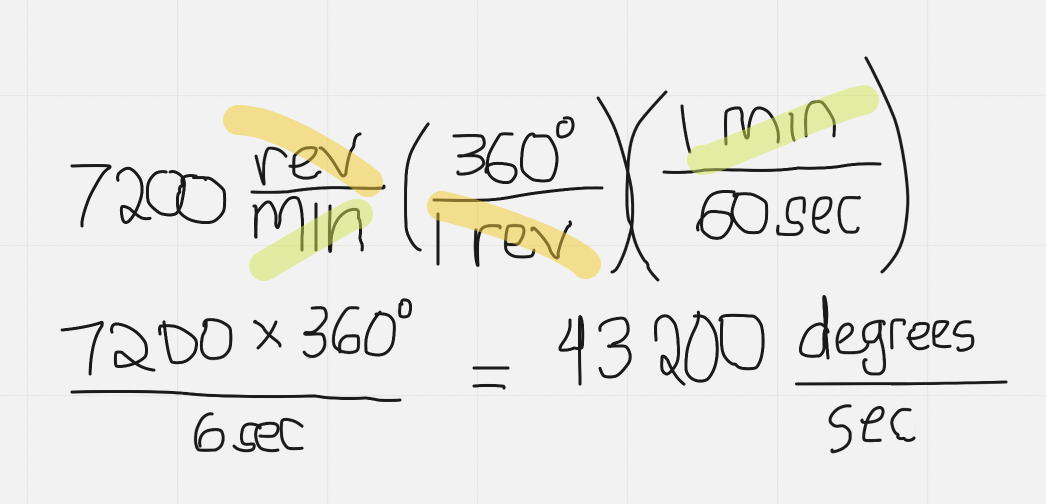
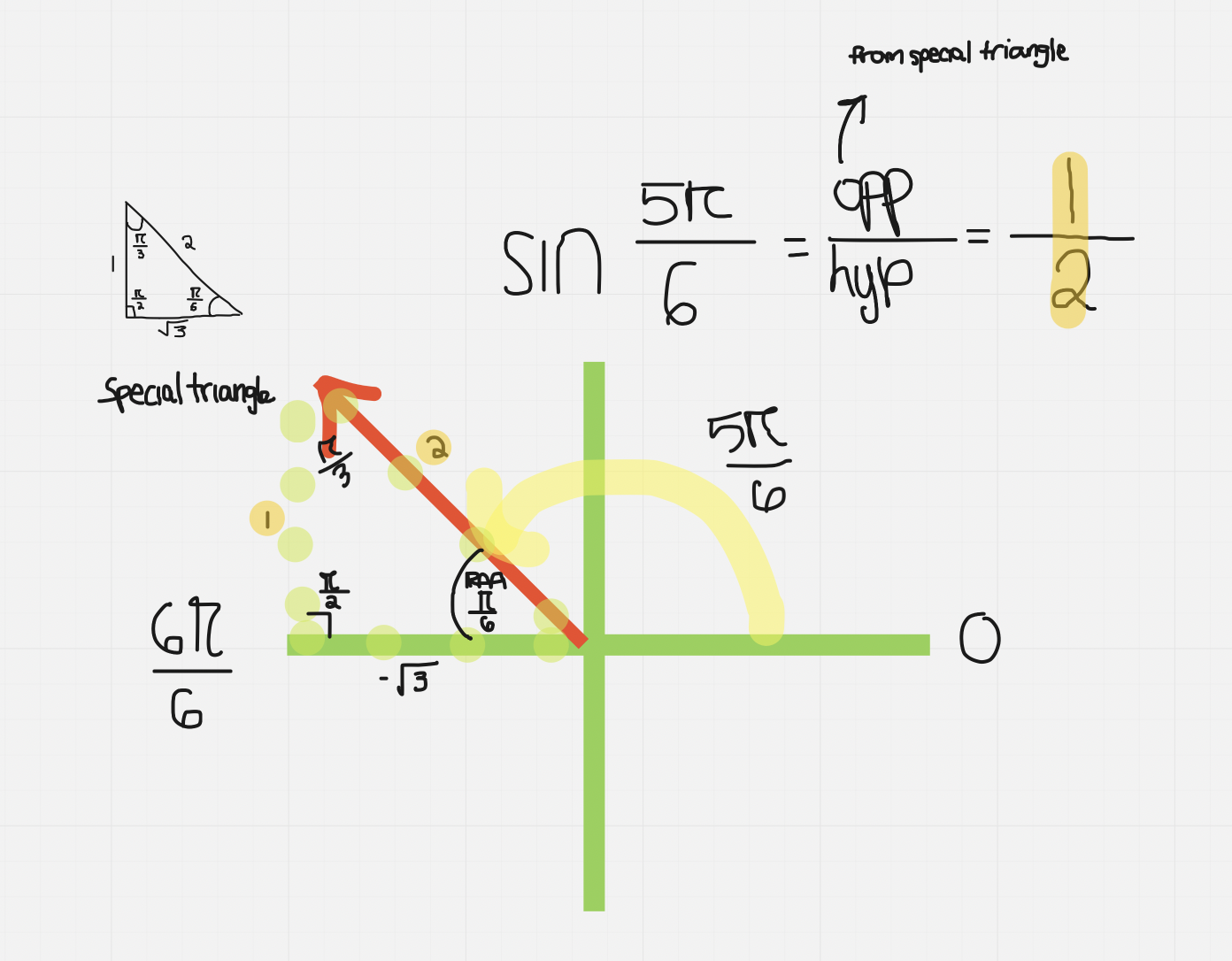
Special Triangles
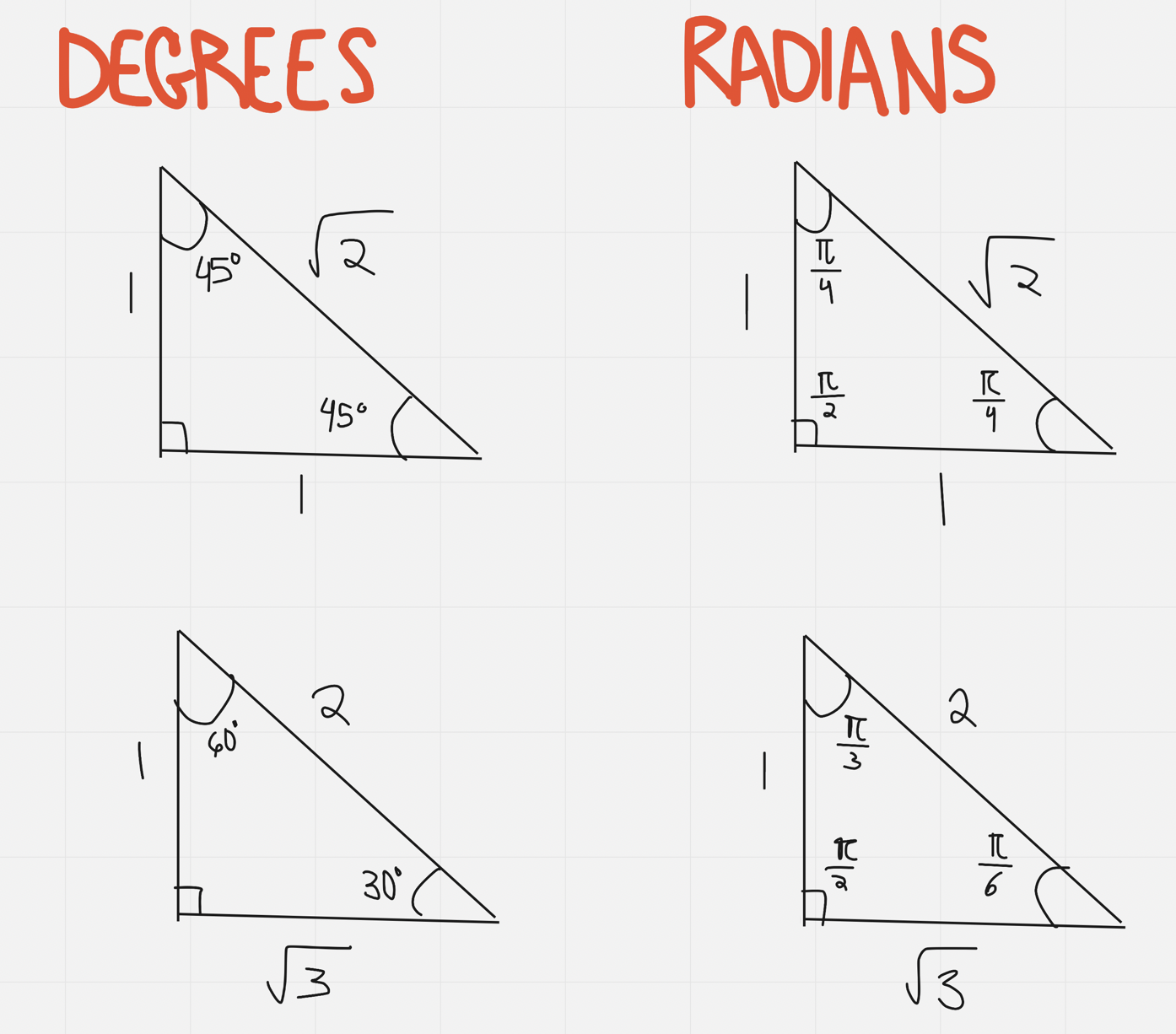
- Special angles have a denominator of 4, 6, or 3 in radians
