NOTES 2
Introduction
Journal applications analyze and translate customer financial activities into records for corporate general ledger. it is like bookkeeping the financial transactions received from billing, line adjustments, payment, refund, and collection processes. when the journal entries accumulates they will be mapped to the GL (general ledger) transactions based on the criteria, in other words the journal maps the original records of CRM and billing to GL, stored in the journal center according to the transaction types/ payment method and then accumulates the same category data according to the journal rule (daily aggregation). the order transaction starts from the order center -> charging center -> journal center.
Overall Journal Process
Legacy UM system GL reports generated by Ericsson Charging and Billing modules.
AS-IS Overall Journal Flow
GL report generated and emailed to Finance for manual mapping to SAP feed file.
TO-BE Overall Journal Flow
ZSmart: generates monthly/daily aggregation data in DB.
ZSmart stat tool: extract the aggregation data from journal DB, then generates feed files for billing, collection, order, adjustment, and month-end accrual.
ZSmart mediation: extracts the feed files from the stat tool to upload files into SAP interface folder.
SAP: uploads the feed files into the system.
ZSmart journal: provide functions like (accounting cycle, G/L management, journal rule, journal object management, daily/monthly aggregation, feed file generation).
Solution
Journal Cycle
The Journal cycle is the process for recording accounting events, generating monthly journals based on different billing cycles.
UM will generate daily and monthly journal.
monthly journal will have both cycles:
financial cycle: it same as BC01 (1st till end of the month).
billing cycle: same as BC01(1st till end of the month), BC07 (7th till 6th), BC15 (15th till 14th), BC21 (21st till 20th).
new billing cycle : half year BC (1st till the end of the 6th month)
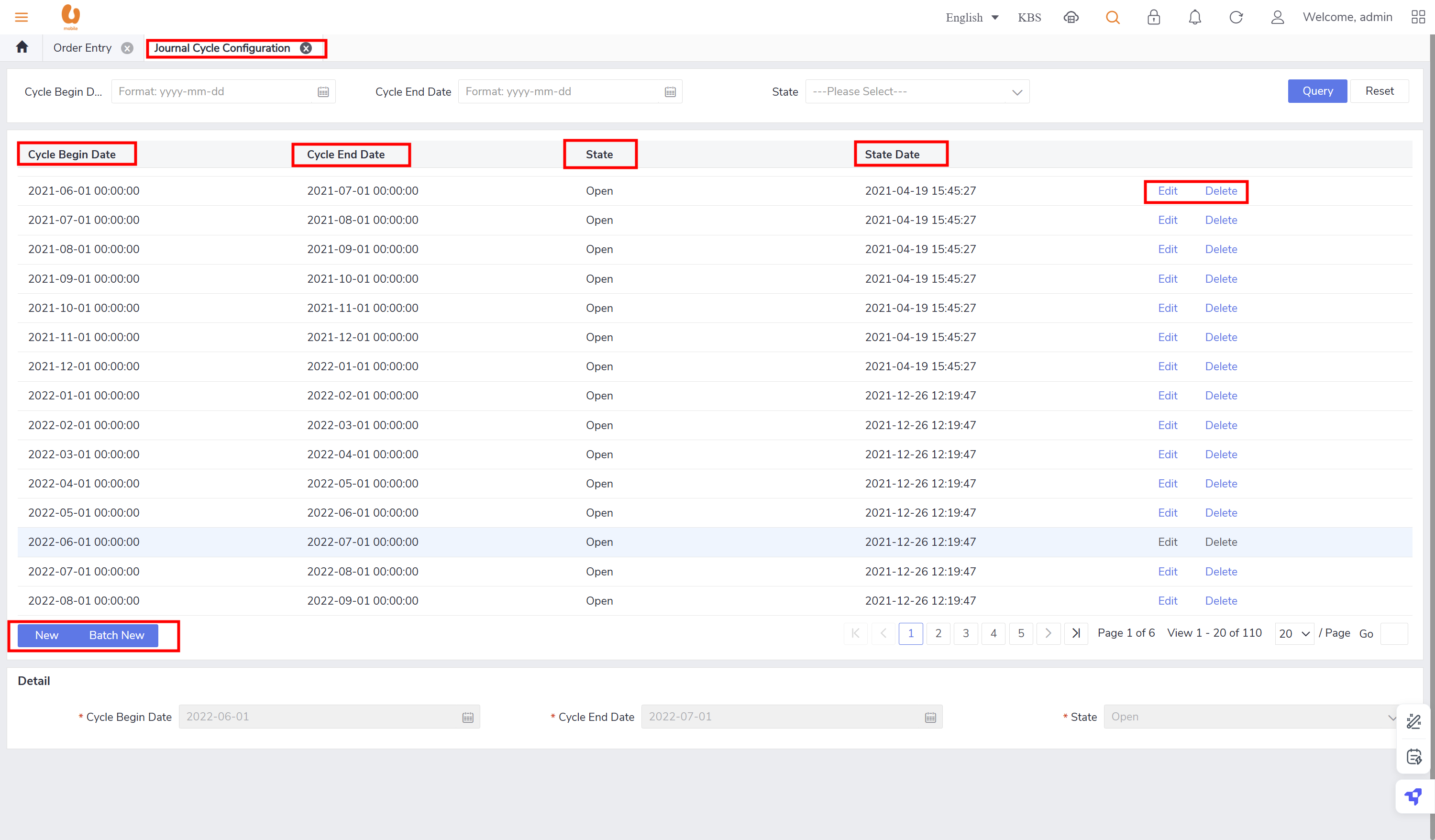
Journal cycle configuration
Journal shall allow defining cycles based on years, months, weeks, etc. the requirement for the solution is support for flexible accounting cycle definitions.
the tab journal cycle configuration shows the details of journal cycle like cycle start/ end date, state of the cycle and the start date on the cycle, in addition to modification actions like edit and delete. new cycle can added or a batch of cycles.
Journal Type
Identification of overall journal file types.
pre = prepaid.
post = postpaid
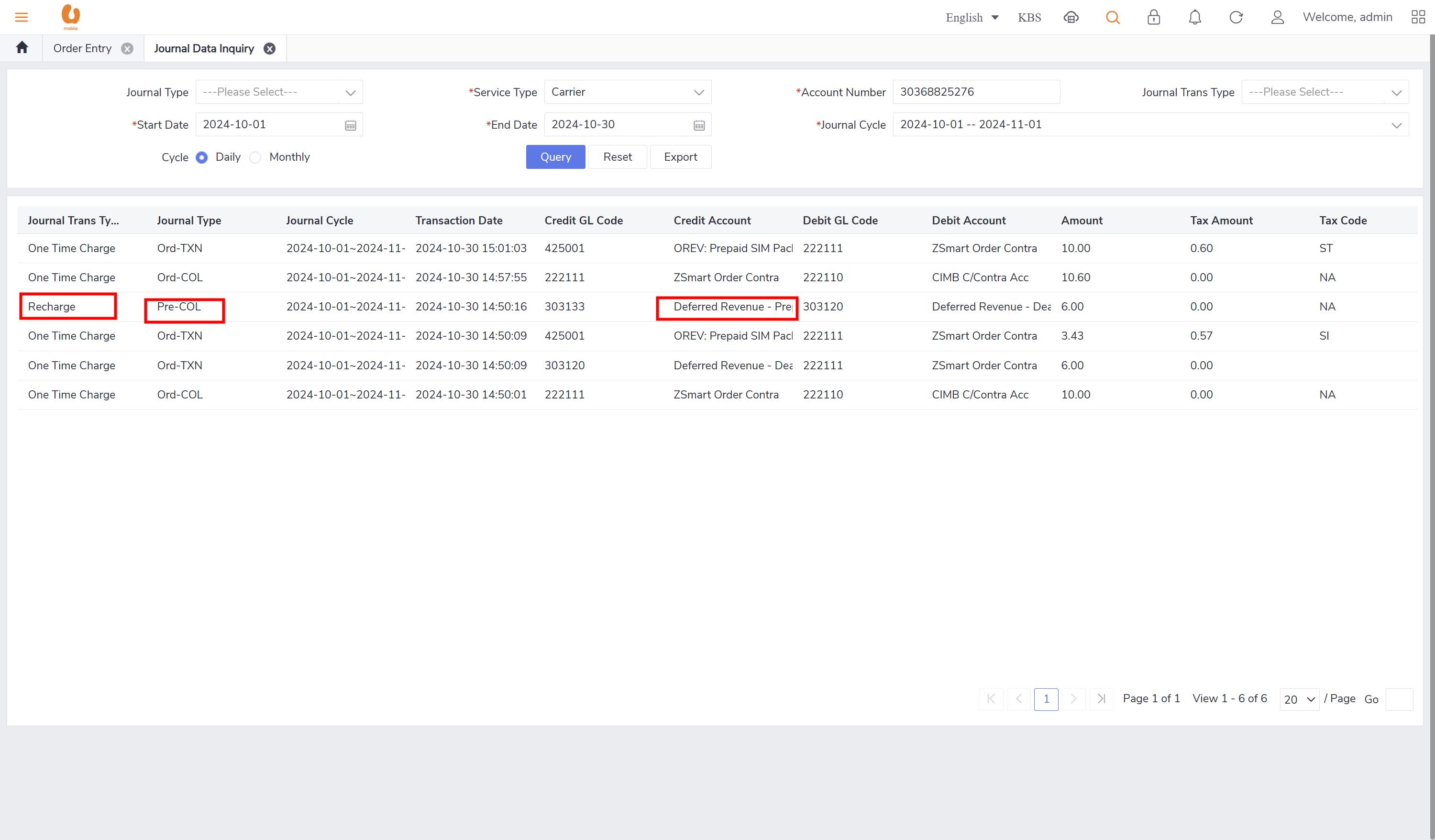
pre-COL: a record that appears when there is recharging/ top-up happened. it will appear daily
post-COL : a record that appears when postpaid payments and reversal is done, is will appear daily.
Ord-COL = cash collection from prepaid/postpaid which includes OTC, device sales, deposit, credit control. the frequency is daily (weekly file). the cut-off happens in the end of the day.
Ord-TXN = transaction and revenue.
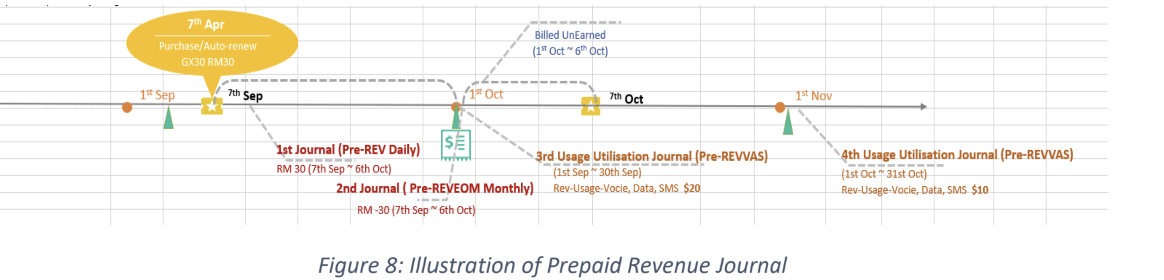
pre-REV: prepaid revenue, including OTC, recurring charge, usage, auto renewal and breakage, loan repay, and credit transfer. the OTC amount found, is supposed to be paid by main wallet not by cash or QR or credit card nor voucher. this journal type appears in transaction that has starter pack.
pre-REVSPLITEOM & post-REVSPLITEOM: includes usage transaction like IDD call, off-net call (a call made from different network other than the caller’s home network like roaming calls), on-net SMS (SMS from the same operator’s home network to another person on the same operator’s home network), these transactions are rated by PAYU mode (deducted from the main wallet / credit transfer wallet).
