Uploaded - Perfusion
Objectives
Review anatomy and physiology of the CV system
Discuss common alterations in perfusion across the lifespan
Discuss diagnostic tests to evaluate perfusion.
Define and discuss common disorders of the CV system
Discuss nursing interventions to promote or improve perfusion
Essential Function of the Cardiovascular System
Perfusion: The process by which oxygenated capillary blood passes through tissues.
Supplies oxygenated blood to the body.
Perfusion affects all body functions and systems.
Cardiovascular & Respiratory Physiology
Deoxygenated blood flows into the right atrium from the superior and inferior vena cava.
Blood flows from right atria to right ventricle, which pushes blood through the pulmonary valve to the lungs for oxygenation.
Oxygenated blood returns to the left atrium, flows into the left ventricle, and is sent to the body via the aorta.
Heart Anatomy
Pericardium: Protective layer surrounding the heart.
Heart Layers:
Epicardium
Myocardium
Endocardium
Chambers of the Heart:
Atria (left and right)
Ventricles (left and right)
Heart Valves: AV valves and semilunar valves.
Heart Conduction System (Figure 17.7)
Key Structures:
Sinoatrial node (pacemaker)
Atrioventricular node
Atrioventricular bundle (bundle of His)
Right and left bundle branches
Purkinje fibers
Heart Valves
Visual Overview:
Tricuspid valve (closed)
Mitral valve (closed)
Pulmonary valve (open)
Aortic valve (open)
Cardiac Cycle
Consists of contraction (systole) and relaxation (diastole).
Normal heart rate: 70-80 bpm.
Reference Video: https://youtu.be/_szVeIwJse0
Heart as a Pump
Pulmonary Circulation: Low-pressure system (blood to lungs).
Systemic Circulation: High-pressure system (blood to the body).
Coronary Circulation: Blood supply to the heart.
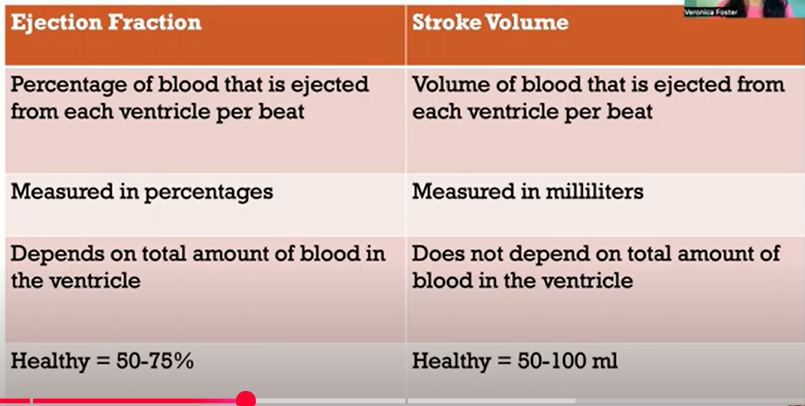
Stroke Volume (SV)
Calculation: Stroke volume = End-diastolic volume (minus) end-systolic volume.
Diastolic (relaxation phase): Ventricles fil by gravity, then by aortic systole.
End-diastolic volume: ~120 ml.
Systole: Blood is pumped from the ventricle. Some blood is left in the ventricle.
End systolic volume approximately 50 ml.
Heart beat: amount of blood leaving the heart with each cardiac cycle: 60-100 ml/beat.
Stroke volume is influenced by preload, afterload, and contractility.
Cardiac Output (CO)
Volume of blood ejected during systole.
Calculation: CO = SV x HR.
Example:
SV = 80 ml , HR = 80 bpm
CO = 6400 ml/min (6.4 liters).
Cardiac Output
Average adult CO: 4-8 L/min.
With poor functioning heart, CO decreases, leading to poor tissue perfusion.
Poor tissue perfusion leads to tissue ischemia (deprived of oxygen), leading to tissue necrosis or infarction (death)tissue ischemia (deprived of oxygen) or necrosis.
Determined by heart rate, preload, afterload, and contractility.
Heart Rate Regulation
Influenced by the autonomic nervous system.
Sympathetic nervous system: increases HR.
Parasympathetic nervous system: slows HR.
Effect of HR on CO:
Increased HR = Increased CO
Note: very rapid HR can reduce filling time and CO.
Decreased HR = Decreased CO.
Preload and Afterload
Preload: Volume of blood in ventricles at end of diastole (end-diastolic pressure).
Increased in conditions like hypervolemia, valve regurgitation, and heart failure.
Preload = Prepared to Pump
Afterload: Resistance the left ventricle must overcome to circulate blood.
Increased in hypertension and vasoconstriction.
Increased afterload = increased cardiac workload
Afterload = Against the Pressure
Understanding Preload
The stretch of cardiac muscle fibers.
Starling’s Law: Greater volume leads to greater stretch and contraction force to accomplish emptying.
Complications:
Too much volume (e.g., renal disease, CHF) leads to overstretch and ineffective contraction.
Too little volume causes too little stretch and decreased CO.
Understanding Afterload
Force the ventricles must overcome to eject blood.
Resistance Levels:
Low pressure in pulmonary circulation (right heart).
High pressure in systemic circulation (left heart).
Contractility
Ability of heart muscle fibers to shorten.
Poor contractility decreases forward flow of blood. Causes decreased CO and increased ventricular pressures.
Case Scenario on Cardiac Output
A patient with hypovolemic shock receives IV fluids. IV fluids will help _____ cardiac output by:
A. Decrease; decreasing preload
B. Increase, increasing preload
C. Increase; decreasing afterload
D. Decrease; increasing contractility
Quiz Question on Stroke Volume
Stroke volume plays an important part in cardiac output. Select all the factors below that influence stroke volume. (Select all that apply):
A. Heart rate
B. Preload
C. Contractility
D. Afterload
E. Blood pressure.
Clinical Indicators of Cardiac Output
Manifested by changes in organ function:
Brain
Kidneys
Skin integrity/tissue
Cardiac Index:CO adjusted for body size (NOT ON NCLEX)CO divided by BSA (M²)Normal:2.5-4.2 L/min/m².
Ejection Fraction (EF)
Calculation: EF = Stroke Volume / End-diastolic volume.
Represents the percent of volume ejected from the heart during contraction.
Normal EF: 50-70%.
Individuals with damaged hearts exhibit reduced EF and decreased perfusion.