Unit Circle: Radius of 1
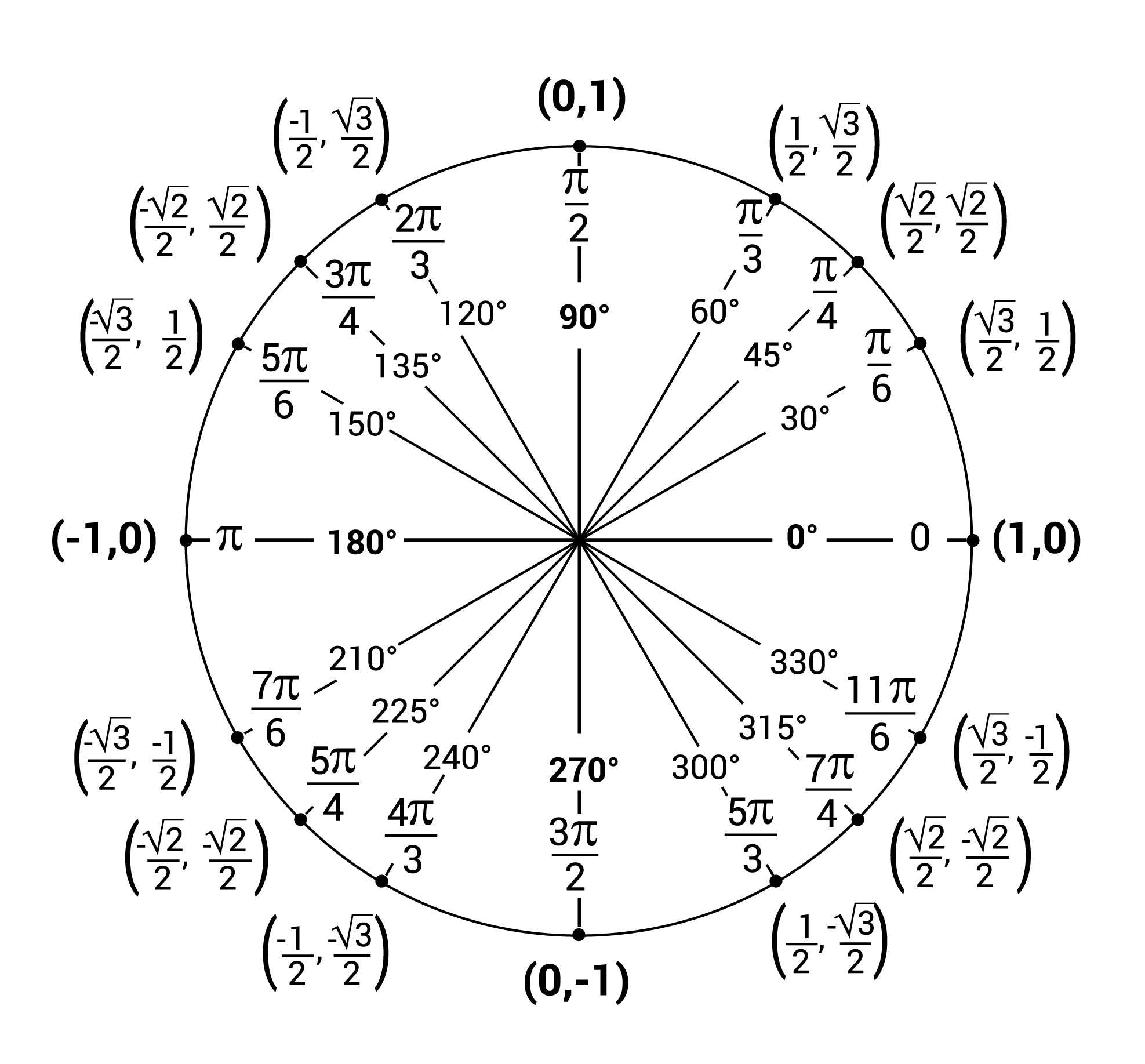
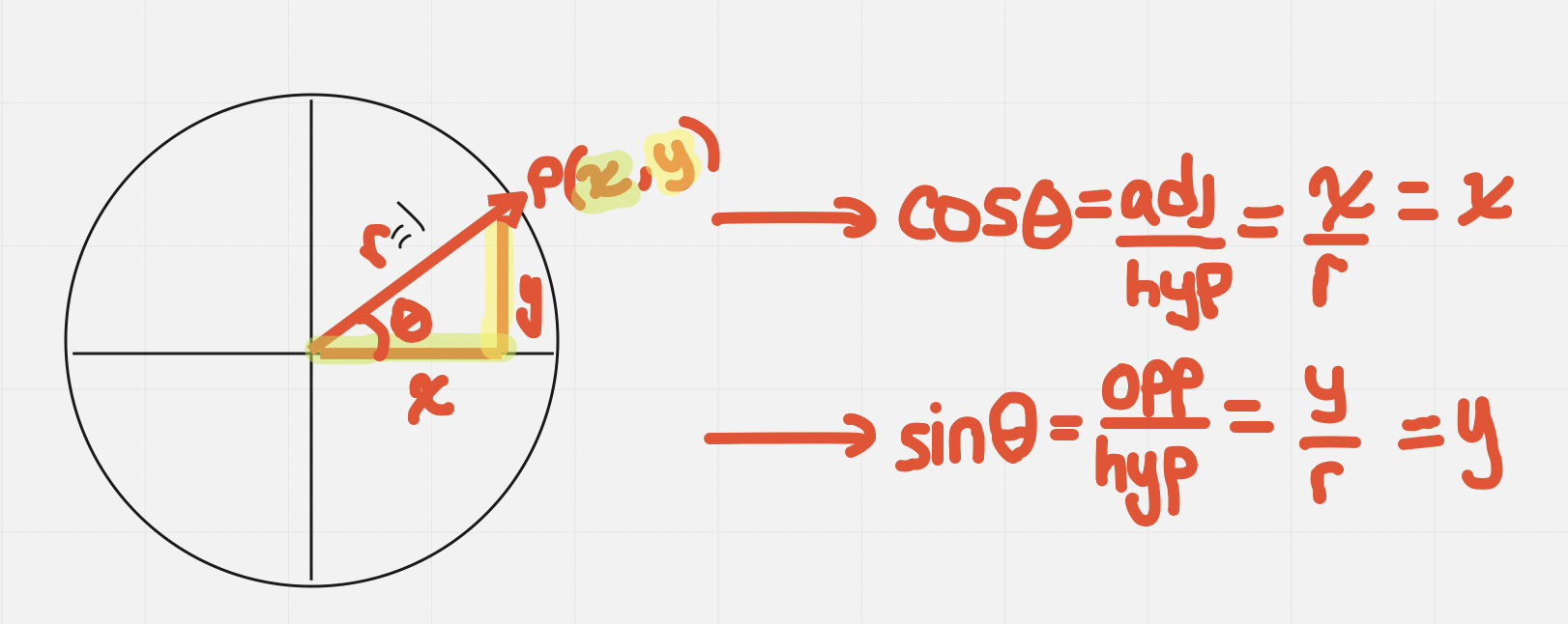
To Use The Unit Circle To Evaluate Trig Ratios For Special Angles
| Cosϴ | x values |
|---|---|
| Sinϴ | y values |