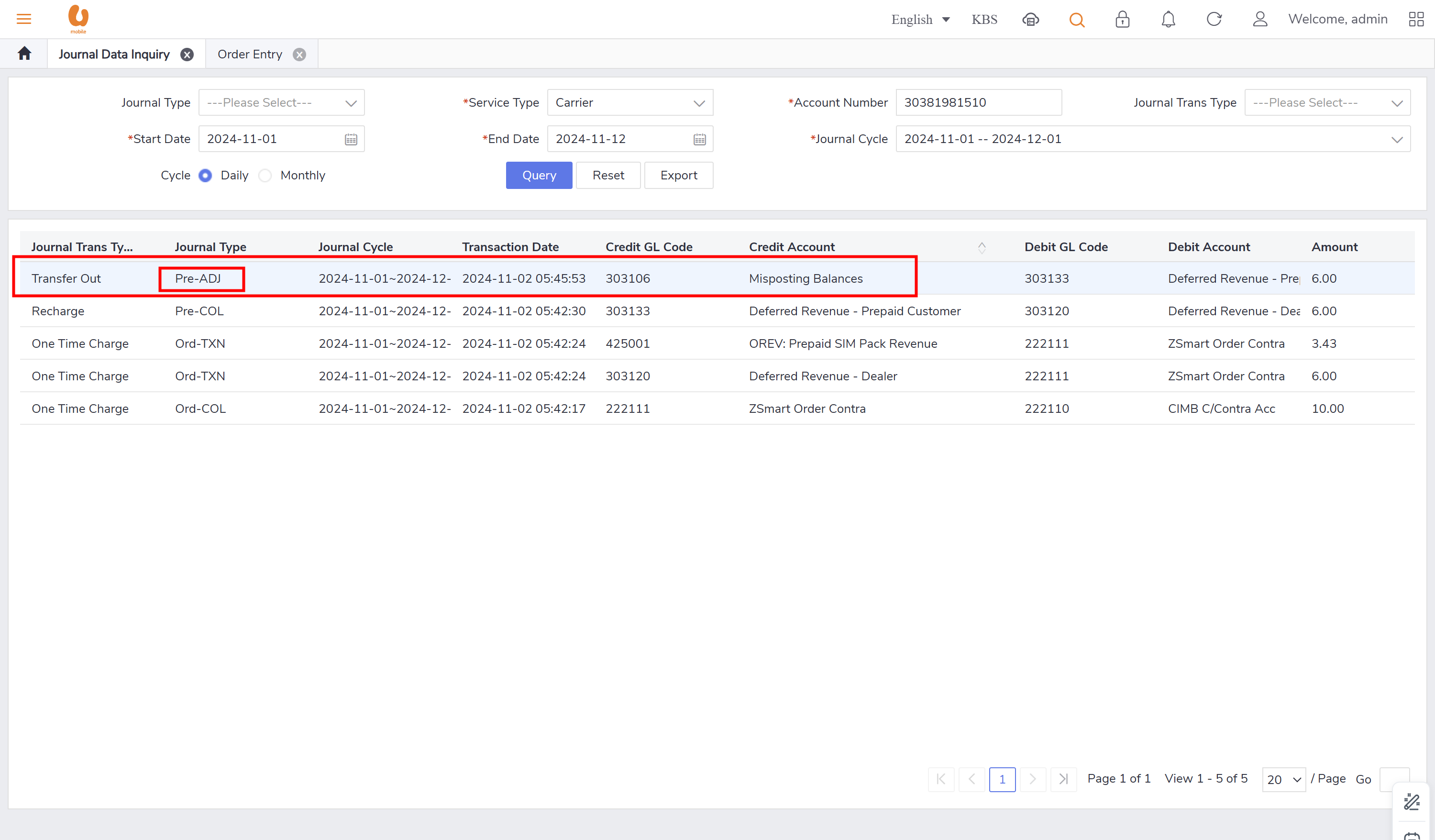
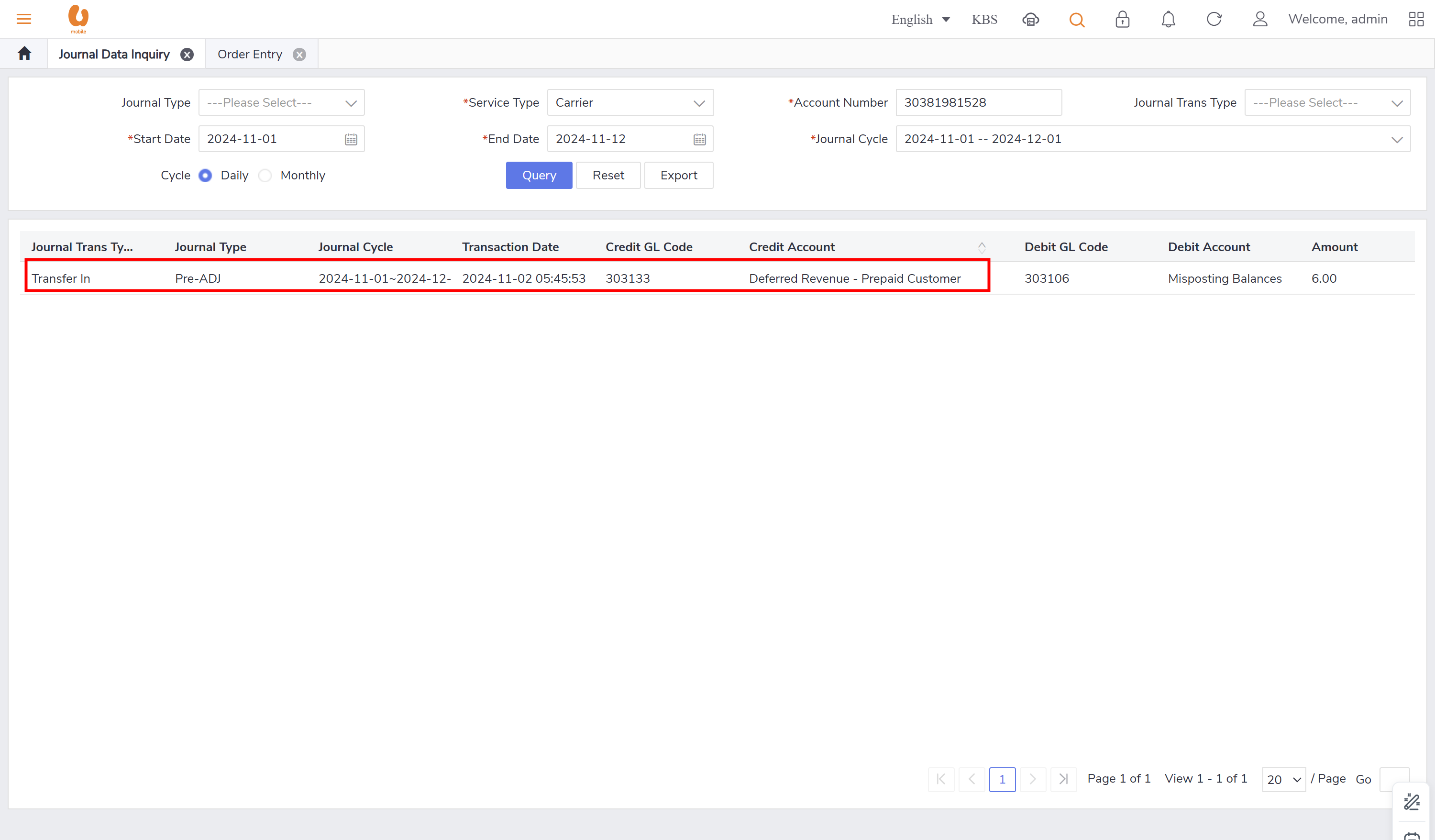
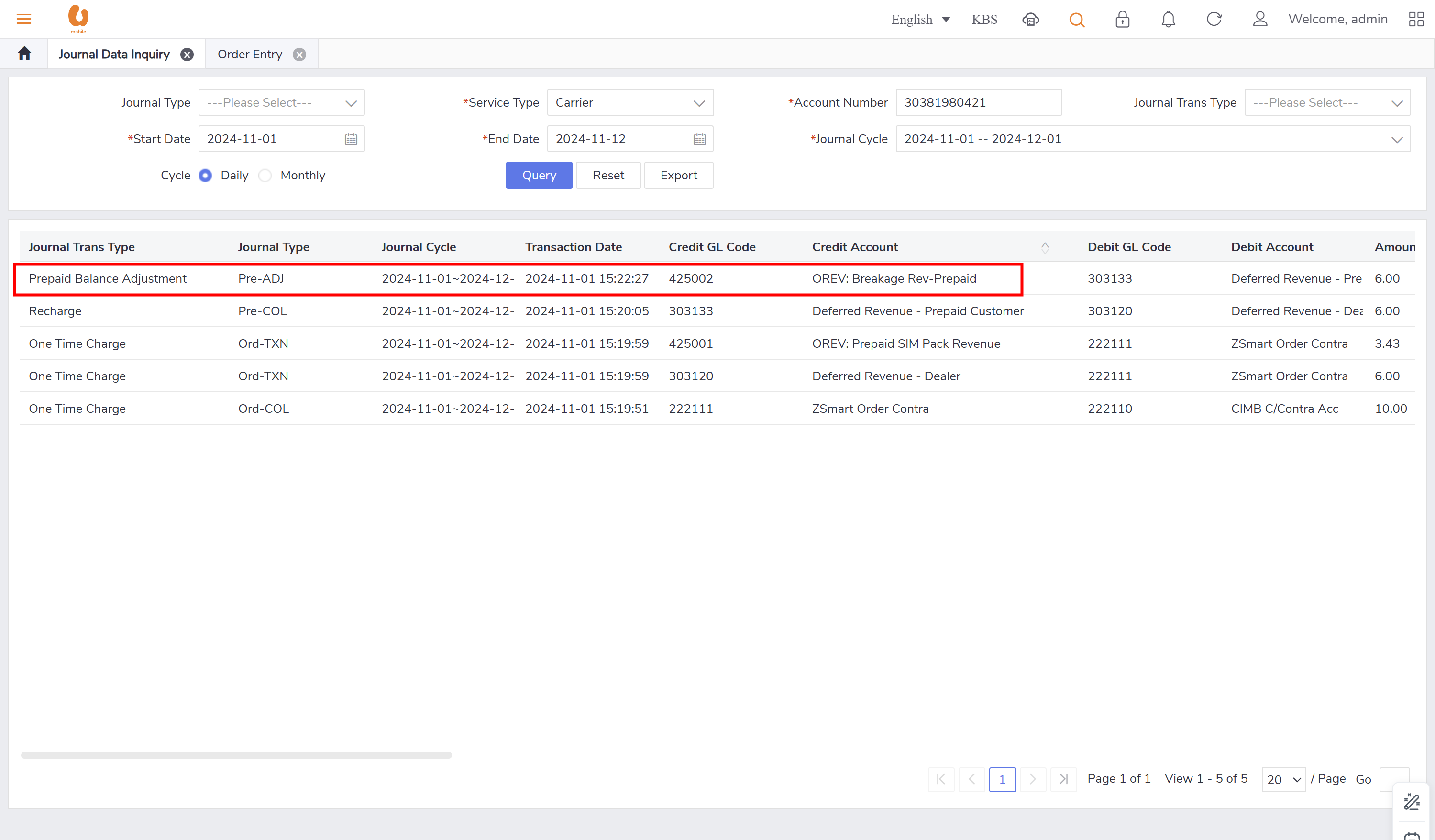
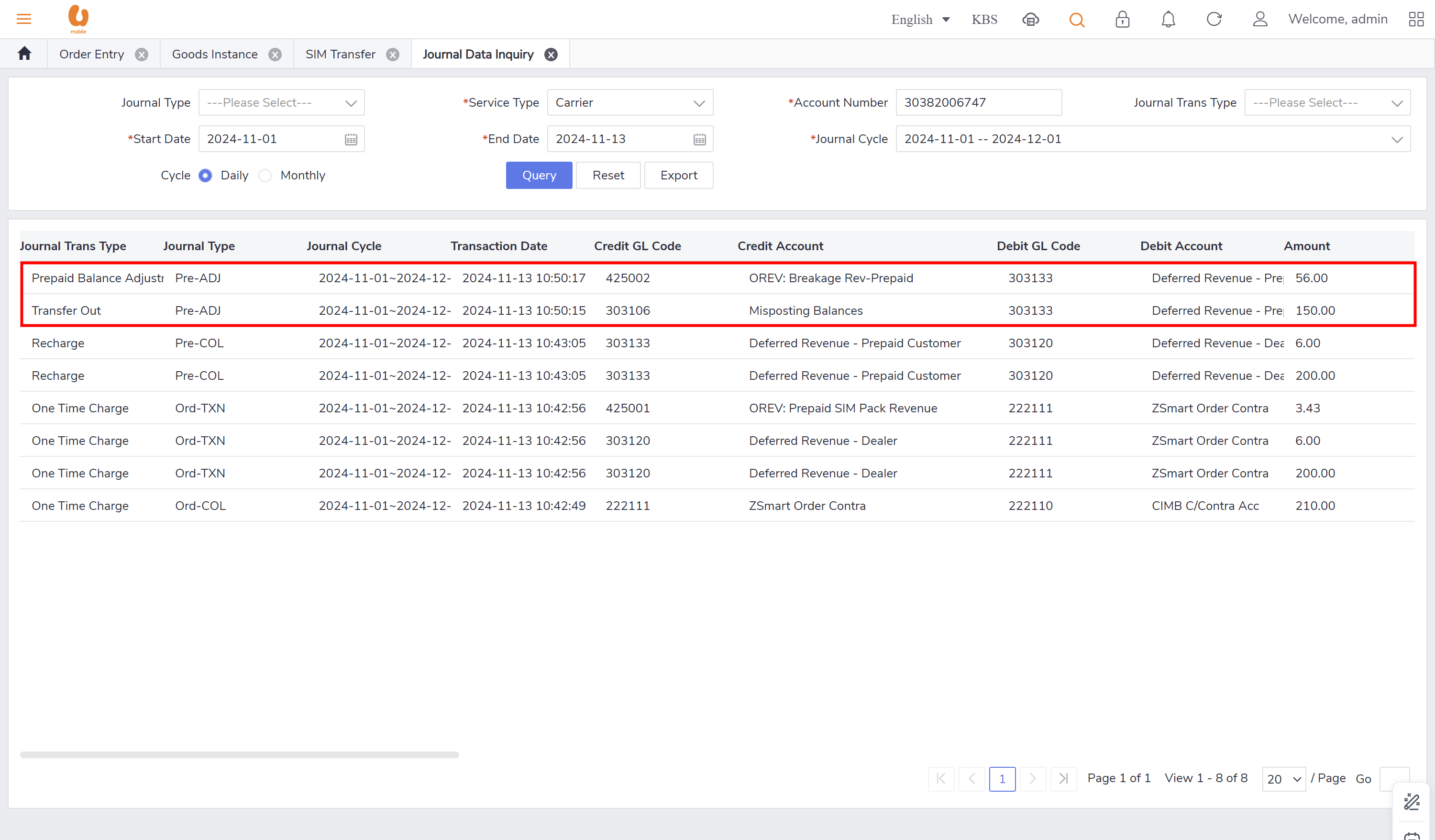
pre-ADJ : this record appears when there is transaction like transfer in and out that has misposting/missing balances, need balance clearance or adjustment in addition to taxes, refund and credit transfer. in case of a tax or a refund it can appear in both postpaid as post-ADJ and prepaid as pre-ADJ.
(today date) - (renewal date amount(end bill cycle day) ) / total date of this month * total plan amount (current amount of the recurring charge before changing offer/ offer amount) = pro-ration amount
(pro-ration amount) - (the renewal date) = the offer amount (ex: 68 or 98, etc.)
based date(30days) - (cycle begin date) +1 = used days
used days * (MRC amount (original offer amount) / base days (30) = (renewal date amount(end bill cycle day) ) or EOM revenue (end of month revenue).
(last day of current month - today's date + 1) / number of days in current month * plan/offer price = the new amount for the new offer (auto reversal concept)
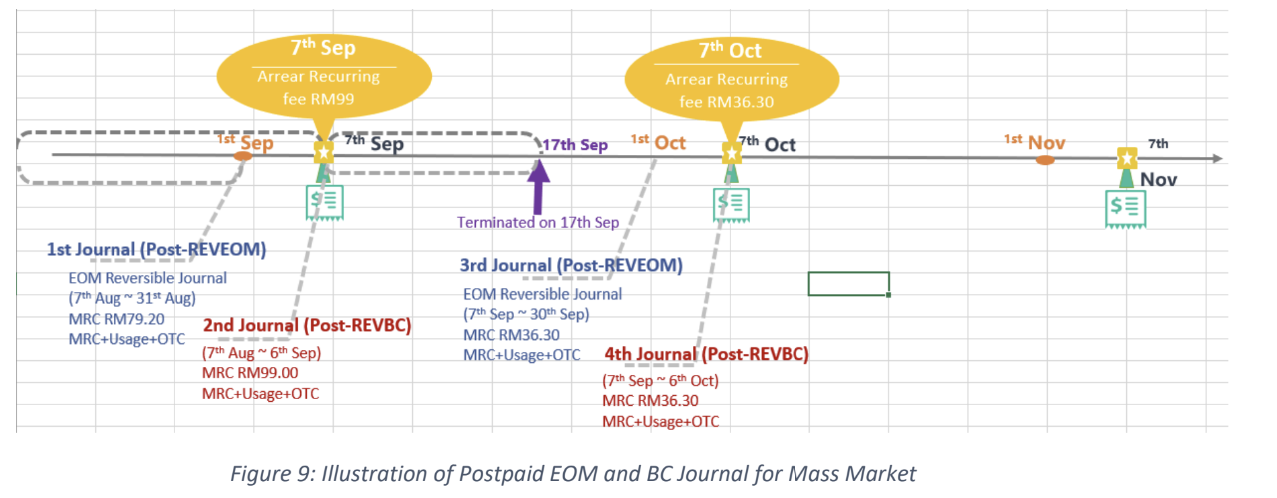
auto reversal concept : bc01, bc07, REVEOM(postpaid plans). the auto reversal concept switch the the credit and the debit. the system does a full reversal, because at the beginning, it will always charge fully, so when the plan is changed later, it needs the fully reversal to be done in order to only charge the exact used amount this concept is called a pro-rate concept.
the post-REVEOM column will appear in the postpaid plans, like (u postpaid 98,u postpaid GX68).
the post-REVEOM will appear each beginning of the month (monthly)
none of the journal types require/ has an auto reversal except for the post-REVEOM.
when the amount is negative, the credit accounting code and the debit accounting code will be reversed by the system automatically.
