Greek Lecture
Introduction
Week Two Overview
Importance of Preparation
Discussion Format (not a formal lecture)
Recap of Ideas from the Unit Site
Student Engagement
Attendance and Participation
Few students accessed the unit site before lecture (only ~7 out of 106)
Quizzes and Journals
Importance of attempting quizzes and journals for understanding
Weekly Tasks Overview
Focus on Completing Weekly Tasks
Weekly journal and quizzes are essential
Group presentations and research papers as additional tasks
Aim to spread workload evenly across the semester
Potential pressure during Easter and final submission weeks
Today's Topic: Greece
Location and Significance
Greece is in Europe, close to Italy
Importance of Greek architecture and its influence on contemporary architects
Greek civilization recognized as one of the earliest recorded civilizations
Civilization & Historical Context
Age of Ancient Greek Civilization
Mention of ancient artworks dating back 27,000 BC
Evidence of human civilization predating recorded history
Comparison with other ancient civilizations such as Indus Valley and Mesopotamia
Greek Contributions to Architecture and Society
Importance of Greek Civilization in Architecture
Greek civilization offers timeless concepts of beauty, order, democracy, and philosophy
Influence on modern understanding and aesthetics in society
Greek Aesthetics and Philosophy
Concept of Beauty and Order
Greek theories suggesting beauty ties strongly to proportion and symmetry
Aesthetic values continue to influence contemporary architecture
Contributions to Political Philosophy
Emergence of democracy and the focus on human rights
Philosophers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle contributed foundational ideas of humanism
Greek Architectural Characteristics
Discussion of Greek Architectural Styles
Classical architecture characterized by the use of columns in three orders: Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian
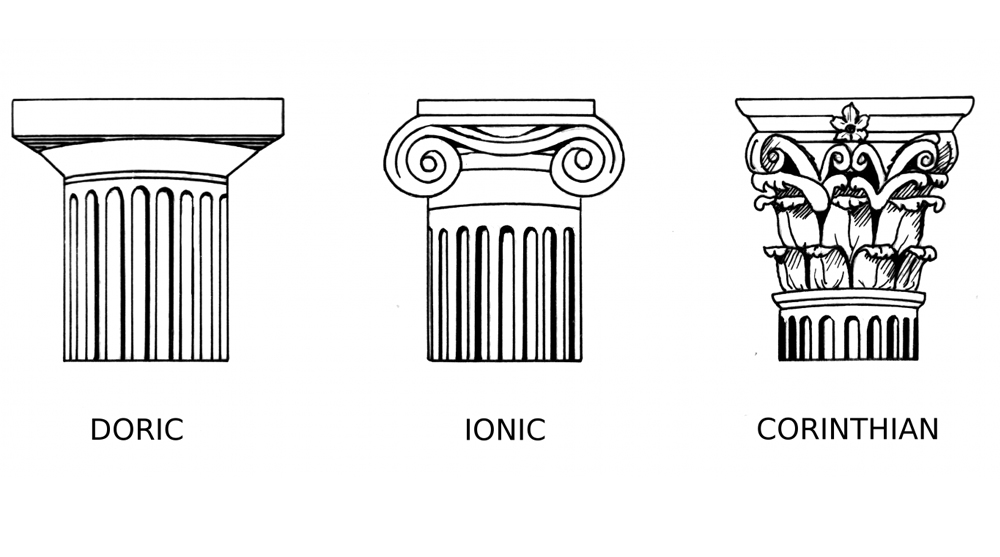
Use of columns reflects societal values and aesthetics
Influence of Humanism
The balance of physical beauty and intellect encouraged through public forums like theaters and stadiums
The Megaron: Foundation of Greek Architecture
Traditional Structure of Greek Homes
The Megaron as the basis for all Greek buildings, characterized by simple columns and a central hearth
Development into Public Structures
Evolution from the Megaron into temples and civic buildings
The Acropolis and Agora
Understanding Greek Urban Planning
Acropolis as the religious center elevated to signify the importance of the gods
Agora as the public space for civic life and democratic activities
The Influence of Mythology on Architecture
Concept of the Gods
Greek gods represented as perfect human forms, influencing architectural design
Temples designed not just for worship but also for public celebration and visibility to the gods
Ongoing Discussion and Critical Thinking
Importance of Regular Attendance and Preparation
Engage actively to enhance understanding and avoid lagging behind
The significance of critical thinking in journals and presentations
Summary and Conclusion
Reinforcement of Greek architectural ideals and humanistic philosophies
Reflection on how these concepts remain relevant in modern architecture and societal frameworks
Encouragement for continued engagement and question-asking in seminars and lectures.