| Tanϴ | Sinϴ/Cosϴ = y/x |
Graph for Non-special Angles (Benchmarks)
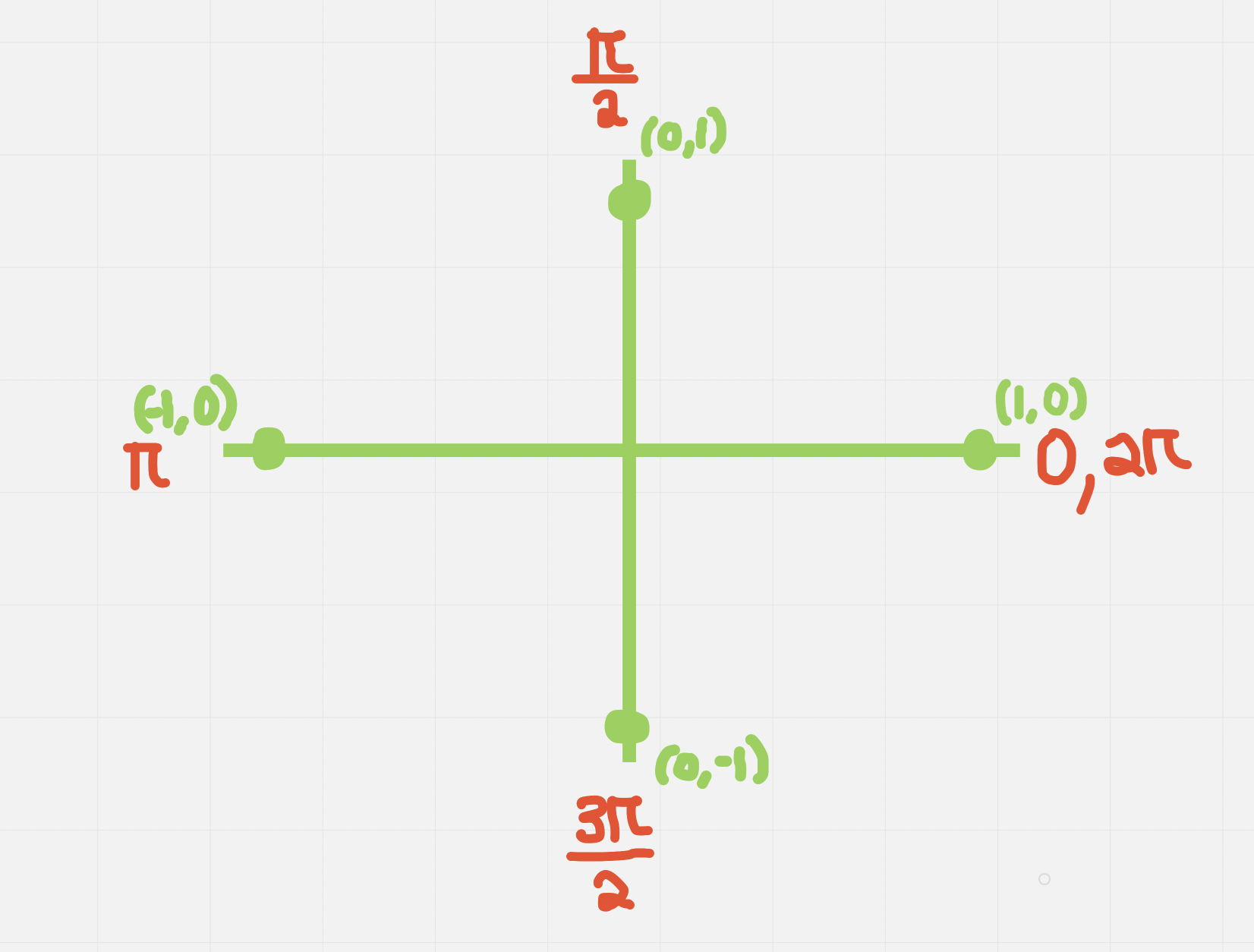
- Can be used with π/2, π, 3π/2, and 2π
- x value is cos, y value is sin
e.g. with special triangles