test done for auto reversal concept:
customer number 1 ( “BC07 OCT“)
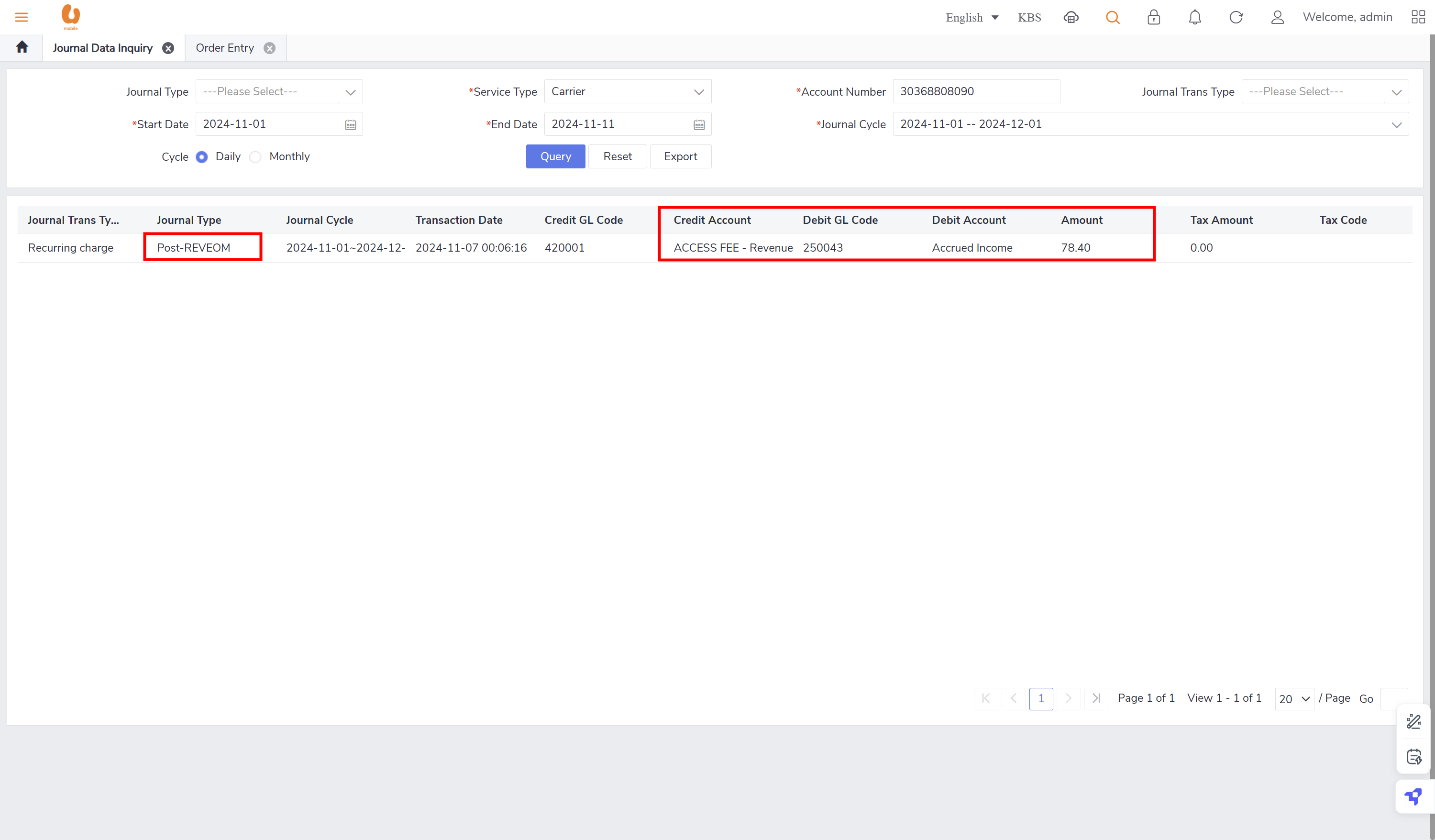
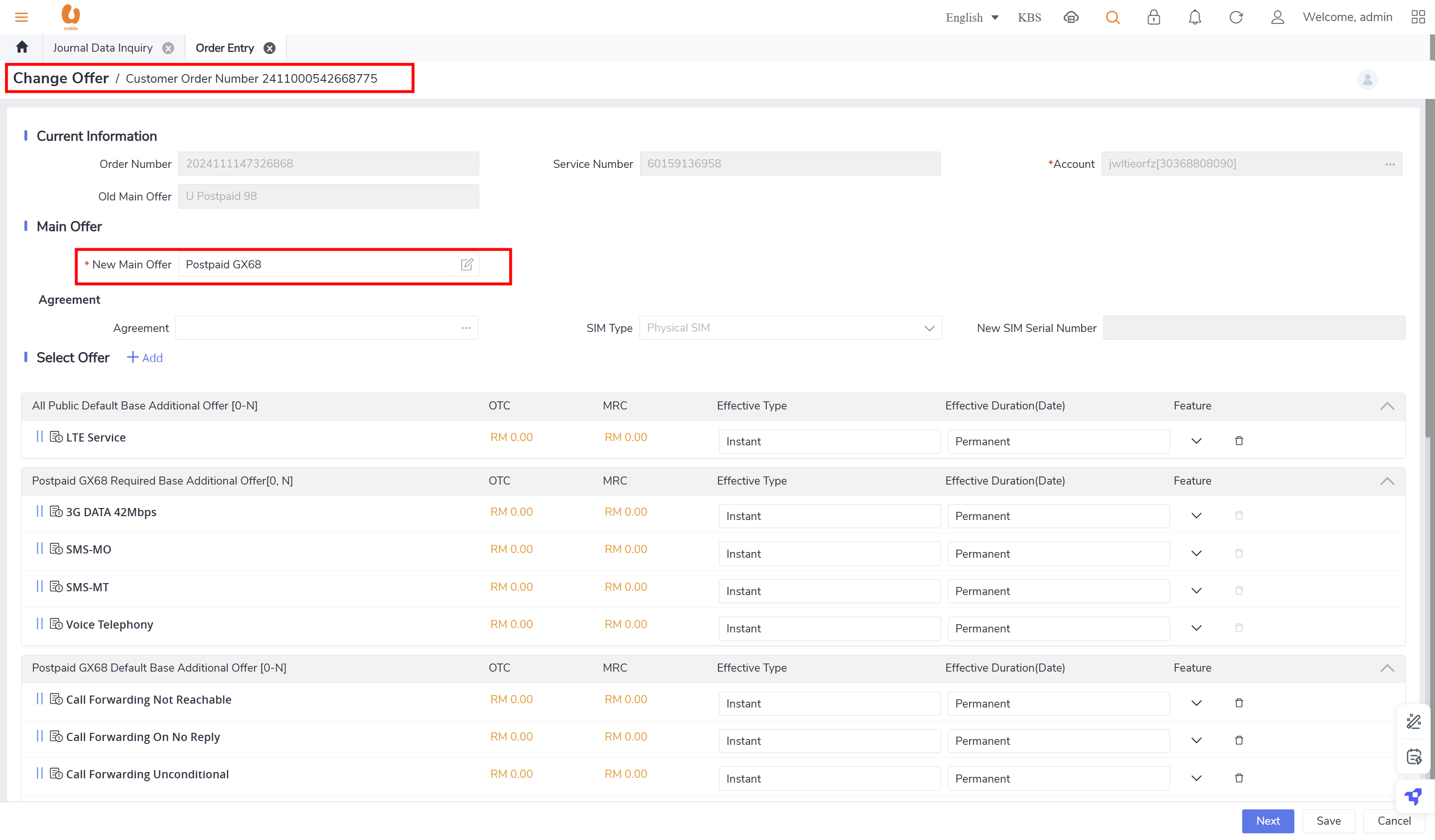
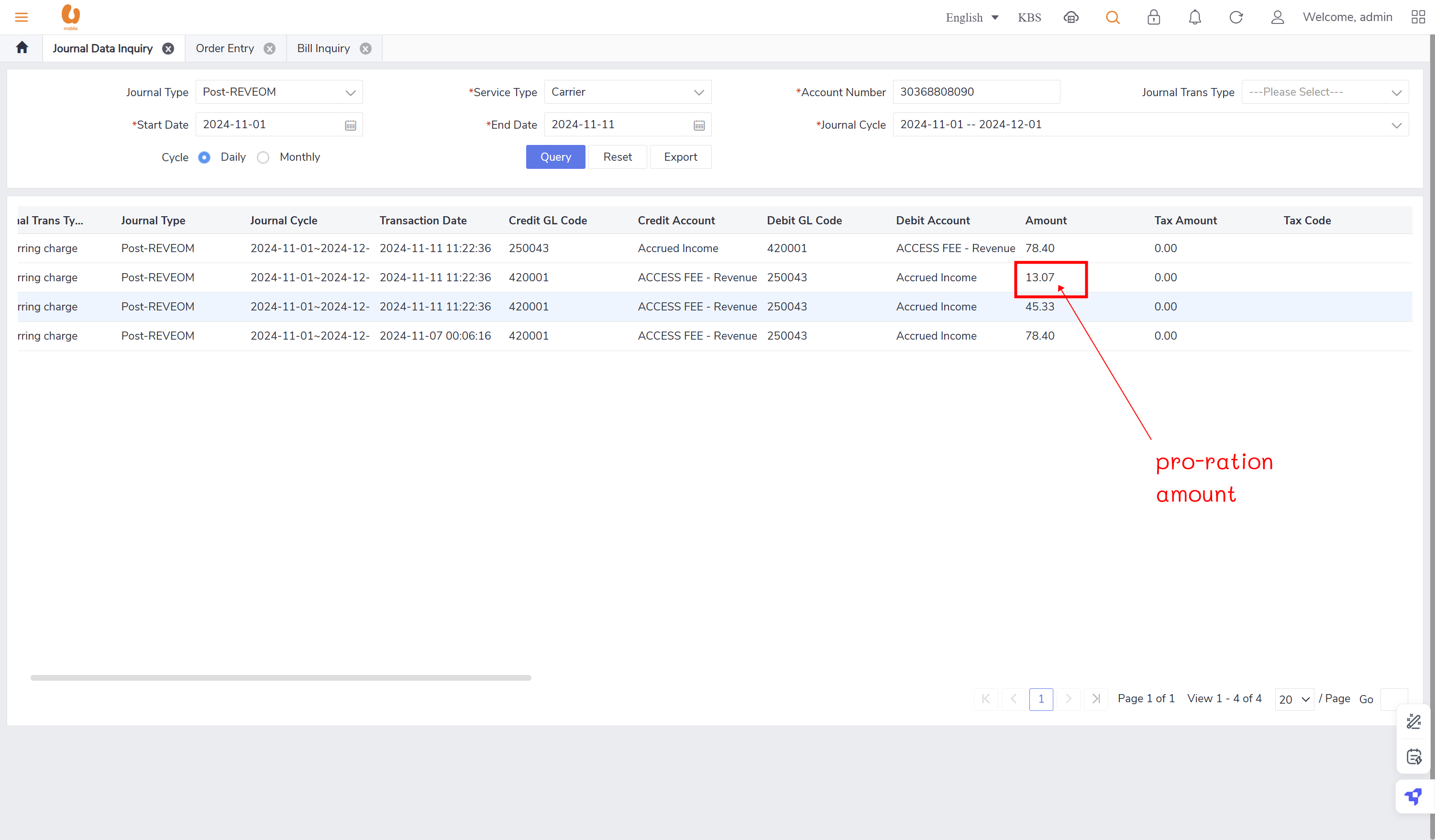
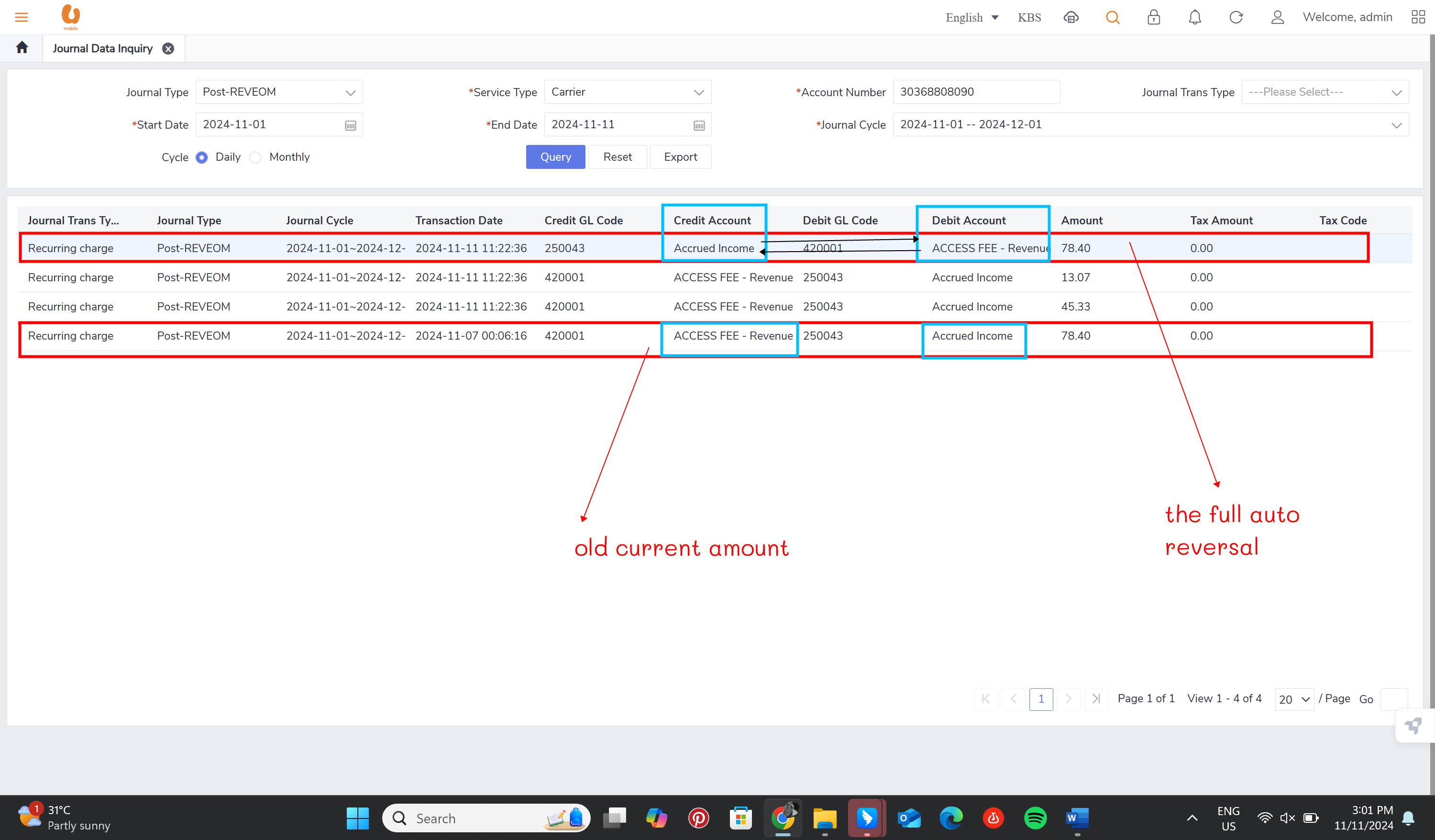
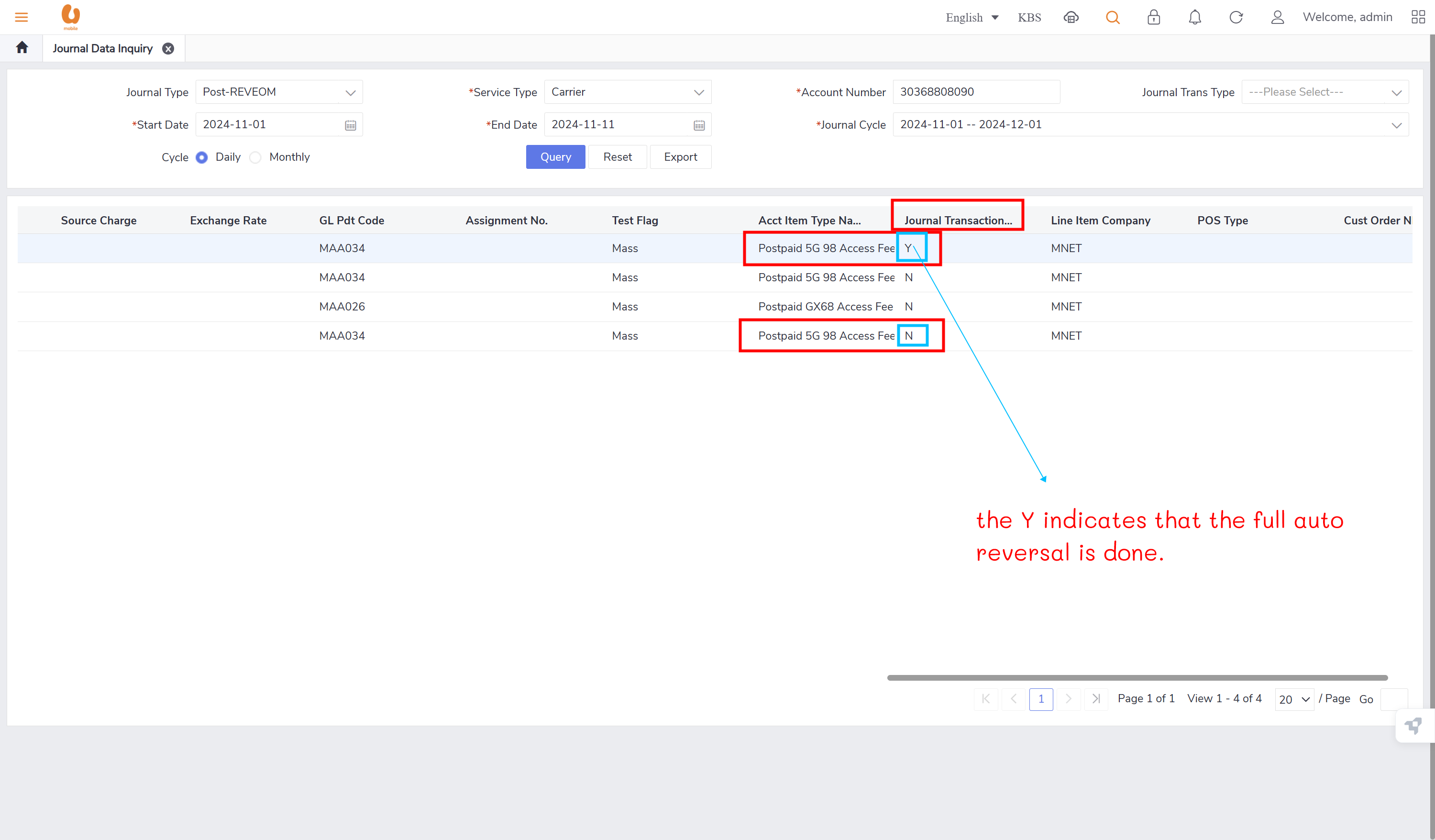
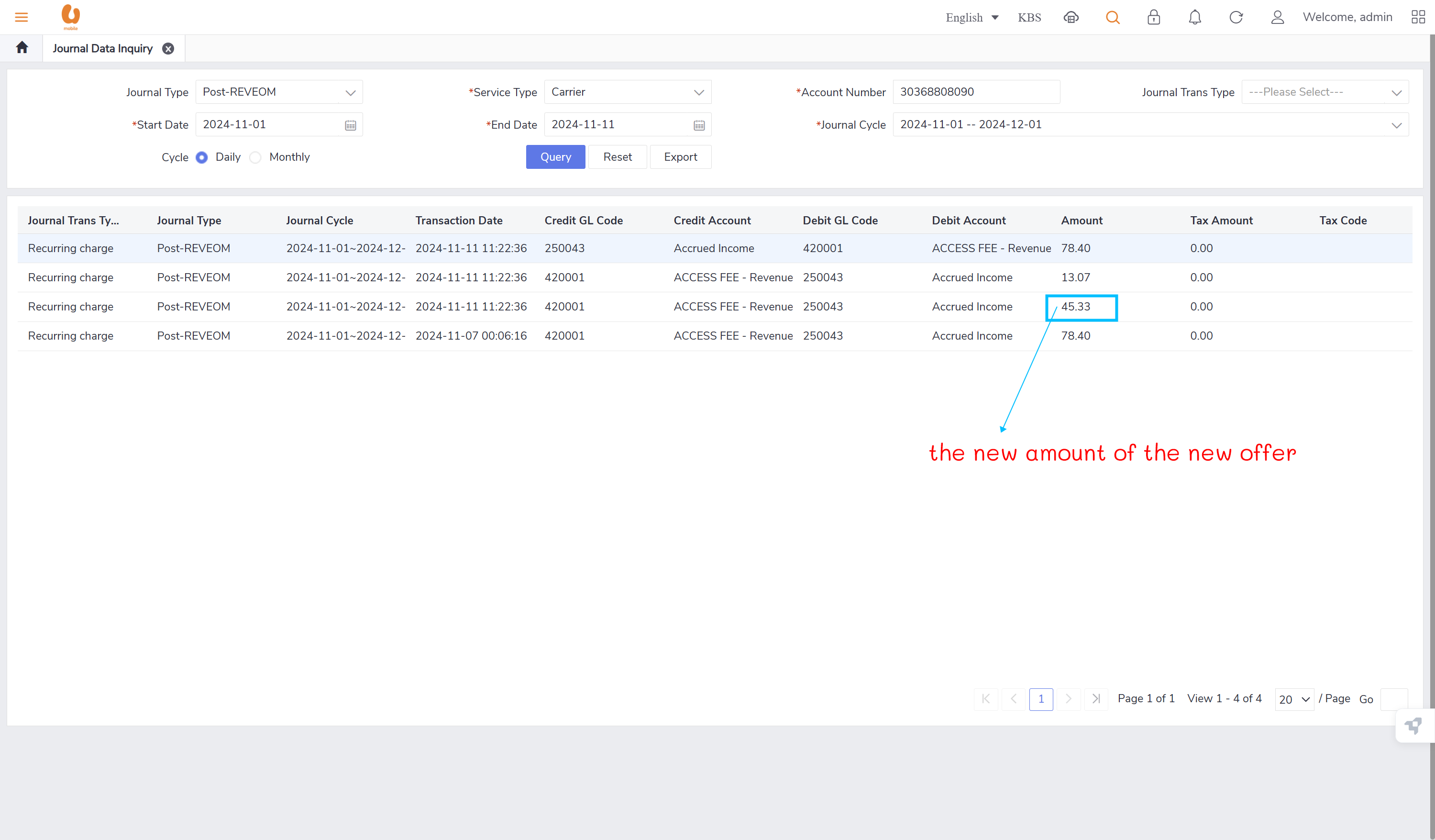
retesting the auto-reversal concept in customer 1 (30368808090):
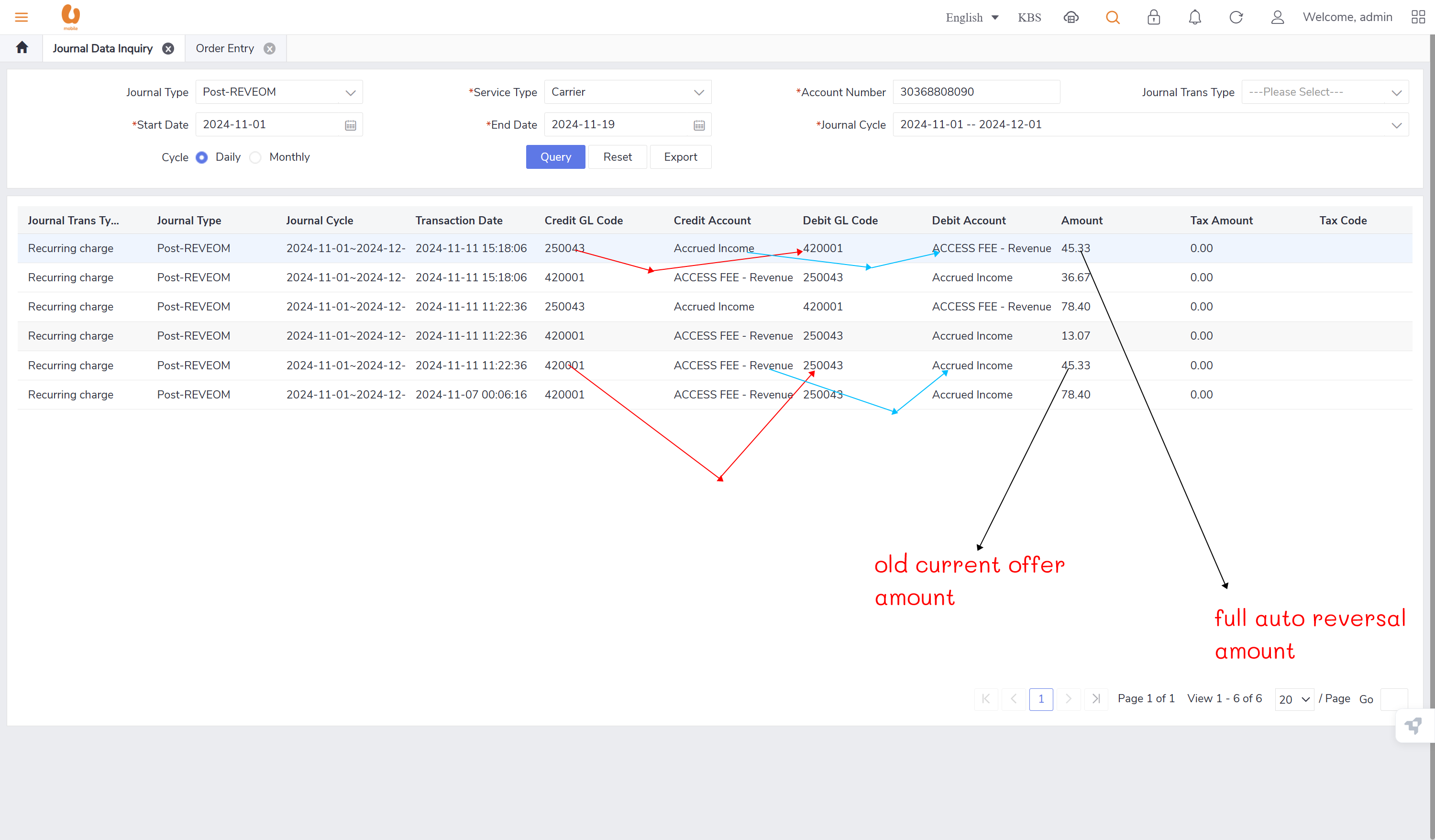
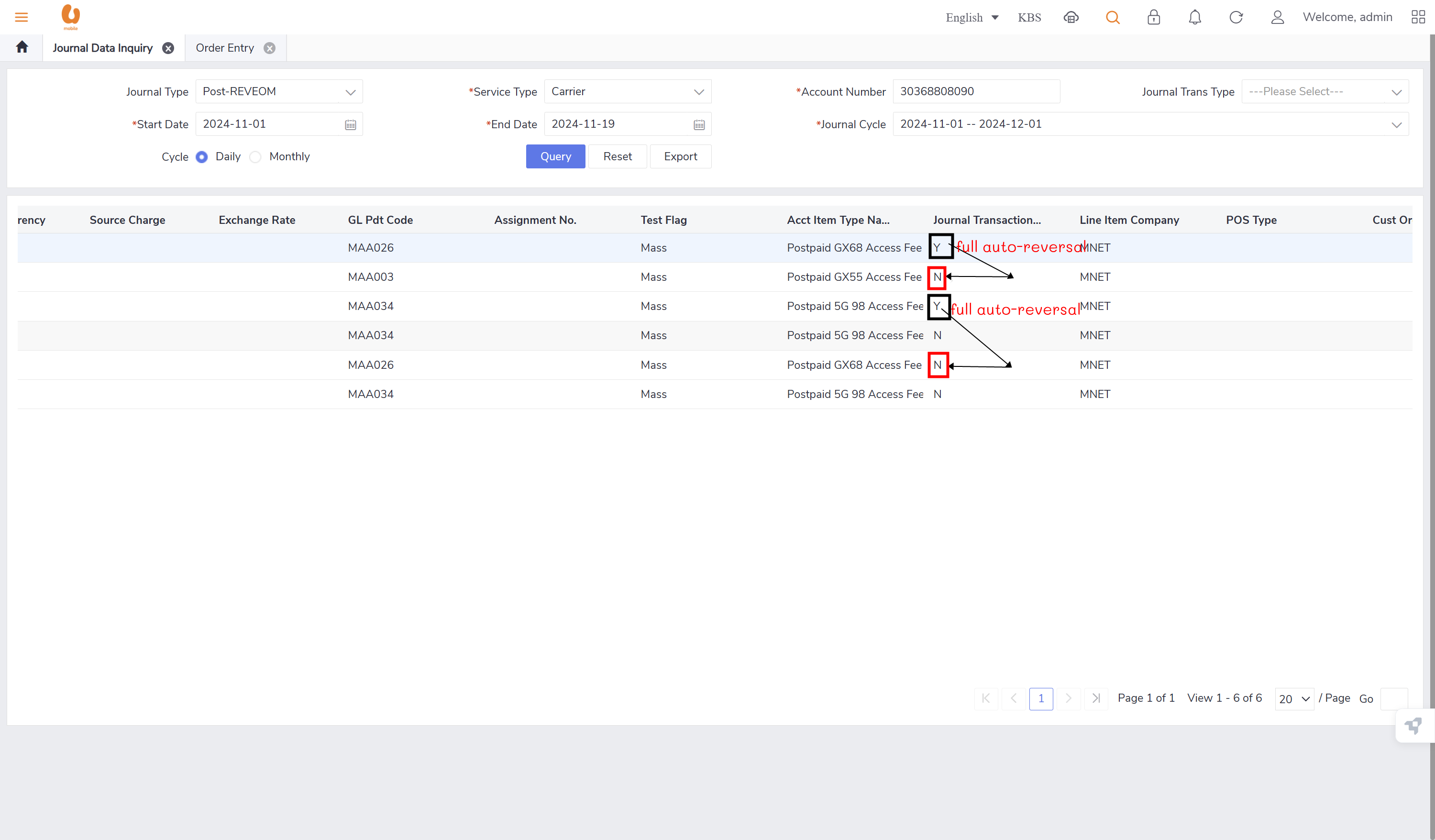
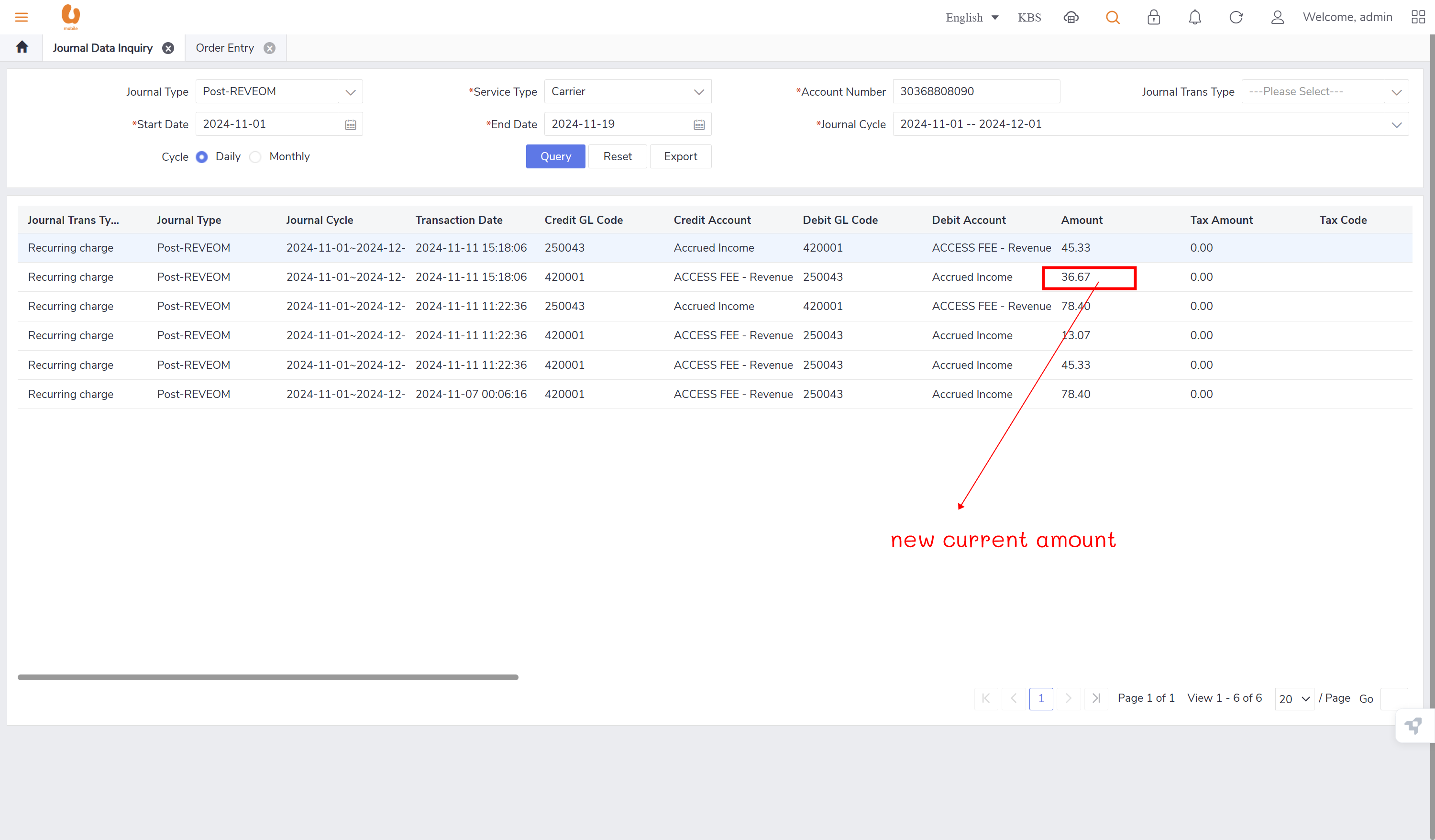