Ejection Fraction Categories
Normal EF: 50-65% (adequate blood delivery).
Below Normal EF: 36-49% (may indicate inadequate pumping).
Low EF: Below 35% (indicates weakened heart and increased risk of sudden cardiac arrest).
Types of Perfusion
Central Perfusion:
Blood pumped by heart to organs
Created by cardiac output
Ex- EKG strips represent central perfusion
Requires adequate function, pressure, and blood volume.
Tissue/Local Perfusion:
Volume of blood flowing to target tissue. Requires patent vessels, adequate hydrostatic pressure, and capillary permeability.
Symptoms of Impaired Perfusion
Impaired Central Perfusion Symptoms:
Hypotension
Tachycardia
Extra heart sounds (S3, S4)
Shortness of breath (SOB)
Dysrhythmias
Shock (Septic = level 4)
Impaired Local/Tissue Symptoms:
Changes in mentation
Cool, pale skin
Decreased or absent pulses
Prolonged capillary refill
Toe/finger pain
Decreased urine output
Peripheral edema
Gidden’s Perfusion Definition
Ischemia:
Blood is available but reduced
Thrombus/Stenosis/Vasospasm
Always results in hypoxia
Leads to pain
Hypoxia
Ischemia was not corrected
Reduced oxygen (turning blue)
Anoxia: Total lack of oxygen resulting in cell death.
Congenital Heart Disease
Focus on developmental aspects in infants, children, and during pregnancy.
Page 28
Impaired Perfusion: Who is at Risk?
Populations at Risk:
Middle and older adults
Before age 64: Men > Women
After age 64: Woman > Men
Black race
Trauma/blood loss
Atherosclerosis
DM
High sodium diet
Smoking
Hyperlipidemia
Immobility/sedentary
Alcohol
Birth control
Pregnancy
Socioeconomic
Genetics
Fetal Circulation
Transition from Fetal to Pulmonary Circulation
First breath expands lungs
Pulmonary resistance drops and blood flows to lungs
Ductus arteriosus closes (10-15 hours after birth)
Permanent closure occurs 10-21 days after birth.
Increased pressure in left atrium stimulates closure of foramen ovale.
Infant Vital Signs
High HR (> 100 bpm) due to high metabolic rate and oxygen needs
Low blood pressure
Increased oxygen demand will cause tachycardia
Little cardiac reserve
Hypoxic or ischemic states: When O2 delivery drops below a critical level, the infant’s metabolism changes and produces lactic acid.
Pulse oximeter sensor positioning: Position of sensor can affect the PI reading, especially in premature infants
Gestational age: Age of infant can affect perfusion
Look for AMS, skin appearance, capillary refill time, urine output, and pulses for abnormalities
Children and Cardiac Function
Heart rate gradually decreases with age
Blood pressure increases with age - Adult ranges by puberty
Responds to severe hypoxemia with bradycardia
Prolonged hypoxia will result sin cardiac arrest
Treatment of hypoxemia is essential to prevent cardiac arrest
Heart disease must be managed to decrease cardiac workload and oxygen demands
Most cardiac arrests in children are results of impaired oxygenation, not defects within the cardiovascular system
Test Yourself
Apprpriate intervention is vital for many children with heart disease in order to go on to live active, full lives. Which of the following outlines an effective nursing intervention to decrease cardiac demands and minimize cardiac workload?
A. Feeding the infant over long periods
B. Allowing the infant to have their way to avoid conflict
C. Scheduling care to provide for uninterrupted rest periods
D. Developing and implementing a consistent care plan
Alterations in Cardiac Function in Children
Congenital heart defects are, excluding prematurity, in first year of life.
Acquired infection - endocarditis
Injury of trauma to the heart
Changes during Pregnancy
Increased cardiac output early in pregnancy
CO peaks at 30-50% above pre-pregnant levels.
HR increases
Enlarging uterus causes stasis of blood in lower extremities - edema and varicose veins
Cardiovascular Changes with Aging
Myocardial hypertrophy
Stiffened heart valves
Heart murmurs
Stenosis or incompetence of valves.
HTN
Varicose veins
Irregular rate or rhythm
Bradycardia determined by genetics, physical health and conditioning, social environment
Atypical presentation - Complaints of fatigue, decreased activity, sleep disturbance, pains that are not normal.
Mental health changes may be first sign of cardiac issues.
Changes of Aging: CV System
Heart may pump less efficiently
Heart cannot accommodate to meet increased need.
Arteries lose elasticity
BP may increase
Blood flow to brain and vital organs may be decreased
Veins are less efficient in returning blood to heart.
Aging Effects on Heart Function
Aging results in gradual changes in the function of the heart, which are minut under resting conditions but are more significant during exercise
Some age-related changes to the heart are:
Decreased CO and HR
Increased arrhythmias
Hypertrophy of left ventricle
Development of stenosis or incompetent valves
Development of CAD and heart failure
Regular exercise improves heart function across all ages.
Vascular System Changes with Aging
Lipid deposits and calcification of vessels occur resulting in decreased elasticity or hardening of vessel walls.
BP changes
PVD versus PAD
Description of Vascular Problems
Vascular problems typically appears at ages 60-80.
Largely underdiagnosed
Risk factors:
Tobacco use
Chronic kidney disease
Diabetes
Hypertension
Hypercholesterolemia
Pts with PAD are more likely to have CAD and/or cerebral artery disease
Renal System Effects of Age
Decreased perfusion to kidneys
Glomerular filtration rate decreased
By age 80, GFR is 30-50%.
Reduced clearance of medications
Decreased ability to clear sodium from the blood
Decreased ability to clear sodium from blood
Decreased renin and aldosterone leading to increased sensitivity to dietary sodium
Cardiac Valves
Types: Tricuspid, Mitral, Pulmonic, Aortic valves.
General Assessment Findings of Heart Failure
Symptoms:
Chest pain
Shortness of breath
Edema
Nocturia
Palpitations
Fatigue
Dizziness
Changes in level of consciousness.
Risk Factors for Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Nonmodifiable factors: age, gender, ethnicity, family history.
Major modifiable factors:
Elevated serum lipids
Cholesterol >200 mg/dL
Triglycerides (>150 mg/dL)
Hypertension
>140/90 mm HG
Goal for >age 60 is <150/90 mmHg
Tobacco use
Increased catecholamine release
Increased LDL, Decreased HDL, Increased oxygen radicals
Increased carbon monoxide
Second-hand smoke
Physical inactivity
Obesity
Common Perfusion Labs
Cardiac enzymes/markers
CK, Troponin, Myoglobin, CRP
Troponin 0.5-2.3 suspicious for cardiac injury.
