37. DMD Occupational Health
Lecture Aims
Describe the infectious risks facing dental practitioners
Employment requirements for practicing dentists related to blood borne viruses
Occupational health aspects of HBV, HCV & HIV
Post-exposure follow-up measures needed after sharps injury
Compliance with occupational health arrangements for dental practitioners in Northern Ireland
Infectious Hazards in Dentistry
Dental professionals face several occupational hazards, including:
Needles and other sharp objects
Spatter and splashes entering the eyes, nose, mouth & mucous membranes
Aerosols
Respiratory and contact spread
Minimising Risks Through Occupational Health
Pre-employment Immunisation
Post-exposure Investigation, Advice & Management
Health Clearance
Prevents risk from infected dentists to patients

Dental Practice Risks
Intra-oral, needle stick & sharps injuries can occur due to:
most treatment classify as EPP
Patient movement or unexpected mouth closure
Poor visibility during procedures
Most sharps injuries happen during:
Resheathing, dismantling, or disposal of needles
Clearing instruments
Manual instrument cleaning
Dentists can acquire infections from patients, such as:
Influenza, B19, TB
Importance of practicing contact and droplet precautions
Keeping vaccinations up to date is crucial
Pre-employment Occupational Health Measures
Pre-employment Health Assessment
Mandatory for new staff
Review immunization needs due to high risk of infection exposures
Immunisation Requirements
up to date Routine vaccinations: Tetanus, diphtheria, polio, MMR
Selected vaccines: BCG for TB, Hepatitis B, Varicella, Influenza
Post-exposure Investigation & Management
Determining:
Nature and timing of exposure
Infectious period at the time of exposure
Dentist's risk of severe illness
Immunization status of the heathcare worker
Availability of post exposure prophylaxis
Example 1: Dental Treatment & TB
Patients with TB symptoms should be assessed; treatment should be deferred until declared non-infectious by a physician
Symptoms include:
Persistent cough, blood in sputum, night sweats, fever, weakness, fatigue, weight loss
Latent TB is non-infectious
Occupational health recommendations include baseline and follow-up tuberculin skin tests for staff
Example 2: Dental Treatment & B19
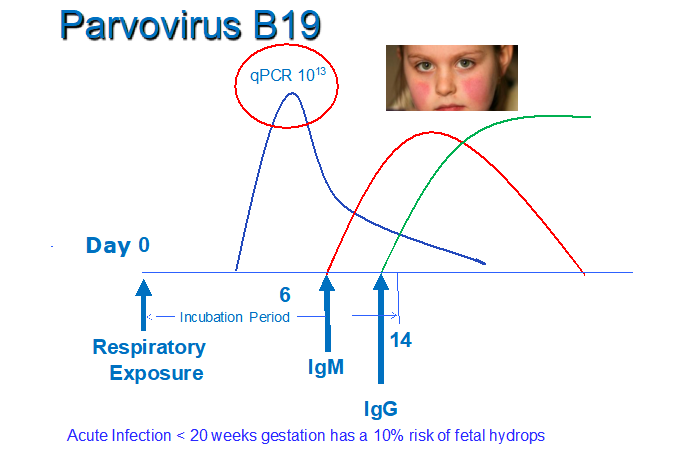
Parvovirus B19 Symptoms - not in ppt
Children: Flu-like illness → "Slapped cheek" rash → Lacy body rash
Adults: Joint pain, mild flu-like symptoms, less rash
Pregnant Women: Risk of fetal complications (anemia, hydrops fetalis)
Immunocompromised: Persistent anemia, no rash
Blood Disorders (e.g., Sickle Cell): Severe anemia (aplastic crisis)
Spread: Respiratory droplets, blood, mother-to-fetus.
Prevention: No vaccine; handwashing helps.