customer number 2 (test_.3 -new connection/change offer “BC07 NOV“), won’t have any post-REVEOM record since it is a new connection, no billing cycle yet.(TRY AGAIN ON DECEMBER)
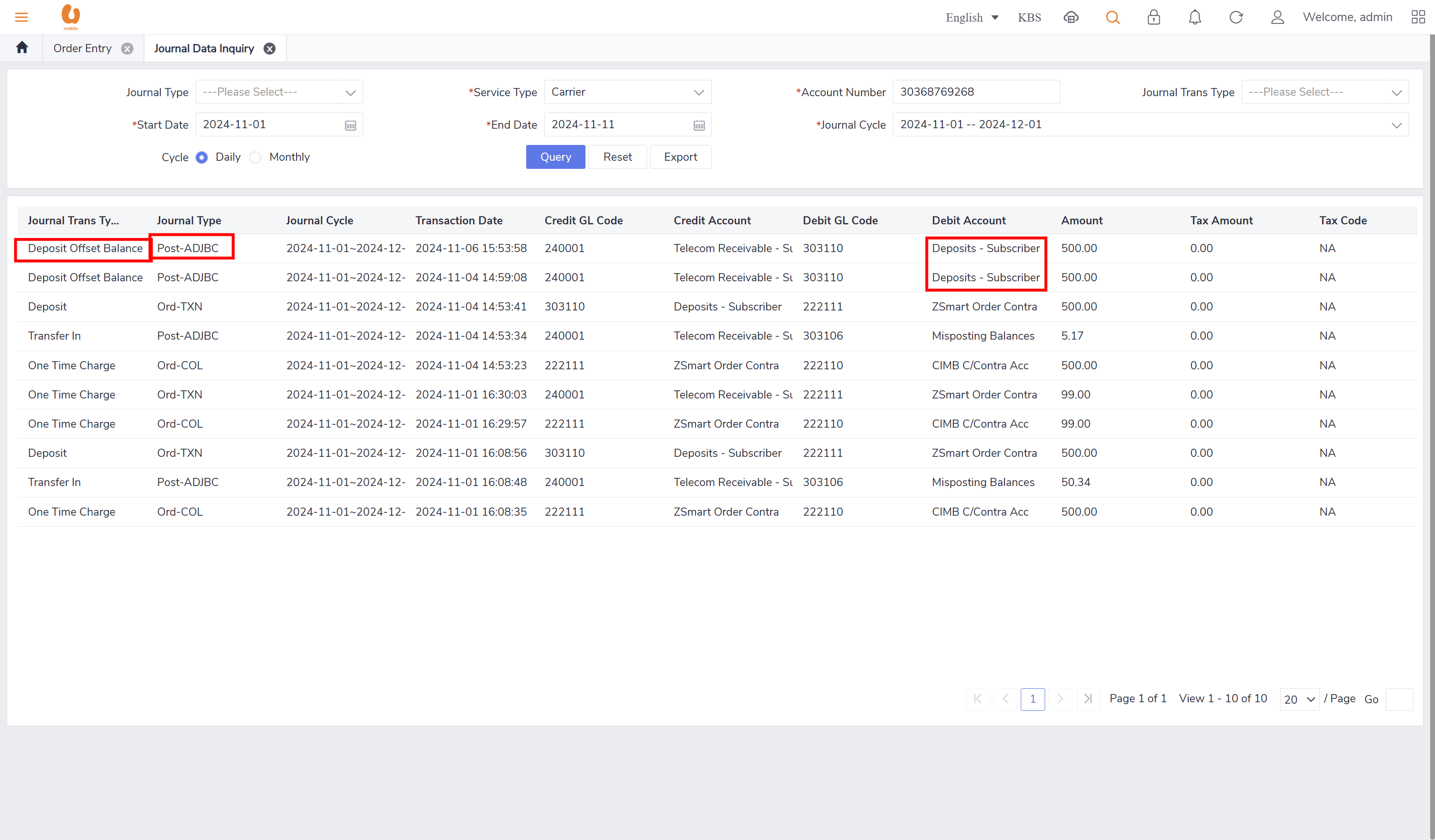
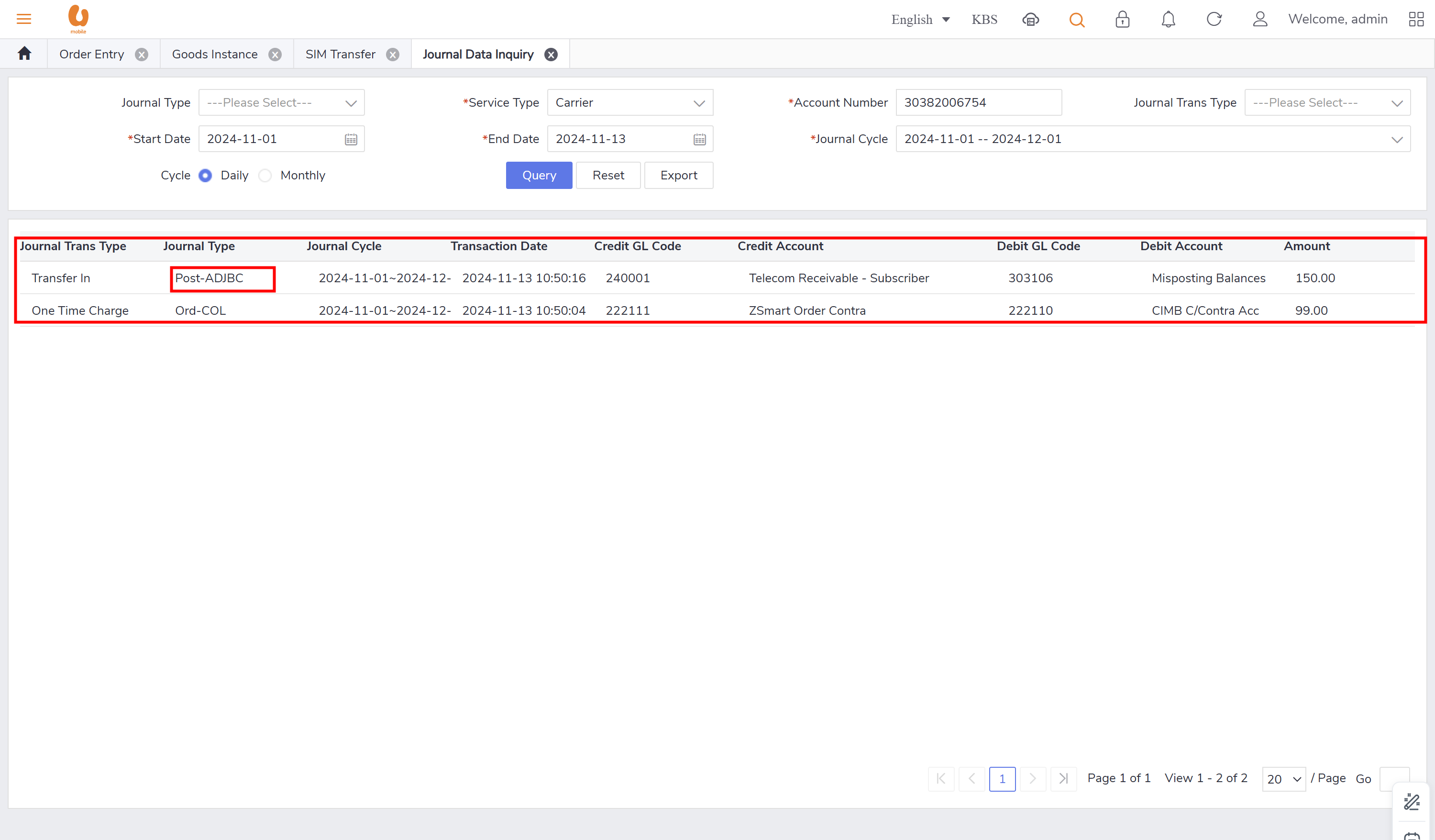
post-ADJBC : this record will appear in Bill adjustment/ account level adjustment/ refund/deposit/ transfer in. it will always appear in postpaid subscribers with foreigner customer. this record will appear every billing cycle. this journal type will also appear during the change from prepaid to postpaid.