Troponin >2.3 positive for myocardial injury
BNP
Blood coagulability
PLTs, Fibrinogen, PT/PTT, INR, D-Dimer
BUN/Creatinine/GFR
HgbA1C
Serum lipids
Total cholesterol, HDL, LDL, Triglycerides
Triglycerides main storage of lipids and constitute approximately 96% of fatty tissue
Cholesterol - Precursor to corticosteroids, sex hormones, and bile salts. Absorbed by food produced by liver.
Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP)
Potassium: 3.5-5 mmol/L
Magnesium:
BUN: 7-20 mg/dL
Creatinine: 0.7-1.2 mg/dL
Sodium: 135-145 mEq/L
Diagnostic Test Continuation
EKG
Cardiac catheterization
Echocardiogram
Used to measure EF
Examines shape, size, movement of cardiac structures
Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) is through mouth into esophagus
Echocardiography
Indications:
Suspected valvular heart disease, CAD, tumors, thrombus, pericardial effusion
To define cardiac chamber size
Evaluate LV function
Visualize vegetations of endocarditis
Pharmacotherapy for Heart Conditions
Vasodilators
Vasopressors
Diuretics
Antidysrhythmic
Antihypertensives
Cardioglycosides,
Anticoagulants
Antiplatelet agents
Thrombolytics
Antilipidemic
Some perfusion disorders
Hypertension
Myocardial Infarction
Congestive heart failure
Peripheral Vascular Disease
Signs and symptoms
HTN often called “silent killer” because it is frequently asymptomatic.
Signs and symptoms
Fatigue
Reduced activity tolerance
Dizziness
Blurred vision
Nape pain
Palpitations
Angina
Difficulty breathing
Complications of Hypertension:
Brain Stroke: Reduced blood supply can lead to loss of brain function or stroke.
Vision Loss: Hypertensive Retinopathy damages blood vessels in the retina, leading to vision loss.
Kidney damage: Can’t effectively filter blood, resulting in dangerous accumulation of fluid and waste.
Bone loss: High blood pressure may increase the amount of calcium in your urine. That excessive elimination of calcium may lead to loss of bone density
Heart attack: HTN causes the heart to pump against high blood pressure, making it work harder than necessary. Over time, this causes the heart muscle to thicken, restricting blood flow, which can lead to heart failure.
Blood vessel damage: HTN is leading cause of atherosclerosis.
Treatment of Hypertension:
Non-Pharmacological Management:
Lifestyle changes:
Reduce salt and fat intake.
Weight loss (BMI 18.5-24.9 kg/m²).
30 minutes of exercise daily.
Quit smoking.
Limit alcohol intake (2 drinks/day for men, 1 for women).
Manage stress.
DASH Diet: Emphasizes fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy; low in saturated fat, cholesterol, and total fat.
Classification and Management of Blood Pressure for Adults:
Blood Pressure Classifications:
Normal: <120/<80
Prehypertension: 120-139/80-89
Encourage lifestyle changes, no drug needed.
Stage 1 Hypertension: 140-159/90-99
Lifestyle changes recommended.
Stage 2 Hypertension: ≥160/≥100
Lifestyle changes and drug therapy (Thiazide, ACEI, ARB, etc.).
Abnormal Findings in the Cardiovascular System:
Myocardial disorders
Pump disorders
Valvular disease
Septal defects
Congenital heart disease
Electrical rhythm disturbances
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS):
3 types:
NSTEMI
STEMI
Unstable angina
Occurs when a blockage causes blood flow to your heart to suddenly slow or stop.
Common Signs:
Chest pain or pressure
Shortness of breath
Dizziness
Valvular Heart Disease:
Types:
Mitral stenosis
Aortic stenosis
Mitral regurgitation
Aortic regurgitation
Mitral valve prolapse
Symptoms of Myocardial Infarction:
Common symptoms include:
Pressure or tightness in the chest
Pain in various body areas (chest, back, jaw)
Shortness of breath
Nausea/vomiting
Sweating/pallor
Anxiety
Crushing chest pain
Acute Myocardial Infarction:
Most serious form of ACS.
Myocardial tissue abruptly and severely deprived of oxygen.
Types include
Subendocardial MI
Transmural MI
Inferior wall MI
Process evolves over hours, requiring dynamic treatment.
Immediate Treatment of MI:
May include medications such as:
Painkiller - Morphine
Antiemetic - Metaclopramide
Anti Thrombotic - Aspirin, Ticagrelor
Oxygen
Metoprolol
Anticoagulant - LMP Heparin, Fondaparinux
Nitrate
If thrombus -
Thrombolytic
PCI (percutaneous coronary intervention)
GA receptor antagonist
Coronary angiography
Maintenance - Statins, beta blocker, ACE inhibitor, Aspirin, Ticagrelor, LMP heparin
Cardiac Stress Test:
Types:
Exercise (treadmill, bike)
Pharmacologic (e.g., persantine, adenosine, dobutamine)
Preparation: Fast for 4 hours; avoid stimulants.
Monitoring: ECG, heart rate, and ischemic changes during the test.
Terminated:
Desired heart rate is reached
BP or HR drops
HTN (220 systolic or 110 diastolic)
Severe ST depression
Pt reached or exceeded predicted maximum heart rate
VT or runs of 3 or more
Atrial tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, or atrial flutter
2nd or 3rd degree heart block
Angina
Dyspnea, faint, or fatigue
Muscular pain of arthritis and claudication
Pt looks pale/clammy
Contraindications to Stress Testing:
Absolute: Congestive heart failure, uncontrolled arrhythmias, severe aortic stenosis, unstable angina, myocardial infarction within last 2 days, acute PE, myocarditis, severe pulmonary HTN, aortic dissection
Relative: Known left coronary artery obstruction, hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy, uncontrolled hypertension, acute illness such as anemia, electrolyte imbalance, uncontrolled hyperthyroidism
Types of Stress Tests:
Regular stress test
With imaging - Used when problem interpreting EKG
With echocardiogram
With nuclear imaging
Chemical stress test - for the person who cannot safely exercise to the level needed
Must be combined with imaging
Echo, nuclear, MRI, PET
Cardiac Catheterization:
Invasive procedure
Femoral or brachial approach
Assess peripheral pulses, capillary refill, temp, and color in the affected extremity
Screening for dysrhythmias
Risk of major complication <1%
Indications for Cardiac Catheterization:
Acute MI with complications.