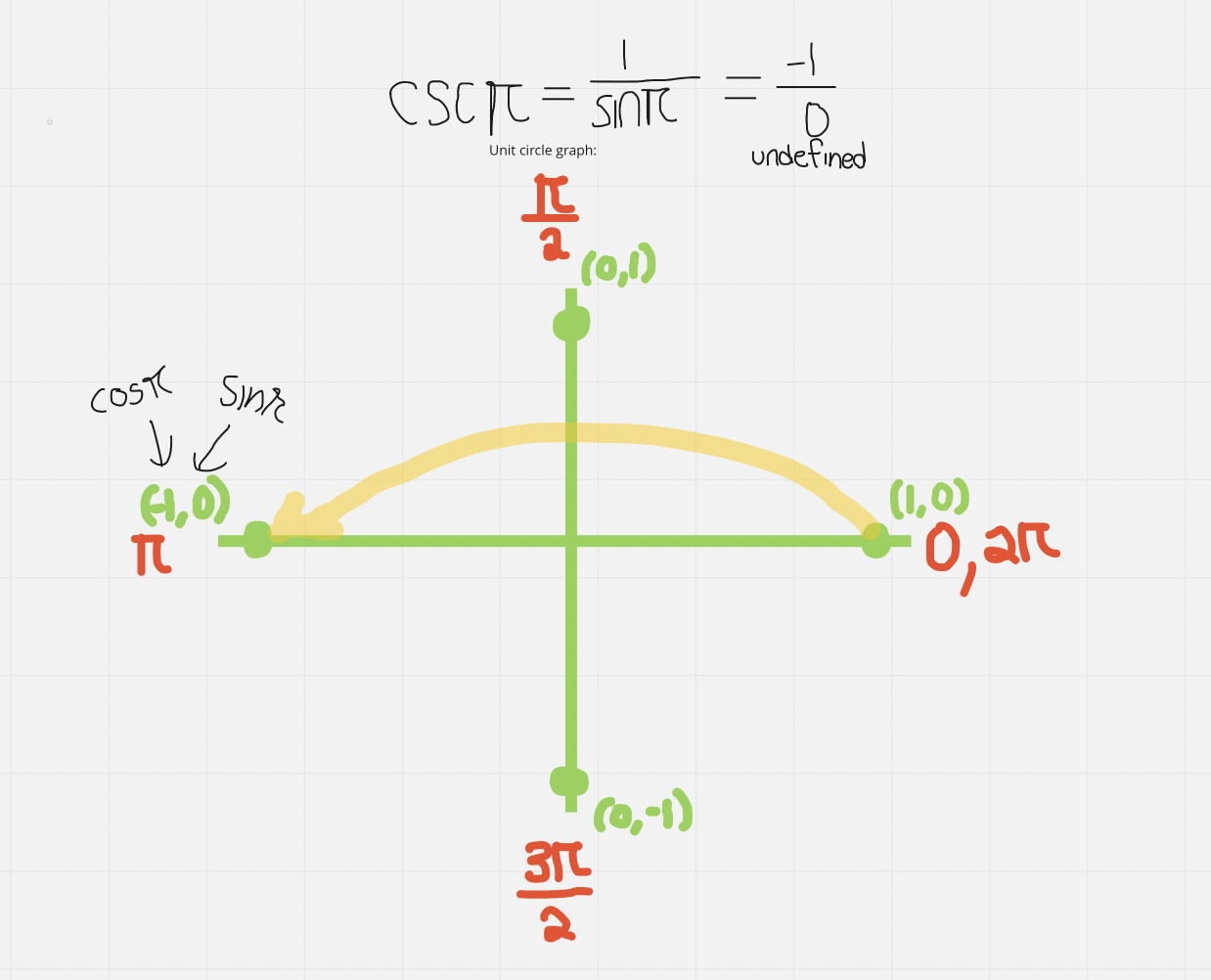
e.g. with non-special angles - note that this only can be used with the benchmarks that are labelled below
Equivalent Trigonometric Expressions