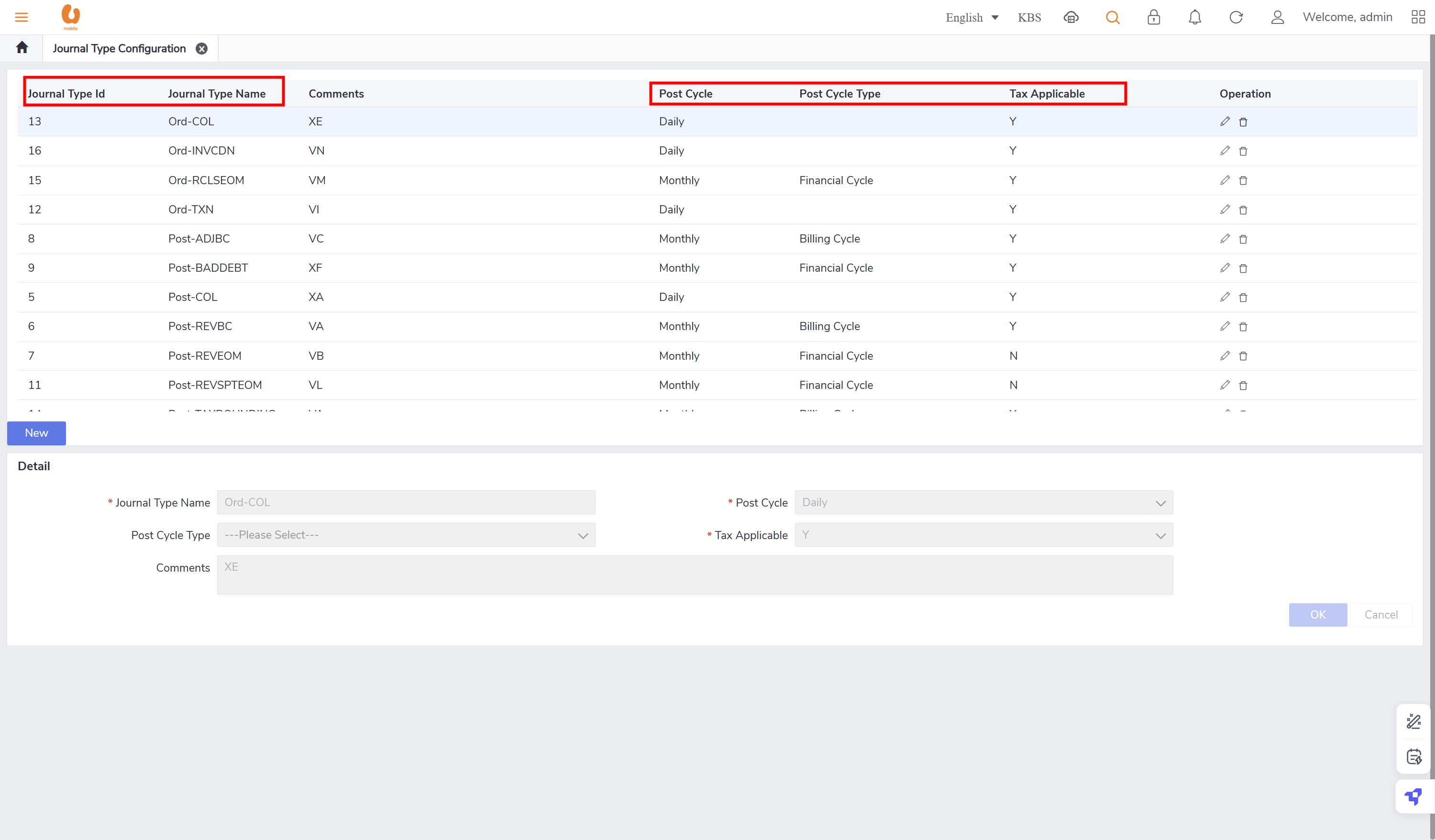
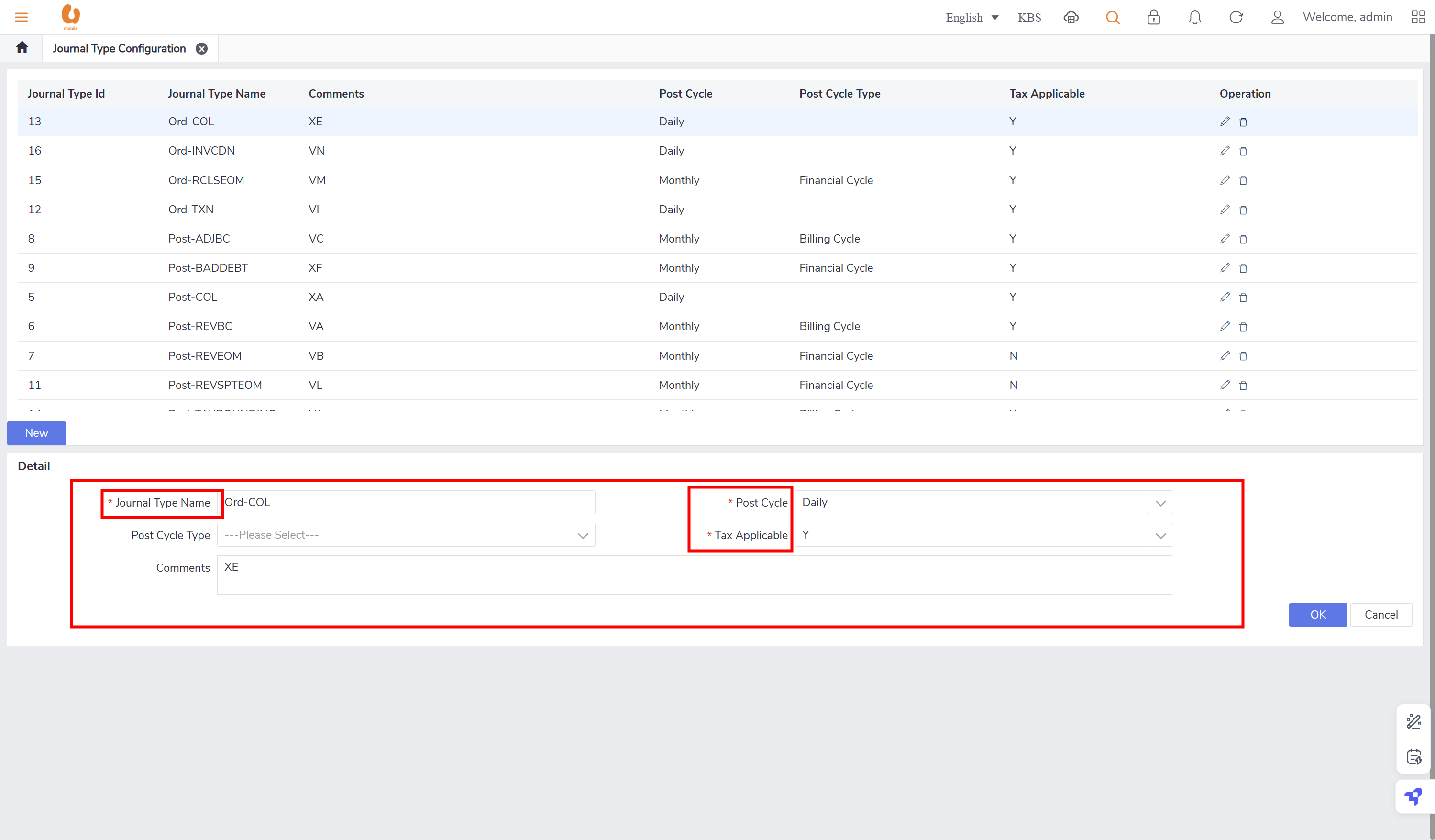
Journal type configuration
a tab where the journal types can be configured, like the journal names, tax applicable or not , and the post cycle and the post cycle type. in addition to deleting or adding a new journal type.
Accounting Treatment
Mapping of transaction types to accounting entries for both prepaid and postpaid services with the journal type, refer to page 29 & 30.