Assessing volume status
Severe LV failure
Cardiac tamponade
Cardiogenic shock
Biopsy of right-sided structures
Differentiate between pericardial and constructive pericarditis
Severe pulm hypertension
High risk cardiac pts pre/intra/post op
Potential complications of cardiac catheterization
Vascular injury/complications involving access site
Retroperitoneal bleeding
Thrombus/cholesterol embolism
CVA
Dissection
Arrhythmias
Stent failure/in-stent thrombosis
MI
Infection
Allergic reaction
Med reaction
Radiation injury
Reaction to anesthesia
Nursing care after cardiac catheterization
Observe for bleeding/hematoma
Assess BP/HR/peripheral pulses in affected extremity every 15 minutes for 1 hour, every 30 minutes for 1 hour, and hourly for 4 hours.
Monitor temp, color, capillary refill in affected extremity
Ensure activity restriction x2-6 hours
Femoral artery access:
Keep leg straight x6 hours
Head of bed no greater than 30 degrees
May turn pt side to side
Radial artery access:
Compression device is placed on wrist, which is typically worn x2 hours
Pt allowed to sit up and eat after procedure
No undue stress to be put on radial artery as it heals
Avoid heavy lifting with affected hand
Resume regular activity in 3 days
Contraindications for cardiac catheterization
Severe CHF
Severe electrolyte abnormalities
Bleeding diathesis
Serum creatinine greater than or equal to 1.5 mg/dL
Poor patient cooperation
Nursing Interventions for CAD:
Cardioprotective nutrition
Monitoring fluid/electrolyte status
Administer fluid as needed
Monitor vital signs
Administer meds/O2 as needed
Assess peripheral pulses
Smoking cessation
Prepare/monitor before/after diagnostic testing
Positioning
Wellness teaching
Evaluation:
Heart rate and blood pressure assessment.
Pain assessment
Stable versus unstable angina
Degree of breathlessness
Pulses/edema/skin temp assessments
Pathophysiology of Heart Failure:
Overview of systolic vs. diastolic dysfunction.
Causes of stiffness and enlargement in ventricles.
Left-sided Heart Failure:
Most common type. AKA “forward failure”
Left ventricle fails, resulting in oxygen-rich blood not being pumped to the rest of the body. Can back up into the left atrium and into the lungs
Causes fatigue because the body is not receiving enough blood, and SOB because of congestion in the lungs.
Symptoms:
Orthopnea
Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
Elevated pulmonary capillary wedge pressure
Restlessness
Confusion
Tachycardia
DOE
Fatigue
Cyanosis
Pulmonary congestion (cough, crackles, wheezes, hemoptysis, tachypnea)
Right-sided Heart Failure:
AKA “backward failure”. Often results from left-sided failure. As failing left ventricle causes fluid to build up in the lungs, the right ventricle unable to pump blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen.
Signs/symptoms:
Enlarged spleen/liver
Ascites
Increased peripheral venous pressure
Fatigue
May be secondary to chronic pulmonary problems
JVD
Anorexia or complaints of GI distress
Weight gain
Dependent edema
CHF Treatment
General measures
Treat underlying cause
Diet modifications
Adequate rest
Mild exercise
Alcohol/smoking cessation
Adequate oxygen
Health maintenance (vaccines, well checks, etc)
Medications
Diuretics
ACE inhibitors
ARBs
Beta blockers
Cardiac glycosides
Surgical
Revascularization (angioplasty, CABG)
Valve repair/replacement
Device therapy
Cardiac resynchronization
Biventricular pacing
Implantable cardioverter device
Ventricular assisted devices
Peripheral Vascular Disease (PAD):
Caused by atherosclerosis. Arterial walls lose compliance
Is usually progressive
May occlude medium and large arteries
May manifest acutely
Risk factors:
Dyslipidemia
Diabetes
CAD
HTN
Renal failure
Smoking
H/o CVA or MI
Arterial vs. Venous Peripheral Vascular Disease:
Arterial Manifestations: Absent pulses, smooth/shiny/dry skin with no hair, painful ulcers, intermittent claudication, no edema, brittle/thick nails
Venous Manifestations: Normal pulses, brown discoloration on lower legs , irregular painless ulcers, dependent edema, dependent cyanosis and pain, no intermittent claudication
Stages of Venous Disease:
Stage 0: Healthy veins
Stage 1: Spider veins.
Stage 2: Varicose veins.
Stage 3: Leg edema.
Stage 4: Skin changes (discoloration).
Stage 5: Healed ulcers.
Stage 6: Active ulcers
Education for PAD:
Exercise and diet modification
Lipid-lowering medications
Management of hypertensions
Management of DM
Nursing interventions:
Assess extremities for peripheral pulses, pain, color, temp, and cap refills every 4 hours and PRN.
Teach client importance of keeping extremities in dependent position
Keep extremities warm using lightweight blankets, socks, and slippers
Encourage change of position at least every hour and avoid leg crossing
Provide thorough leg and foot care daily
Heart sounds:k
S1: Closure of the mitral and tricuspid valves (beginning of systole).
S2: Closure of the aortic and pulmonic valves (end of systole).
S3: Occurs after S2 and is associated with volume overload or heart failure.
S4: Occurs before S1 and indicates a stiff ventricle.
1.) A nurse is assessing a client’s radial pulse and determines that the pulse is irregular. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
a. Assess the apical pulse for a full minute
b. Assess the apical pulse with a doppler device
c. Assess the pedal pulses for a full minute
d. Assess the pedal pulses with a doppler device
2.) A nurse is caring for a newborn and auscultates an apical heart rate of 130/min. which of the following actions should the nurse take?
a. Ask another nurse to verify the heart rate
b. Document this as an expected finding
c. Call the provider to further assess the newborn
d. Prepare the newborn for transfer to the ICU
3.) A nurse is auscultating a client's heart sounds and hears an extra heart sound before what should be considered the first heart sound s1. the nurse should document this finding as which of the following heart sounds?
a. The fourth heart sound (S4)
b. A friction rub
c. The third heart sound (S3)
d. A split second heart sound (S2)
4.) A nurse is preparing to measure an infant's vital signs. the nurse should use which of the following sites to assess a heart rate
a. Carotid artery
b. Apex of the heart
c. Brachial pulse
d. Radial pulse
5.) A nurse is teaching the partner of a client who had an acute myocardial infarction about the reason blood was drawn from the client. which of the following statements should the nurse make regarding cardiac enzymes studies?
a. “These tests help determine the degree of damage to the heart tissue”.
b. “Cardiac enzymes will identify the location of the MI”.
c. “These tests will enable the provider to determine the heart structure and mobility of the heart valves”.
d. “Cardiac enzymes assist in diagnosing the presence of pulmonary congestion”.