Post-exposure Follow-Up
Referral to GP for follow-up immunity testing
Possible exclusion from work during infectious periods
Example 3 - Needle stick injury
High-risk sources include:
Intravenous drug users
Sex workers
Individuals from sub-Saharan Africa
if the source is a child, they have a high risk if mum has HIV
unprotected sex with above high risk
if the source patient is unknown, usual approach is to assume a low risk exposure
BBVs - Occupational Infection Routes for Healthcare Workers (HCWs) - Parenteral
Percutaneous Routes: Sharp objects penetrate the skin
Mucocutaneous Routes: Contamination of nose, eyes, broken skin, or mouth
Increased risk factors:
Deep injury
Visible blood on the device used
Injury from a needle entering a blood vessel of the source
Source has terminal HIV-related illness
Immediate Management of Sharps/Needlestick Injury
Immediate first aid:
Encourage bleeding, clean under water, dress the wound
Seek urgent medical advice (Occupational Health/A&E)
Record in the accident book
Assess injury for BBV transmission risk
Request source patient blood if consent given and test for BBVs
Actions for Dentist/Recipient:
Baseline blood sample for storage
Check Hepatitis B immunity
Vaccination and immunoglobulin for Hepatitis B as required
Initiate HIV post-exposure prophylaxis (antiretrovirals drug)HAART
Hepatitis C early follow up testing for RNA at 6 and 12 weeks
- Follow up Hepatitis C serology at 12 and 24 weeks
Post-exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) & Testing for High-Risk Injury
HIV:
No vaccine; Only for high risk - initiate antiretroviral drugs ASAP within 24-72 hours, Truvada AND Rategravir for 28 days
but not 100% effective, less effective if delay start
HIV antibody test 12 weeks after PEP
HBV:
Vaccine available; accelerated vaccination for non-immune individuals. Booster available if ongoing risk of exposure
If not immune AND known positive HBsAg —> given Hep B immunoglobin
HbsAg checked at 24 weeks (6months)
HCV:
No vaccine; no specific PEP,
Hepatitis C early follow up testing for RNA at 6 and 12 weeks
Follow up Hepatitis C serology at 12 and 24 weeks
Health Clearance Overview
UKHSA Guidance: Integrated guidance on health clearance for healthcare workers living with BBV
Health clearance protects patients from exposure to HBV, HCV, & HIV
Hepatitis B vaccination is offered along with necessary tests
Non-Exposure Prone Procedures (Non-EPPs)
Non-Exposure Prone Procedures (Non-EPPs)
1. Procedures where hands and fingertips are visible and outside the body at all times.
Involves internal examinations or procedures 2. without risk of injury to gloved hands, 3. adhering to routine infection control.
Examples:
Intravenous sedation
Minor surface suturing
Incision of external abscesses
Teeth bleaching
Categories of Exposure Prone Procedures (EPPs)
Category 1: 1. Hands visible and outside the body most of the time. 2. but slight risk of injury to gloved hands. Examples include local anaesthetic injections, teeth polishing
Category 2: Hands may not be visible at all time; BUT unlikely to injure gloved hands from sharp instument or open tissue. If injury → can immediately notice
. Example: routine tooth extraction, periodontal and implant surgery
Category 3: fingertips are out of sight during procedure. Significant risk of injury to hands. → patients open tissue expose to HCW blood and is unnoticed.
No example
how to ensure samples are from the HCW
take sample in the OH service and transport by OH to lab
show identification
standard health clearence for NEW HCW and students
Check HbsAg
Hep B vaccine (with recombonant DNA inactvated), check vaccne response - antibpdy level > 100 mIU/ml → immune
no response - reuquire immunoglobulin
pre test discussion → test Hep C antibodies → negative - never infected. positive → test Hep C RNA
pre test discussion → HIV serology test(4th generation)
Specific Health Clearances for HCWs Performing Exposure Prone Procedures (EPPs)
Additional health clearance needed for individuals performing EPPs
HCW who DO NOT perform EPPs do not require ongoing OH supervision
HCW have Right to decline BBV testing, but they will not be allowed to perform exposure-prone procedures, since there's no confirmation they are BBV-negative.
Tests for:
Hepatitis B surface antigen HbsAg
Hepatitis C antibody
HIV antibody
all negative to do EPP
Requirements if infected to preform EPP
HCV Infected DEntist: Testing for Hepatitis C RNA by PCR, CANNOT preform EPPs if positive.
Can do EPP when 1. negative 3months after treatmet and 2. negative after anotehr 3 months
HBV Infected Dentists: test Hep B DNA by PCR, can do EPP if HBV DNA is less than 200 IU/ml, and on oral antiviral therapy, test every 6 months
HIV Positive Dentists