Equivalent expressions: expressions that yield the same value for all values of the variable
Rule of “co”
Sine
Secant
Tangent
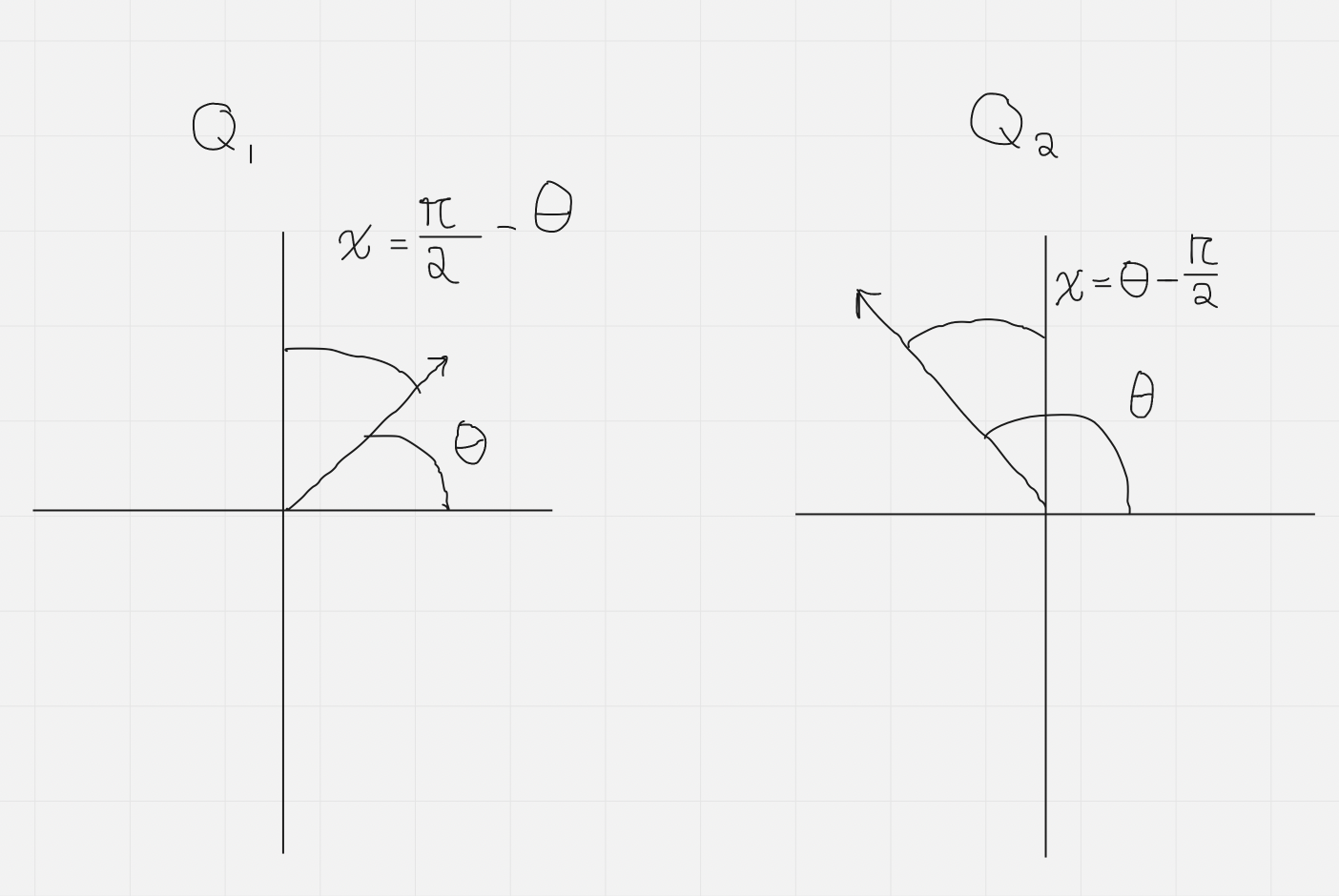
Steps for Determining Equivalent Trig Expressions Using Cofunction Identities