6.) A nurse is providing teaching about a heart healthy diet to a group of clients with hypertension. which of the following statements by one of the clients indicates a need for further teaching?
a. “I may eat 10 ounces of lean protein each day”.
b. “Fresh fruits make a good snack option”.
c. “I will replace table salt with dried herbs”.
d. “I may thicken gravy with cornstarch as I cook”.
7.) A nurse is performing a cardiac assessment on a client and auscultates an s3 sound. the nurse should recognize that this sound represents which of the following heart conditions?
a. Atrial gallop
b. Ventricular gallop
c. Closer of the mitral heart valve
d. Closure of pulmonic valve
8.) A nurse is assessing a client's cardiovascular system. To palpate for unexpected pulsations in the pulmonic area, at which anatomical location should the nurse place her fingers?
a. The left 2nd intercostal space
b. The right second intercostal space
c. The left fifth intercostal space
d. The left intercostal space at the mid-clavicular line
1.) A - Assess the apical pulse for a full minute
2.) B - Document this as an expected finding
3.) A - The fourth heart sound (S4)
4.) B - Apex of the heart
5.) A - “These tests help determine the degree of damage to the heart tissues”.
6.) A - “I may eat 10 ounces of lean protein each day”.
7.) B - Ventricular gallop
8.) A - The left 2nd intercostal space
A nurse is assessing a client’s radial pulse and determines that the pulse is irregular. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?a. Assess the apical pulse for a full minuteb. Assess the pedal pulses for a full minutec. Assess the apical pulse with a Doppler deviced. Assess the pedal pulses with a Doppler device
A nurse is caring for a newborn and auscultates an apical heart rate of 130/min. which of the following actions should the nurse take?a. Ask another nurse to verify the heart rateb. Document this as an expected findingc. Call the provider to further assess the newbornd. Prepare the newborn for transfer to the ICU
A nurse is auscultating a client's heart sounds and hears an extra heart sound before what should be considered the first heart sound S1. The nurse should document this finding as which of the following heart sounds?a. A split second heart sound (S2)b. A friction rubc. The third heart sound (S3)d. The fourth heart sound (S4)
A client with hypertension is prescribed a medication regimen. Which of the following should the nurse monitor? (Select all that apply)a. Blood pressureb. Pulsec. Body weightd. Blood glucosee. Calcium levels
A nurse is preparing to measure an infant's vital signs. The nurse should use which of the following sites to assess a heart rate?a. Apex of the heartb. Carotid arteryc. Brachial pulsed. Radial pulse
A nurse is teaching the partner of a client who had an acute myocardial infarction about the reason blood was drawn from the client. Which of the following statements should the nurse make regarding cardiac enzyme studies?a. “Cardiac enzymes will identify the location of the MI.”b. “These tests help determine the degree of damage to the heart tissue.”c. “These tests will enable the provider to determine the heart structure.”d. “Cardiac enzymes assist in diagnosing the presence of pulmonary congestion.”
A nurse is providing teaching about a heart healthy diet to a group of clients with hypertension. Which of the following statements by one of the clients indicates a need for further teaching?a. “I may thicken gravy with cornstarch as I cook.”b. “I may eat 10 ounces of lean protein each day.”c. “I will replace table salt with dried herbs.”d. “Fresh fruits make a good snack option.”
A nurse is performing a cardiac assessment on a client and auscultates an S3 sound. The nurse should recognize that this sound represents which of the following heart conditions?a. Atrial gallopb. Closure of pulmonary valvec. Ventricular gallopd. Closure of the mitral valve
To assess peripheral perfusion in a client with suspected peripheral vascular disease, the nurse should check which of the following?a. Capillary refill time in the toesb. Appearance of the chestc. Heart rated. Blood pressure
A nurse is assessing a client’s risk for coronary artery disease. Which of the following nonmodifiable risk factors should be considered? (Select all that apply)a. Ageb. Genderc. Smokingd. Family historye. High cholesterol
A pediatric nurse is assessing a child with a history of multiple congenital heart defects. Which observation would indicate the need for immediate intervention?a. A heart rate of 120 bpmb. Cyanosisc. Mild exercise intoleranced. Presence of a heart murmur
The nurse is admitting an older adult patient with heart failure. Which symptom would be most indicative of fluid overload?a. Hypotensionb. Orthopneac. Fatigued. Agitation
A nurse is reinforcing discharge teaching with a client about managing hypertension. Which statement indicates the need for further teaching?a. “I will check my blood pressure daily.”b. “I can stop taking my medications once my blood pressure is normal.”c. “I will maintain a low-salt diet.”d. “I should reduce my alcohol intake.”