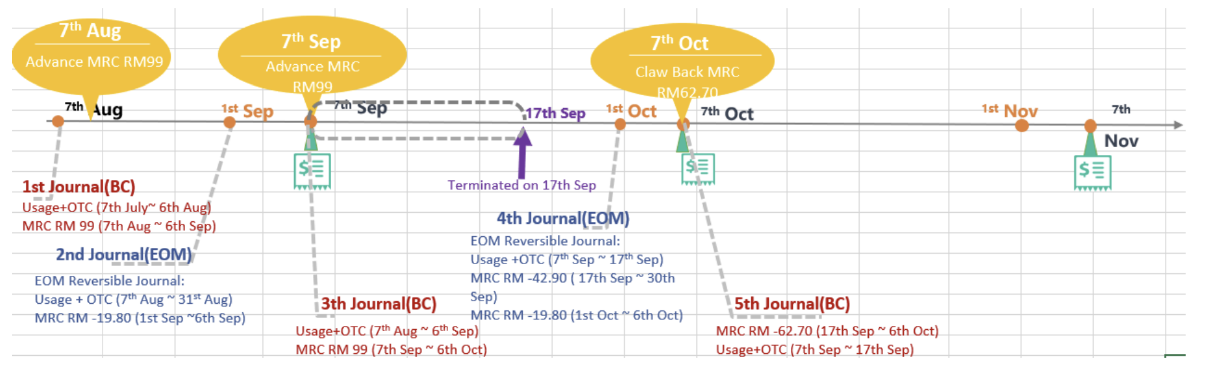
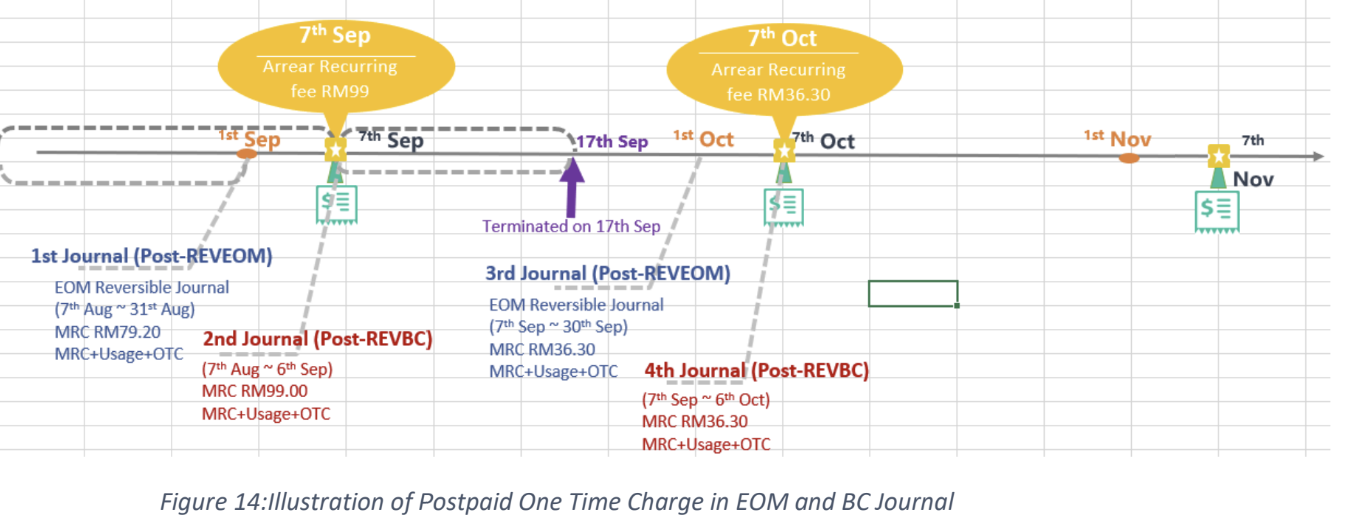
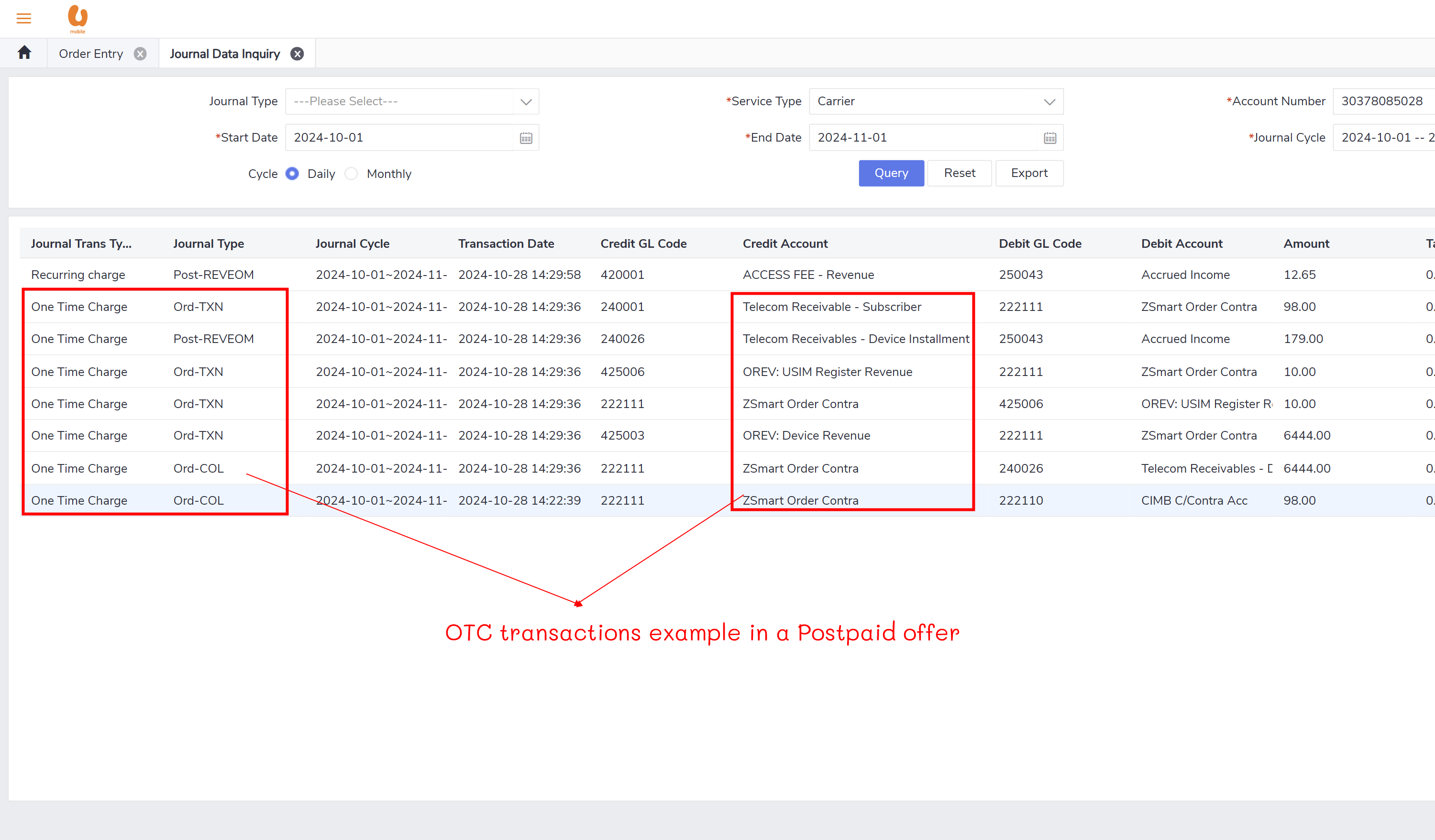
OTC (one-time charge): transactions like device retail fee, SIM replacement, ownership transfer, reactivation charges for involuntary suspension, additional offer, ETP, and credit SOS. some of these transactions are paid by credit card, cash, voucher but other are paid by main wallet. for the transaction paid by main wallet the will be posted under the daily journal (pre-REV) for prepaid and transaction that need to paid by bill payment during the beginning current BC till the end of the month will be posted under the monthly reversible journal post-RVEOM for postpaid. for cash/credit card, etc. it will be under ord-TXN. some transaction like prepaid VAS and UMI purchase or a prepaid basic plan, or apportion of a plan , and the ownership period(tenure) is 30 days or more then complete amount will be posted under the monthly journal (Pre-REVRCLSEOM), and the actual revenue will be posted under the (Pre-REVSPLITEOM). at then end of the BC all the OTC paid by the bill payment will be posted under the BC journal (post-REVBC).
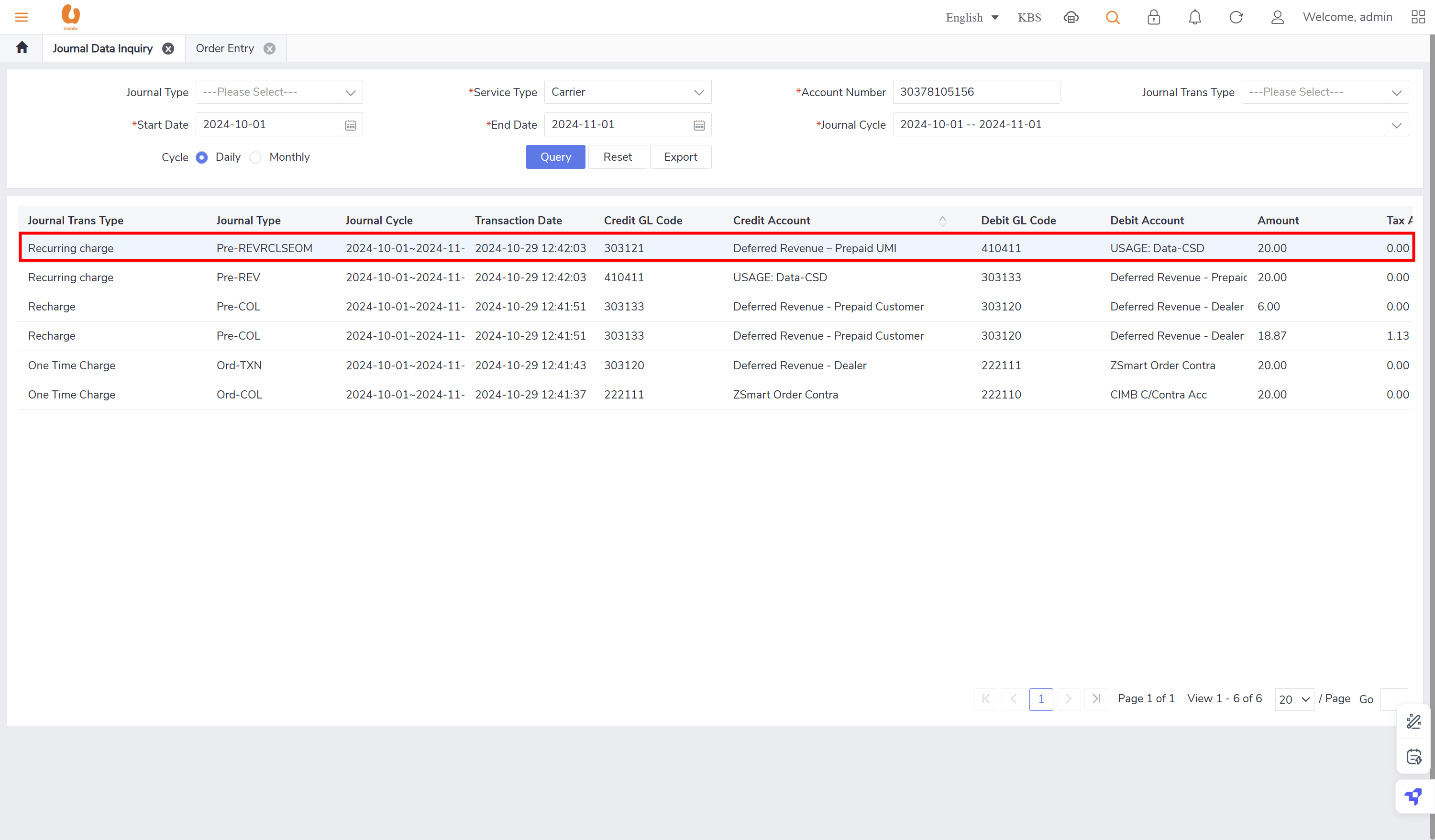
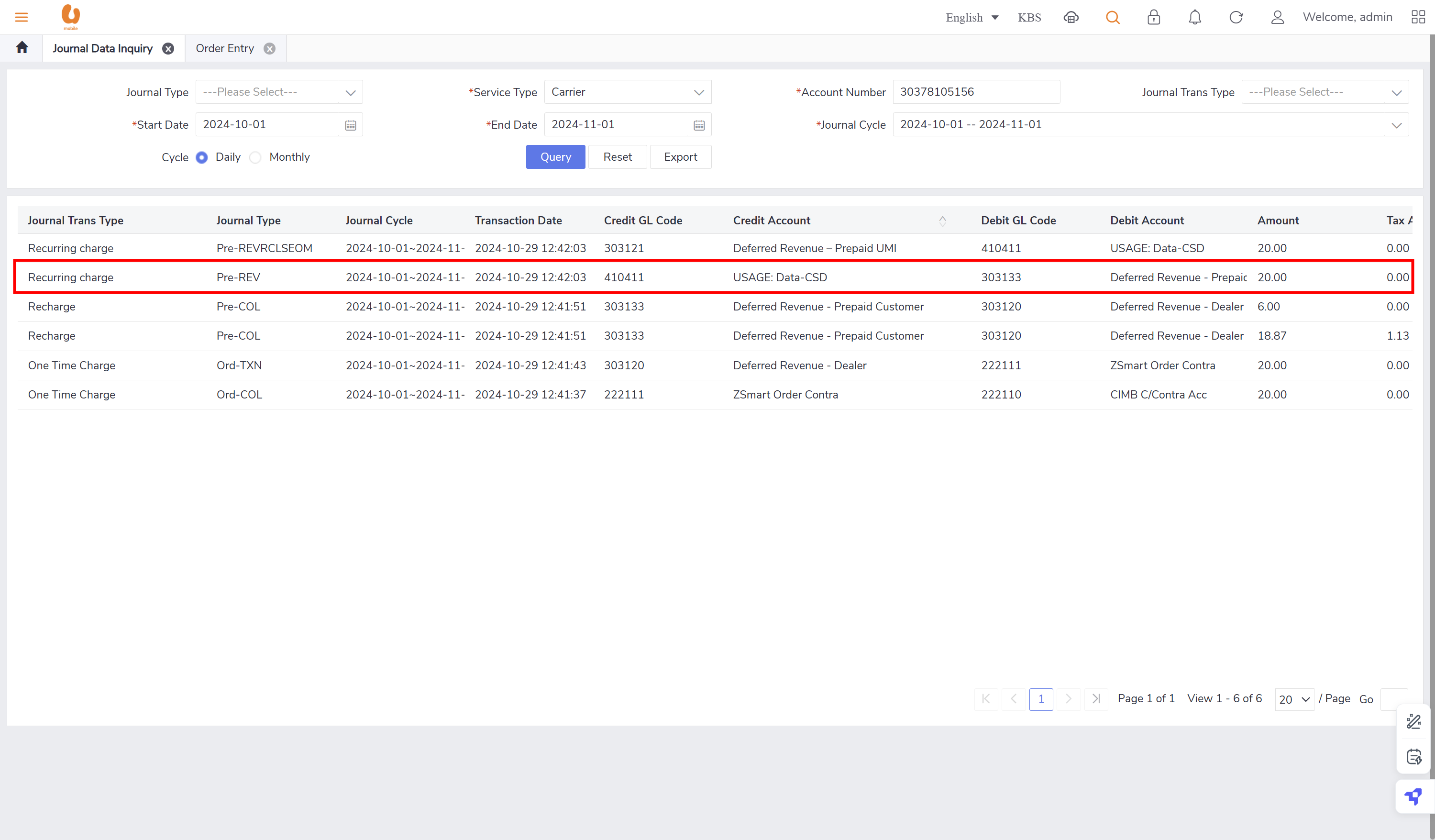
Recharge: is the top-up transaction made by the prepaid customers, it can be paid by credit card, cash, voucher, softpin, and e-recharge. such transaction will be posted under the daily journal (pre-col).