Is the angle in Q1 or Q2
Find the CO related angle
Rule of CO for ratio (CAST rule in Q2, so only sine/cosecant are positive)
Compound Angle Formulas
Compound angle expression: Trig expression that depends on 2 or more angles
| cos(x-y)= cosxcosy + sinxsiny |
|---|
| cos(x+y)= cosxcosy - sinxsiny |
| sin(x-y)= sinxcosy - cosxsiny |
| sin(x+y) = sinxcosy + cosxcosy |
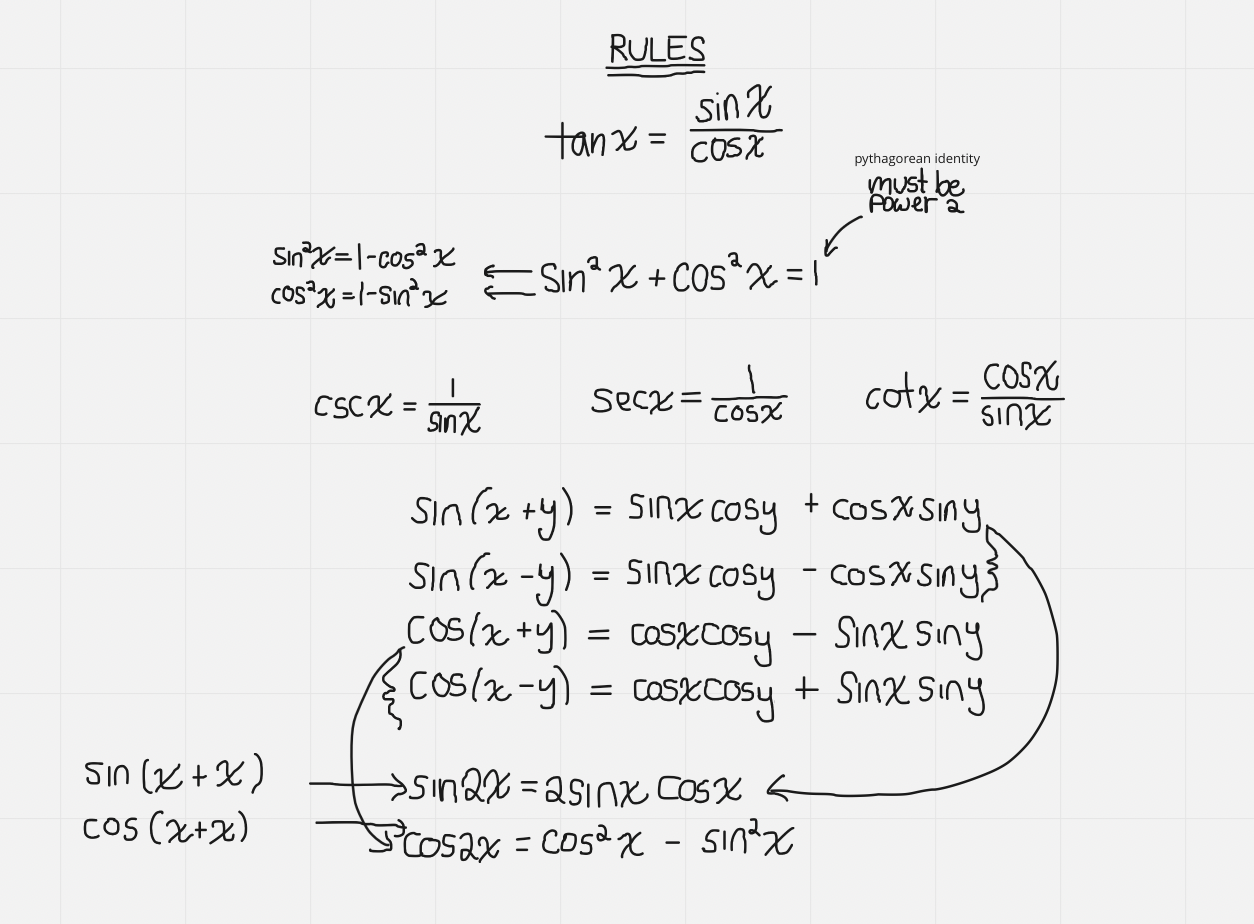
Trig Identities
Trig identities: both LS and RS should be equal
“Prove” tells you to do trig identities
Split LS and RS
No rearranging
No skipping steps
Replace everything with sin and cos
Simplify each side