Which of the following findings would the nurse anticipate assessing in a patient with right-sided heart failure? (Select all that apply)a. Ascitesb. JVDc. Peripheral edemad. Crackles in the lungse. Fatigue
A client with myocardial infarction is prescribed a beta-blocker. What is the primary purpose of a beta-blocker in this scenario?a. Decrease heart rateb. Increase blood pressurec. Increase oxygen delivery to tissuesd. Promote vasodilation
The nurse is preparing to assess a client’s cardiovascular status. Which assessment finding would indicate impaired central perfusion? (Select all that apply)a. Tachycardiab. Cool, pale extremitiesc. Extra heart sounds (S3, S4)d. Shortness of breathe. Warm skin
After a cardiac catheterization, which nursing care should be prioritized?a. Monitor vital signsb. Maintain strict bedrestc. Assess the insertion site for bleedingd. Keep the extremity straight for 6 hours
An older adult patient presents with symptoms of cardiac arrest. Which of the following should be the priority nursing action?a. Assess the patient's airwayb. Call for immediate helpc. Start chest compressionsd. Defibrillate the patient
A hypertensive client asks the nurse about lifestyle changes they can make to improve their condition. Which of the following recommendations should the nurse include? (Select all that apply)a. Increase physical activityb. Reduce sodium intakec. Increase alcohol consumptiond. Maintain a healthy weighte. Avoid smoking
A nurse is assessing a client for peripheral vascular disease. Which assessment finding would indicate arterial insufficiency?a. Brown discoloration of legsb. Dependent edemac. Thickened toenailsd. Painful ulcers on legs
A patient diagnosed with BNP levels > 100 pg/mL is suspected of having heart failure. Which nursing assessment is of immediate importance?a. Monitoring blood sugar levelsb. Assessing oxygen saturation levelsc. Checking for elevated blood pressured. Auscultating lung sounds
In caring for a patient with dysrhythmias, the nurse should understand that which of the following can cause decreased cardiac output?a. Normal heart rhythmb. Atrial fibrillationc. Bradycardiad. Tachycardia|
A nurse is assessing a client with chest pain. Which assessment findings would warrant immediate intervention? (Select all that apply)a. Sudden onset of diaphoresisb. Complaints of fatiguec. Chest pain radiating to the left armd. Heart rate of 110 bpme. Decreased level of consciousness
A cardiac patient is receiving anticoagulant therapy. Which statement by the client indicates understanding of teaching related to this therapy?a. “I will need to monitor my INR regularly.”b. “I can take aspirin for headaches while on this medication.”c. “It’s okay to skip a dose if I miss it.”d. “I don’t have to worry about bleeding while on this medication.”
A patient is prescribed statins to manage cholesterol levels. Which of the following lab results should be monitored regularly?a. Potassium levelsb. Liver function testsc. Serum calciumd. Thyroid function tests
When reviewing lab values, which of the following would reflect an increased risk for coronary artery disease? (Select all that apply)a. LDL cholesterol > 130 mg/dLb. Total cholesterol > 200 mg/dLc. HDL cholesterol < 40 mg/dLd. Triglycerides < 150 mg/dLe. Total cholesterol < 200 mg/dL
A nurse is caring for a patient with peripheral vascular disease. Which teaching point should be included about the importance of regular foot care?a. To reduce risk of infectionb. To improve circulationc. To reduce discomfortd. To avoid skin irritation
Which nursing intervention is important when caring for a patient with a thrombosis?a. Encouraging ambulationb. Applying heat to the affected areac. Encouraging high-protein dietd. Providing anticoagulant therapy
A client with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) presents with heart failure symptoms. Which problem is priority for the nurse to address?a. Excess fluid volumeb. Impaired gas exchangec. Activity intoleranced. Ineffective coping
When planning care for a client with end-stage heart failure, which intervention is most important for improving quality of life?a. Frequent assessment of vital signsb. Providing emotional supportc. Teaching diet modificationsd. Facilitating advanced care planning
A nurse should monitor which lab values in a patient receiving diuretics? (Select all that apply)a. BUNb. Creatininec. Electrolytesd. Hemoglobine. Blood glucose
A nurse is presenting a health promotion program to a group of older adults. Which age-related changes should be included regarding cardiovascular health? (Select all that apply)a. Decreased cardiac outputb. Increased heart ratec. Decreased vessel elasticityd. Increased stroke volumee. Increased risk for dysrhythmias
A client presents with acute hypertension. What is the priority nursing diagnosis?a. Decreased cardiac outputb. Impaired tissue perfusionc. Risk for injuryd. Anxiety
The nurse prepares to administer a dose of lisinopril to a hypertensive patient. Before administering, the nurse should check which of the following?a. BUN and creatinineb. Serum calciumc. Lipid profiled. Electrolytes
After a heart transplant, the nurse should monitor the patient for which complication first?a. Dehydrationb. Infectionc. Rejectiond. Arrhythmias
In providing care for a client with chronic heart failure, which action should be prioritized?a. Monitor weight dailyb. Restrict fluid intakec. Administer prescribed medicationsd. Educate the client on a low-sodium diet
A nurse is reviewing risk factors for heart disease. Which of the following conditions are modifiable? (Select all that apply)a. Ageb. Geneticsc. Smokingd. Obesitye. Hypertension
When providing discharge instructions for a client with a newly diagnosed heart condition, which of the following should the nurse include?a. Limit exercise to avoid strainb. Report any new swellingc. Increase sodium intaked. Reduce fluid intake
A nurse employs rigorous infection control practices while caring for a transplant patient. What infection is the patient at greatest risk for due to immunosuppressant medications?a. Fungal infectionsb. Bacterial infectionsc. Viral infectionsd. Parasitic infections
A nurse should instruct a client with hypertension to monitor which of the following? (Select all that apply)a. Weightb. Blood pressurec. Fluid intaked. Body temperaturee. Pulse
A client with diabetes mellitus is at increased risk for which cardiovascular condition?a. Atrial fibrillationb. Mitral valve stenosisc. Atherosclerosisd. Pericarditis
A nurse is assessing a client presenting with chest pain. What should the nurse anticipate as primary treatment?a. Administering oxygen therapyb. Performing chest compressionsc. Administering pain reliefd. Preparing for immediate surgery
Which of the following lifestyle changes would a nurse recommend to decrease the risk of coronary artery disease? (Select all that apply)a. Increase physical activityb. Decrease saturated fat intakec. Maintain a healthy weightd. Start smokinge. Reduce alcohol consumption
A patient is at risk for developing pneumonia following a myocardial infarction. Which nursing intervention can help decrease this risk?a. Encourage ambulationb. Administer antibiotic prophylaxisc. Encourage hydrationd. Instruct coughing and deep breathing exercises
A client being treated for heart failure is prescribed digoxin. Which of the following is an important assessment prior to administering this medication?a. Heart rateb. Blood pressurec. Pulse oximetryd. Respiratory rate
A nurse is monitoring a patient for signs of cardiac tamponade. Which assessment finding would be most indicative of this condition?a. Hypotensionb. Elevated heart ratec. Muffled heart soundsd. Respiratory distress
In client education regarding hypertension, what should the nurse emphasize?a. Medication adherenceb. Life expectancyc. Importance of bed restd. Protein intake
A patient diagnosed with heart failure is experiencing shortness of breath. Which evaluation should the nurse prioritize?a. Pulse oximetryb. Blood pressurec. Heart rhythmd. Temperature
A nurse is assessing a 70-year-old client for heart failure. Which change is most likely seen in older adults?a. Increased heart efficiencyb. Increased resting heart ratec. Decreased cardiac outputd. Increased blood volume
A nurse is conducting health teaching about the impact of smoking on cardiovascular health. Which statement should the nurse include?a. “Smoking improves circulation.”b. “Smoking increases the risk of myocardial infarction.”c. “Quitting smoking has no effect on cardiovascular health.”d. “Smoking helps regulate blood pressure.”