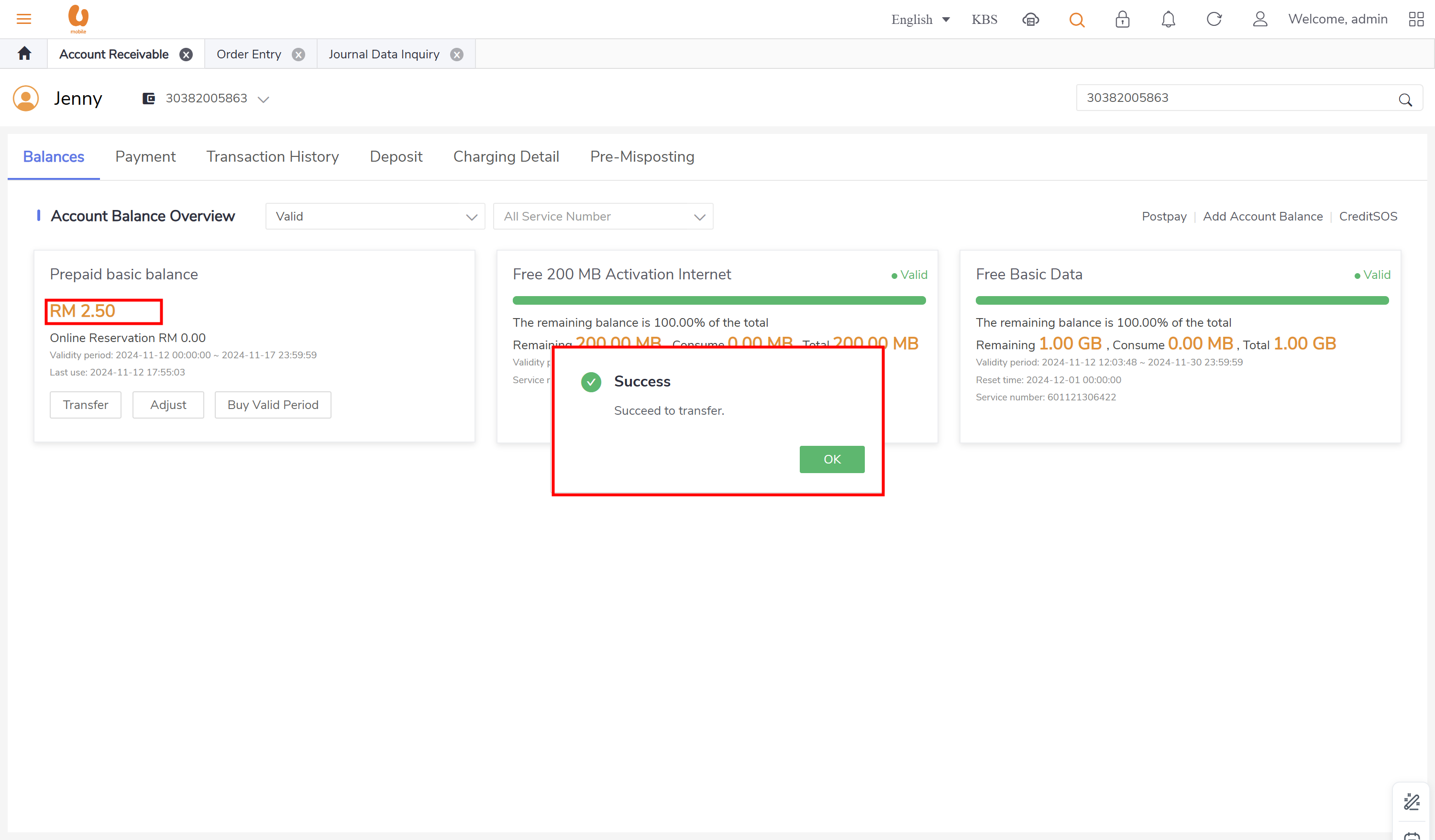
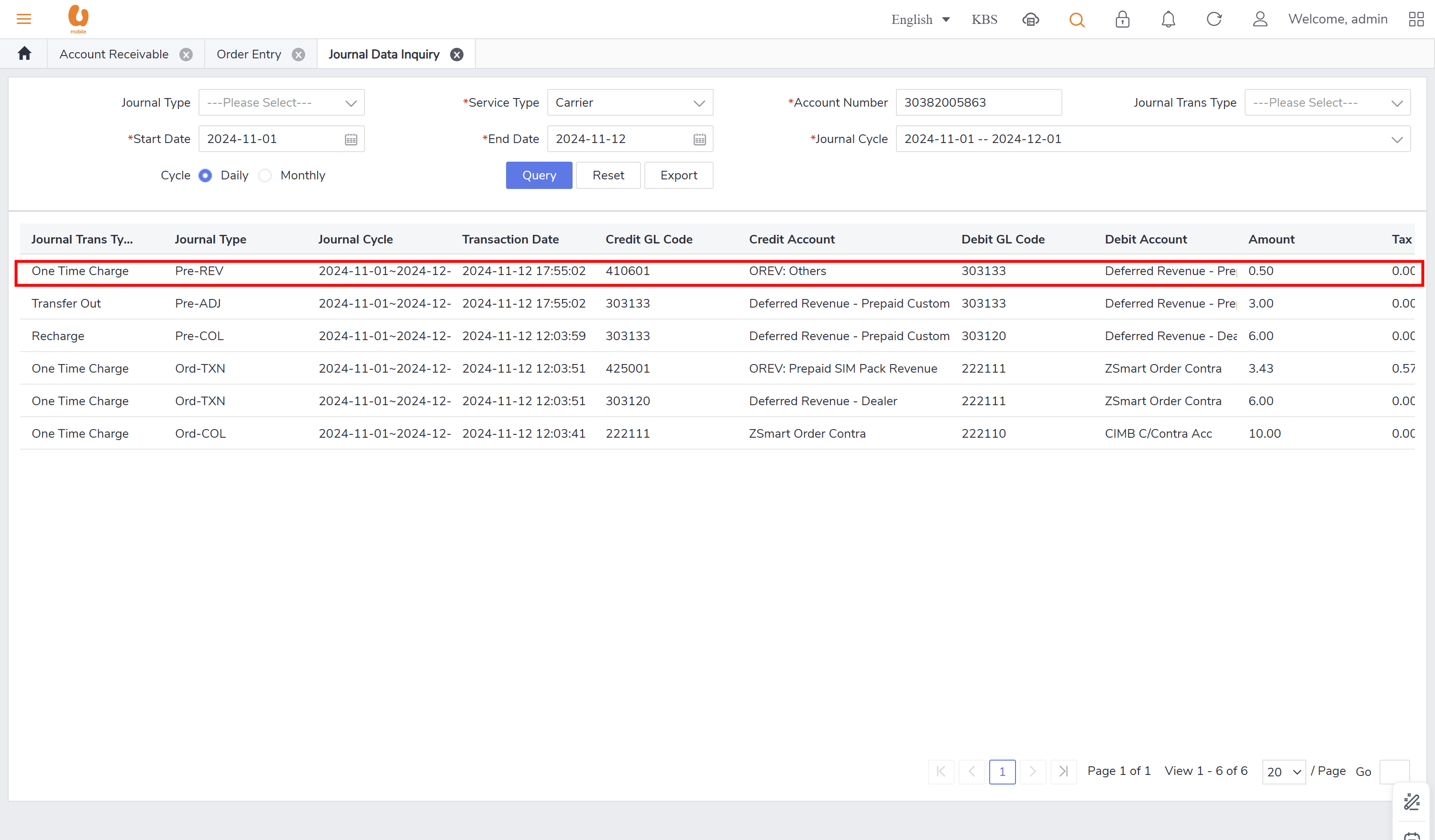
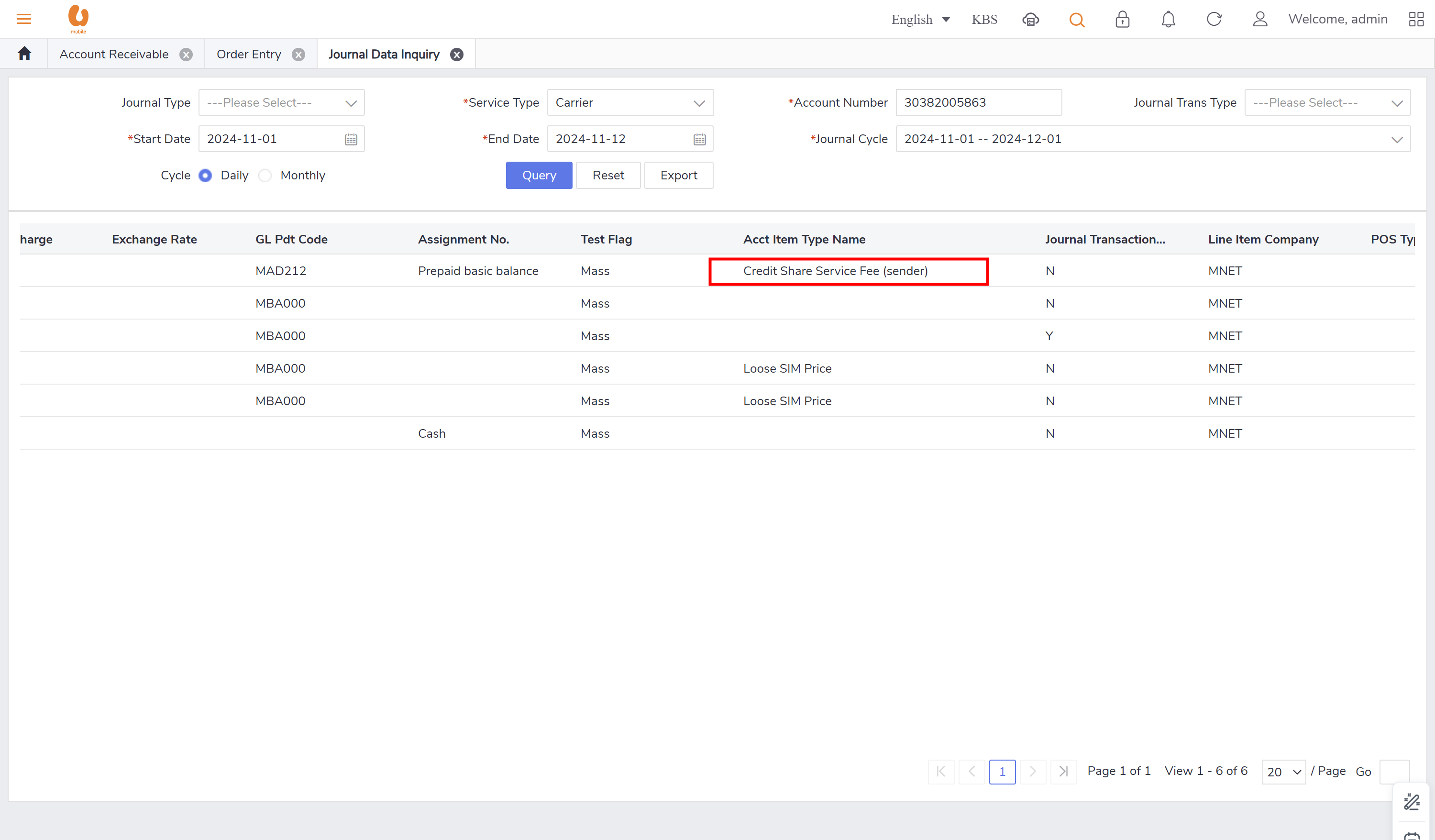
credit transfer: it is transaction where an active prepaid subscriber can transfer credit to another active/passive prepaid subscriber. the transaction itself of credit transfer will be posted under the daily journal (pre-adj) , the charges fees from transfer and transferor will be posted under the daily journal (pre-rev). in order to preform the credit transfer action, use the account receivable tab, ensure that the subscriber to be chosen is a prepaid subscriber and active.
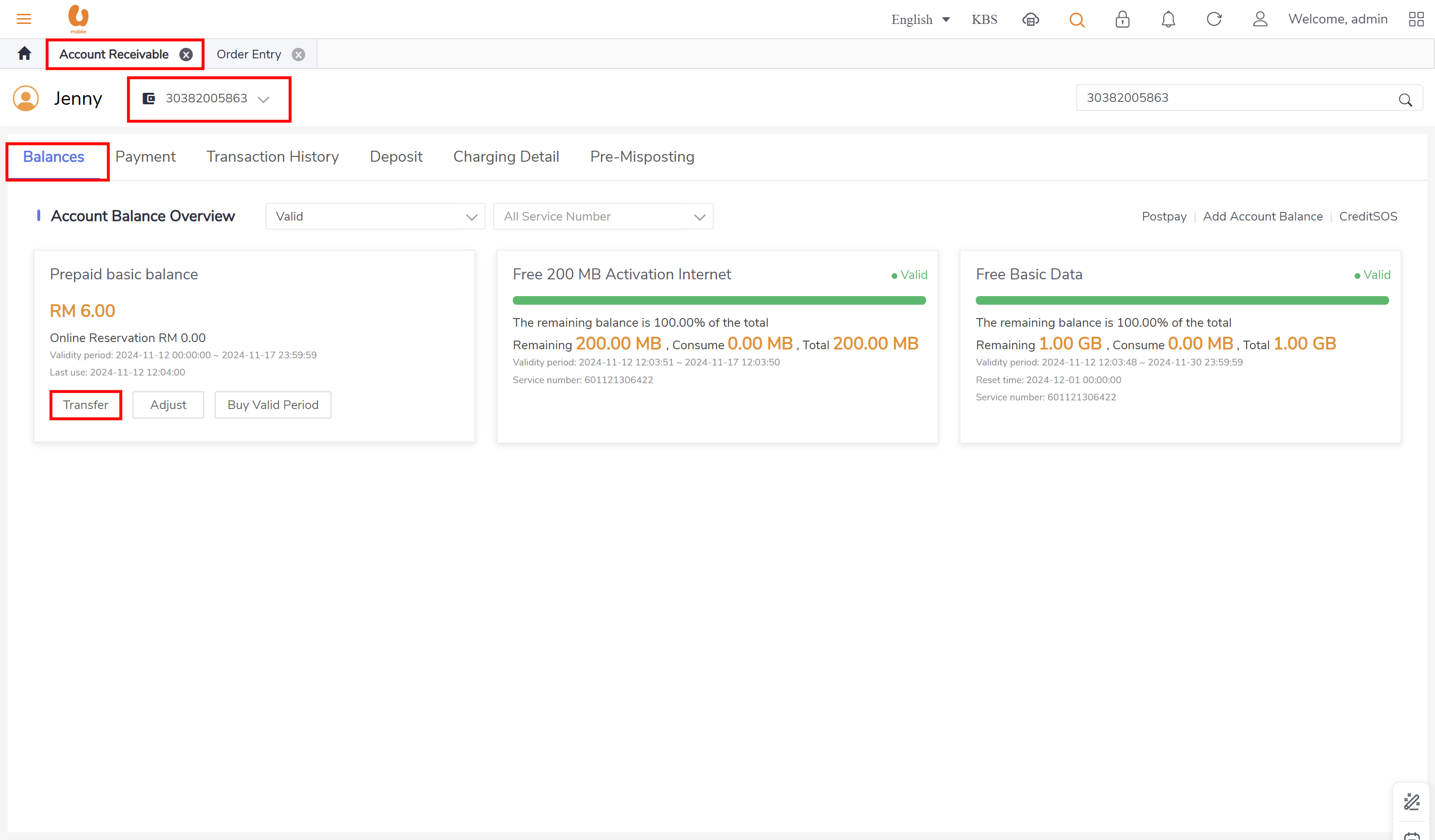
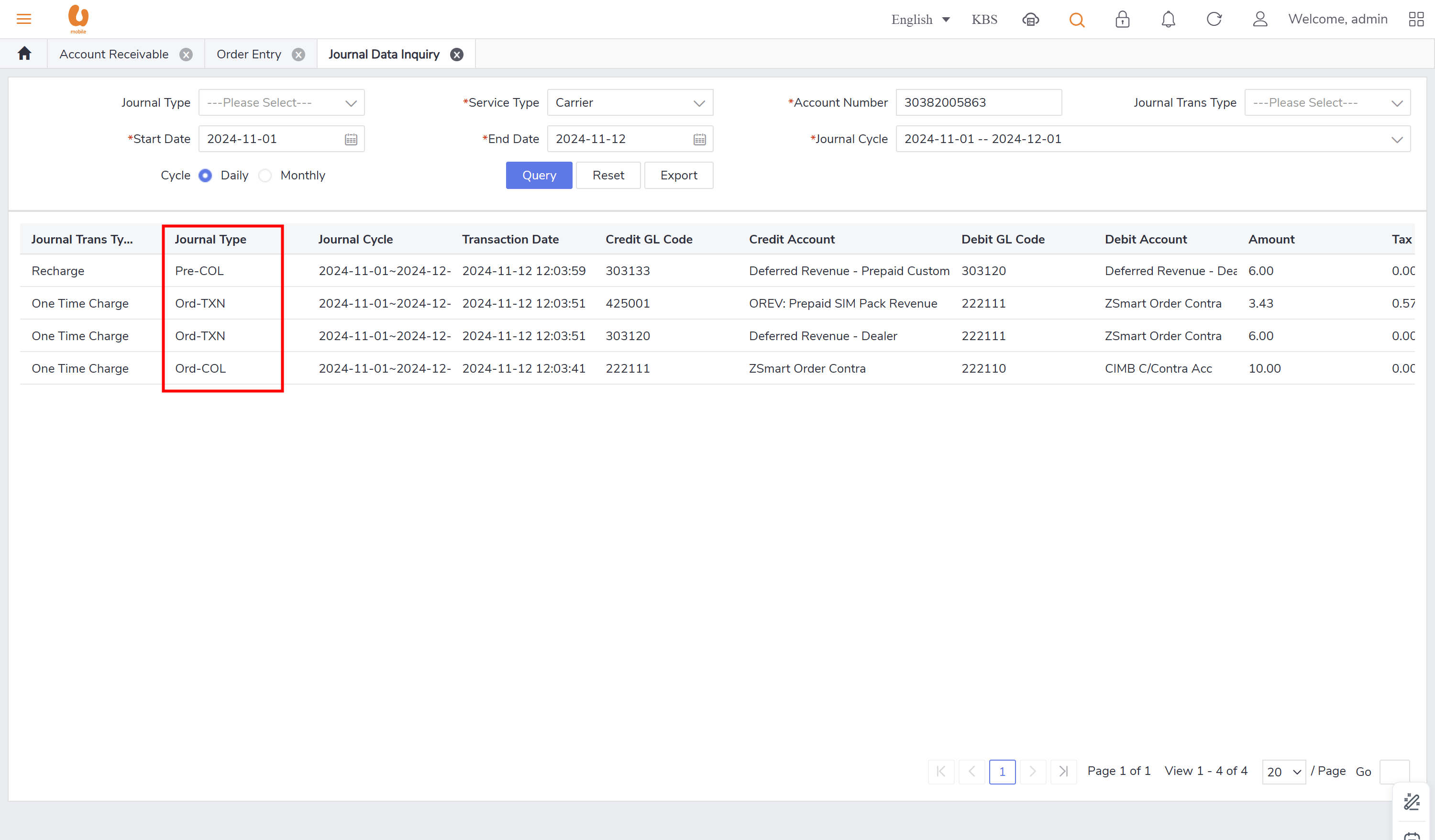
credit SOS and credit SOS repay: a prepaid subscriber can borrow credit from UM for emergency purposes, and this borrowed credit will be deducted from their next top-up, in other words when the subscriber top-up the system will check if there any credit SOS transaction history then deduct from the new top-up amount, in some cases like if the top-up amount is less than the credit SOS loan amount the system will allow partial repay. The transactions related to credit SOS and credit SOS repay will be recorded in the daily journal (pre-ADJ). the charge fee is considered as OTC and will be posted under the daily journal (pre-rev).