Answers:
a
b
d
a, b, c
a
b
b
c
a
a, b, d
b
b
b
a, b, c
a
a, b, c, d
c
a
a, b, d, e
d
d
b, c, d
a, c, e
a
b
a, b, c
a
d
b
d
a, b, c
a, c, e
b
a
c
a
c, d, e
b
b
a, b, e
c
a
a, b, c, e
d
a
c
a
a
c
b
NCLEX-Style Cardiovascular Quiz
1. Which of the following is the primary function of the cardiovascular system? A. Producing red blood cells B. Supplying oxygenated blood to the body C. Generating white blood cells D. Producing oxygen
2. Blood returning from the body enters which chamber of the heart first? A. Left atrium B. Right atrium C. Left ventricle D. Right ventricle
3. Which layer of the heart is responsible for contraction? A. Pericardium B. Epicardium C. Myocardium D. Endocardium
4. The sinoatrial (SA) node is also known as the: A. Heart muscle B. Purkinje fibers C. Pacemaker of the heart D. Right bundle branch
5. Which of the following valves prevents backflow of blood into the right atrium? A. Mitral valve B. Tricuspid valve C. Aortic valve D. Pulmonary valve
6. The phase of the cardiac cycle when the heart is contracting is known as: A. Diastole B. Systole C. Perfusion D. Relaxation phase
7. Which circulation system is responsible for sending blood to the lungs? A. Pulmonary circulation B. Systemic circulation C. Coronary circulation D. Lymphatic circulation
8. Cardiac output is determined by which of the following formulas? A. CO = HR x BP B. CO = SV x HR C. CO = SV / HR D. CO = HR - SV
9. Which of the following factors influence stroke volume? (Select all that apply) A. Preload B. Contractility C. Afterload D. Blood pressure E. Heart rate
10. A patient experiencing impaired central perfusion may exhibit which symptoms? A. Bradycardia and hypotension B. Tachycardia and hypotension C. Hypertension and bradycardia D. Normal heart rate and blood pressure
11. The left ventricle must overcome which force to eject blood? A. Preload B. Afterload C. Stroke volume D. Cardiac output
12. The normal ejection fraction (EF) range is: A. 20-40% B. 30-50% C. 50-70% D. 80-100%
13. Which of the following describes preload? A. The resistance the ventricle must overcome B. The amount of blood in the ventricles at the end of diastole C. The ability of the heart to contract D. The amount of blood ejected per beat
14. A very rapid heart rate can lead to: A. Increased cardiac output B. Decreased filling time and cardiac output C. Increased stroke volume D. Increased preload
15. Which part of the conduction system carries electrical impulses to the ventricles? A. SA node B. AV node C. Bundle of His D. Purkinje fibers
16. A patient with heart failure may exhibit which of the following signs? (Select all that apply) A. Shortness of breath B. Edema C. Hypertension D. Fatigue E. Increased urine output
17. Which of the following factors increase the risk of coronary artery disease (CAD)? (Select all that apply) A. Hypertension B. Smoking C. Hypolipidemia D. Diabetes E. Physical inactivity
18. In fetal circulation, the ductus arteriosus closes: A. Immediately after birth B. 10-15 hours after birth C. At 3-5 days of age D. By the first month of life
19. Which change in pregnancy affects cardiovascular function? A. Decreased cardiac output B. Increased cardiac output C. Decreased heart rate D. Decreased blood volume
20. Which cardiovascular change is commonly seen in aging adults? A. Decreased cardiac output B. Increased artery elasticity C. Increased stroke volume D. Decreased risk of hypertension
21. Which condition increases afterload? A. Hypotension B. Vasodilation C. Hypertension D. Low blood volume
22. Which diagnostic test measures ejection fraction? A. Electrocardiogram (EKG) B. Echocardiogram C. Cardiac catheterization D. Chest X-ray
23. Which lab test is most specific for myocardial injury? A. BNP B. Troponin C. CK D. Myoglobin
24. Which of the following is an effective nursing intervention to minimize cardiac workload in infants with congenital heart disease? A. Feeding the infant slowly over long periods B. Scheduling care to provide for uninterrupted rest periods C. Allowing the infant to cry freely D. Frequently waking the infant for care
25. A patient with hypovolemic shock is receiving IV fluids. The IV fluids will help cardiac output by: A. Decreasing preload B. Increasing preload C. Decreasing afterload D. Increasing contractility
Answer Key:
B
B
C
C
B
B
A
B
A, B, C
B
B
C
B
B
D
A, B, D
A, B, D, E
B
B
A
C
B
B
B
B
A patient with long-standing hypertension is at risk for which complication? a. Increased bone density b. Hypertensive retinopathy c. Decreased cardiac workload d. Decreased risk of stroke
Which dietary recommendation is most appropriate for a patient diagnosed with hypertension? a. Increase intake of red meat b. Follow the DASH diet c. Increase sodium intake d. Consume more processed foods
Which blood pressure reading is classified as Stage 1 Hypertension? a. 118/78 mmHg b. 124/80 mmHg c. 148/92 mmHg d. 162/102 mmHg
What is a primary symptom of left-sided heart failure? a. Jugular vein distension b. Dependent edema c. Pulmonary congestion d. Enlarged liver and spleen
Which intervention should the nurse prioritize for a patient undergoing a cardiac stress test? a. Encourage the patient to eat a heavy meal before the test b. Monitor ECG for ischemic changes c. Keep the patient on complete bed rest before the test d. Administer an ACE inhibitor immediately prior to testing
Which of the following conditions is a contraindication for cardiac catheterization? a. Well-controlled hypertension b. Serum creatinine of 1.8 mg/dL c. History of mild anemia d. Stable angina
A patient diagnosed with right-sided heart failure is likely to experience which symptom? a. Pulmonary congestion b. Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea c. Peripheral edema d. Crackles in the lungs
What is the first-line medication for treating Stage 2 Hypertension? a. Beta-blockers only b. Thiazide diuretics and ACE inhibitors c. Digoxin and calcium channel blockers d. Anticoagulants
Which is a common sign of acute coronary syndrome? a. Hypertension only b. Chest pain or pressure c. Hyperglycemia d. Decreased heart rate
What is an absolute contraindication for a cardiac stress test? a. Controlled diabetes b. Unstable angina c. Mild asthma d. Controlled atrial fibrillation
A nurse is providing education to a patient with hypertension. Which of the following lifestyle changes should be included? (Select all that apply.) a. Reduce sodium intake b. Increase saturated fat intake c. Exercise for at least 30 minutes daily d. Quit smoking e. Maintain BMI between 18.5-24.9
Which of the following medications are used for the immediate treatment of myocardial infarction? (Select all that apply.) a. Morphine b. Aspirin c. Ticagrelor d. Lisinopril e. Atorvastatin
Which are risk factors for developing peripheral artery disease? (Select all that apply.) a. Diabetes mellitus b. Hypertension c. History of CVA or MI d. Low cholesterol levels e. Smoking
The nurse is assessing a patient with valvular heart disease. Which conditions are classified under this category? (Select all that apply.) a. Mitral stenosis b. Aortic stenosis c. Atrial fibrillation d. Mitral regurgitation e. Aortic regurgitation
The nurse is monitoring a patient for complications after a cardiac catheterization. Which findings require immediate intervention? (Select all that apply.) a. Bleeding at the catheter insertion site b. Decreased peripheral pulses in the affected extremity c. Capillary refill <2 seconds d. Severe back pain e. Numbness in the affected extremity
Which findings are indicative of left-sided heart failure? (Select all that apply.) a. Orthopnea b. Jugular vein distension c. Pulmonary congestion d. Peripheral edema e. Tachycardia
The nurse is preparing to educate a patient with coronary artery disease (CAD). Which interventions should be included? (Select all that apply.) a. Smoking cessation b. Cardioprotective nutrition c. Increased alcohol consumption d. Routine wellness checks e. Avoiding all exercise
Which conditions are associated with acute myocardial infarction? (Select all that apply.) a. NSTEMI b. STEMI c. Stable angina d. Unstable angina e. Hypertension
The nurse is caring for a patient with peripheral arterial disease (PAD). Which assessment findings are expected? (Select all that apply.) a. Absent pulses b. Brown discoloration of lower legs c. Intermittent claudication d. Smooth, shiny skin e. Dependent edema
Which are indications for cardiac catheterization? (Select all that apply.) a. Acute myocardial infarction with complications b. Severe left ventricular failure c. Differentiating between pericardial and constructive pericarditis d. Routine blood pressure monitoring e. Diagnosing severe pulmonary hypertension
Which symptoms may indicate myocardial infarction? (Select all that apply.) a. Chest pain or tightness b. Pain in jaw or back c. Shortness of breath d. Nausea/vomiting e. Increased appetite
The nurse is reviewing post-procedure care for a patient following cardiac catheterization. Which nursing interventions should be performed? (Select all that apply.) a. Monitor BP and HR every 15 minutes for the first hour b. Keep the affected extremity straight c. Encourage the patient to ambulate immediately d. Observe for bleeding or hematoma at insertion site e. Monitor temperature and color of affected extremity
Which factors contribute to right-sided heart failure? (Select all that apply.) a. Left-sided heart failure b. Chronic lung disease c. High sodium diet d. Increased peripheral venous pressure e. Smoking
Which medications are commonly used in the long-term management of heart failure? (Select all that apply.) a. Diuretics b. ACE inhibitors c. Beta-blockers d. Statins e. Anticoagulants
Which findings indicate that a patient has progressed to Stage 3 of venous disease? (Select all that apply.) a. Spider veins b. Varicose veins c. Leg edema d. Healed ulcers e. Skin discoloration
What troponin level is suspicious for cardiac energy?
What troponin level is positive for myocardial injury?
What are lipids bound to as they circulate in the blood?
What is the primary form of lipid storage? What percent of fatty tissue does it constitute?
What is the precursor to corticosteroids, sex hormones, and bile salts? What is it produced by?
Answer Key
B – (Hypertensive retinopathy damages blood vessels in the retina, leading to vision loss.)
D – (Hypertension is the leading cause of atherosclerosis.)
A, B, C, D, E – (All are lifestyle modifications for hypertension.)
C – (Stage 2 hypertension is defined as ≥160/≥100 mmHg.)
B – (Hypertension can lead to excessive calcium excretion, increasing bone loss risk.)
A, B, D – (Chest pain, shortness of breath, and dizziness are common ACS symptoms.)
C – (Myocardial infarction involves severe deprivation of oxygen to myocardial tissue.)
B – (The DASH diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy while being low in saturated fat.)
A, C, D, E – (Nitrates, beta-blockers, aspirin, and oxygen are used in MI management.)
D – (Mitral regurgitation is a form of valvular heart disease.)
B, C, D – (Absolute contraindications include CHF, unstable angina, and recent MI.)
A – (A cardiac stress test is stopped if blood pressure reaches 220 systolic or 110 diastolic.)
A, B, C, D – (All are nursing interventions after cardiac catheterization.)
D – (An invasive procedure performed via the femoral or brachial artery.)
C – (Peripheral pulses, temperature, and color should be monitored post-procedure.)
B – (Dyspnea, crackles, and orthopnea indicate left-sided heart failure.)
C – (JVD, ascites, and weight gain indicate right-sided heart failure.)
A, C, D, E – (Diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and ARBs are used in CHF management.)
D – (Biventricular pacing is a form of cardiac resynchronization therapy.)
B – (Atherosclerosis is the main cause of PAD.)
A, B, C, D – (Risk factors for PAD include diabetes, smoking, HTN, and dyslipidemia.)
D – (Intermittent claudication is a hallmark symptom of arterial PVD.)
B – (A patient with varicose veins has stage 2 venous disease.)
A, B, D – (Educating patients on exercise, diet, and hypertension management helps control PAD.)
C – (Keeping extremities warm, monitoring pulses, and avoiding leg crossing are essential interventions.
0.5-2.3 ng/ml
>2.3 ng/ml
Proteins
Triglycerides. 95%.
Cholesterol. Liver.
SLIDES 1-36 (PERFUSION 1) Incorrect answers
A patient is diagnosed with left ventricular failure. Which symptom is most commonly associated with this condition?
A. Peripheral edema
B. Jugular vein distention
C. Pulmonary congestion
D. Hepatomegaly
What is a risk factor for impaired perfusion?
A. Low sodium diet
B. Active lifestyle
C. Diabetes mellitus
D. Hypotension