credit SOS clearance: it is when a prepaid customer requests a credit SOS but never top-up again, the number will be terminated, and before the termination the system will preform balance/credit SOS clearance. the transaction will be posted under the daily journal (pre-ADJ).
breakage: it is when the prepaid customer is terminated due to lifecycle control, the balance clearance will be preformed by the charging center, the breakage will include all currency balance type (main wallet, credit transfer wallet, reward wallet, MNP rebate wallet, reward wallet, bonus credit, CMS DA- monthly data plan. the balance clearance transactions will be stored under the daily journal (pre-rev). the breakage revenue will mapped into different GL codes based on the currency type.
refund: both prepaid and postpaid customers can request for a refund the refund method is cash/chargeback to payment channel (credit card, FPX) /e-wallet/ IBG ( transfer fund to customer’s bank account). for prepaid refund it will be posted under the daily journal (pre-ADJ). for postpaid refund it will be posted under the daily journal (pre-ADJBC).
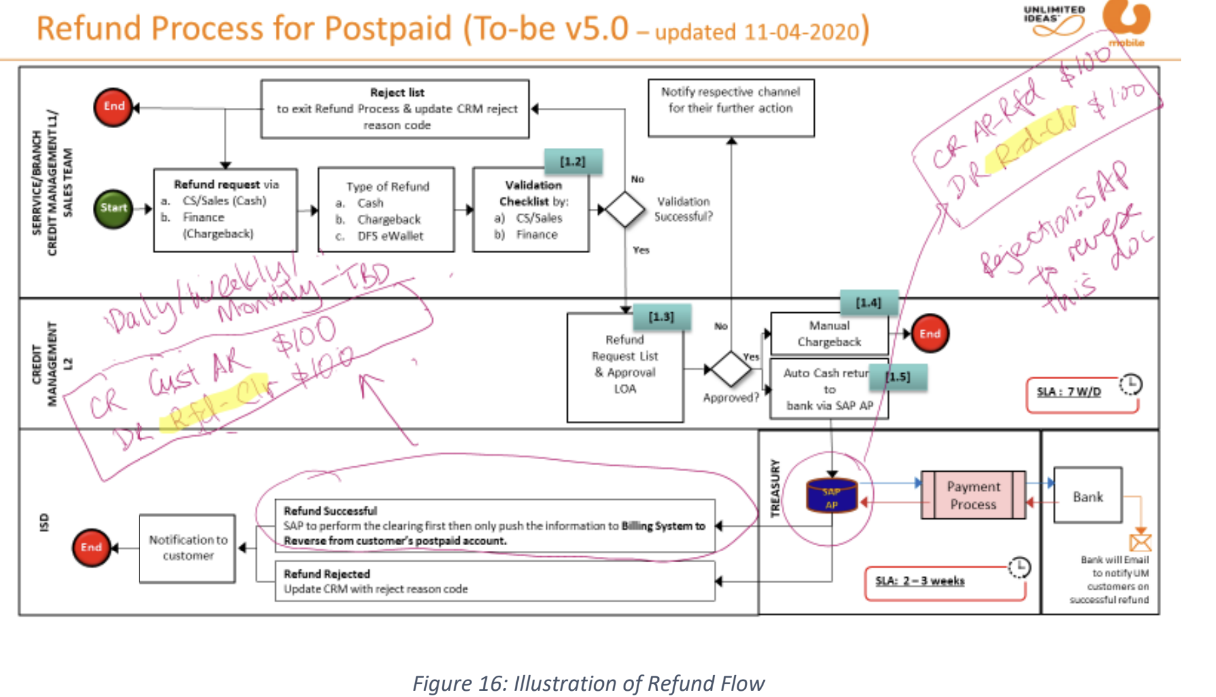
payment: there two kinds of payment:
1- order payment (postpaid and prepaid).
2- bill payment (postpaid).
the payment can be preformed by any payment method (cash/credit card/voucher/ etc).
the payment transaction will be posted under the daily the journal (ord-COL) under OTC transactions.
for the transactions like bill payment/bill payment reversal, they will be posted under the daily journal (post-COL).
different payment channels and payment methods will be stored under different GL codes.
Deposit: there are 5 types of deposit:
1- foreigner deposit = 500rm.
2- UCL (usage credit limit deposit) = 100rm.
3- advance access fee deposit = 99rm.
4- IR (international roaming) deposit = 200rm.
5- IDD deposit = 200rm.
the deposit purchase transaction will be posted under the daily journal (ord-TXN).
the deposit refund transactions will be posted under the daily journal (post-ADJBC).
for the sake of the accounting treatment the, the journal will recognize the transactions according to different GL codes based on the deposit type.
deposit to advance: when all the subscribers under a certain customer are all terminated then the system will return the deposit to the customer’s bank account. the deposit transaction will posted under the billing journal (post-ADJBC).
Bill discount: there are two types of discount:
one-time discount: specific discounts like VAS during public holidays.
accumulative discount: such as barney discount, staff discount.
to differentiate the discount from the original plan/VAS the one-time discount will be map to different GL codes and will be in a different account item type name.
the accumulative discount will use the same it account item type as the original charges, but the discount transaction will be created during the bill run and will have different type of transaction (invoicing).
the bill discount transaction will be posted under the BC journal (post-REVBC) and will be differed by the account item type name.
postpaid adjustment before invoicing: this refers to before bill adjustment, this transaction will be posted under the daily journal (post-REVEOM) and the (post-REVBC). the adjustment before bill will be mapped to the same account item name as the original from the receivable center.
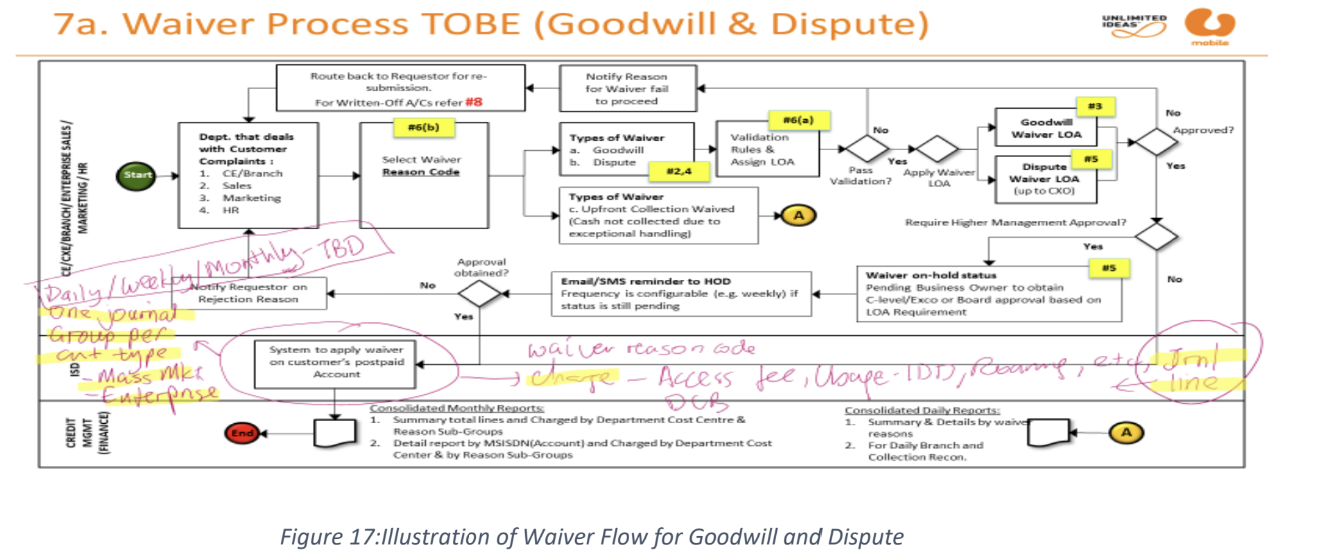
postpaid adjustment after invoicing (invoice level): this refer the after bill adjustment. these transaction will posted under the daily journal (post-ADJBC). there are two kinds of adjustment:
waiver flow for goodwill & dispute
waiver flow for internal line
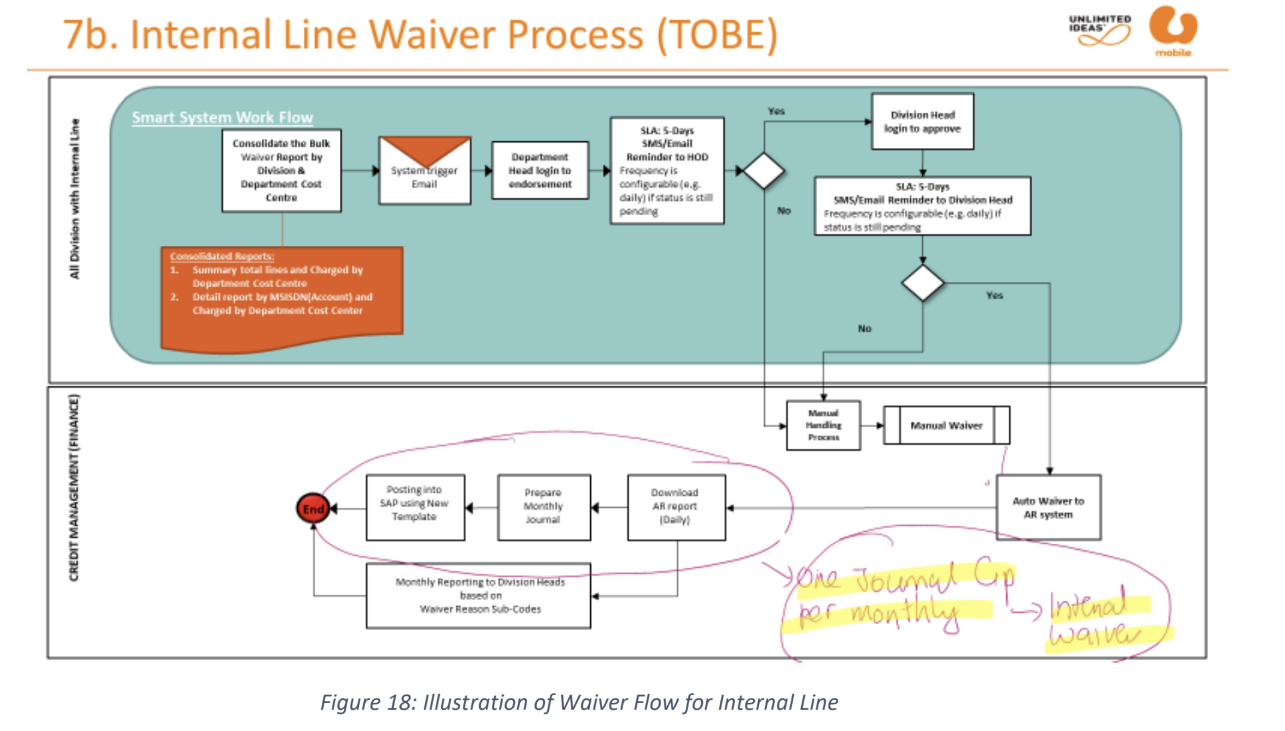
postpaid adjustment after invoicing (item level): this refers to the after bill adjustment. these transaction will posted under the daily journal (post-ADJBC).
account level adjustment: applied in the following scenarios:
the customer complaints can be marked to any charge items, and the customer service provides a goodwill waiver to the customer’s account.
adjustment waiver for a charge item that has been archived after 6 months, in which it will impact the PRM settlement.
the rules of the function of account level adjustment:
the account level adjustment will be posted under the daily journal (post-ADJBC).
the account level adjustment for postpaid should not belong to any existing specific charge item, in order to map the transaction to different GL codes by adjustment reason codes.
in the case of the adjustment waiver for a charge item has been archived, the system should allow the account adjustment to be done at account level with adjustment reason, mapped to the GL codes that are related to the original charge.
prepaid balance adjustment: prepaid waiver flow:
the transaction will be posted under the daily journal (Pre-ADJ).
when the user preform the balance adjustment to the original charge then the change reason code should be chosen in addition to the account item type name, in order to map the transactions with the original charge GL codes.
when the user preforms the balance adjustment to any existing charge then the change reason code should be chosen and the the account item type name, so it can be mapped to different GL codes from the original charge.
Late fee: the invoicing center will collect the late fee in case of the involuntary termination due to dunning at the last bill. this transaction is related to postpaid and it will recognized as (invoicing), and it will be posted under the BC journal (Post-REVBC).
write off: this transaction occurs in postpaid customers who did not paid the fee for a certain period of time , and fall into bad debt therefore this transaction will be managed independently. this transaction will be posted under the monthly journal (post-BADDEBT).
write back: when the customer paid off all the bad debt, a write back will be preformed to release the customer from blacklist. this kind of transaction will be posted under the monthly journal (post-BADDEBT).in case of a partial payment transaction is will posted under the daily journal (post-COL)
Unit wallet: usage recognition of unit wallet (the quota balance that the customer gets from the prepaid basic plan purchase, VAS tenure that exceeds or equals 30 days) in which it needs to be posted to SAP. the prepaid plans has 1-limited plans (30GB per certain period) and 2-unlimited plans (no data pool limit)
for example if a customer subscribes for a 30 days data plan with 30GB data pool, and the subscription date is in the 15th of the month and the customer has used 10GB for a month , then the remaining 20GB will be in the coming month , it like splitting the revenue in case of cross month. another example if the customer has a 60 days tenure for a 30GB plan then the remaining revenue will be split for the 3 months if subscription happened on 15 Nov then it will end on 15 Jan.
in order to utilize the unit wallet there are pro-ration rules to be used:
limited quota: recognized by the actual used amount (used amount = (unit wallet value / total volume) * used volume)
unlimited quota: recognized by the actual used days (used amount = (unit wallet value / total effective days) * used days).
example: if there is 3 types of VAS with tenure of 30 days and a customer purchase the three types with total price 40 and the vas has a month to expire the first EOM(end of month) and first unit wallet utilization is on the 1st day of the month of expiry month and the 2nd unit wallet utilization will be on the 1st of the month after the expiry month :
vas1: unlimited quota + limited quota.
vas2: limited quota: plans with limited pool, will be accounted based on the usage.
vas3: unlimited quota: plans with unlimited pool, will be accounted based on the day count similar to (post-REVEOM).
Tax: the tax for rating and charging will be be rounded to 6 decimal output for the sake of system precision. however for invoicing and journal feed it will be rounded to 2 decimal output. the system will use two levels to calculate the tax:
transaction record level: journal center will extract the tax amount from each transaction record and will calculate the tax for each piece of charge or transaction like :
the charges in prepaid, postpaid, retail sales order transaction which are paid immediately.
the prepaid recharge.
the postpaid bill adjustment, and the account level adjustment.
bill summary level: since the journal has different grouping summary dimensions with invoicing, it can’t extract the tax amount directly from the invoicing data, and it will calculate the tax based on the group of the summarized amount of transactions and the behaviors separately like:
the postpaid usage/ otc/ recurring charges paid by bill.
bill discount.
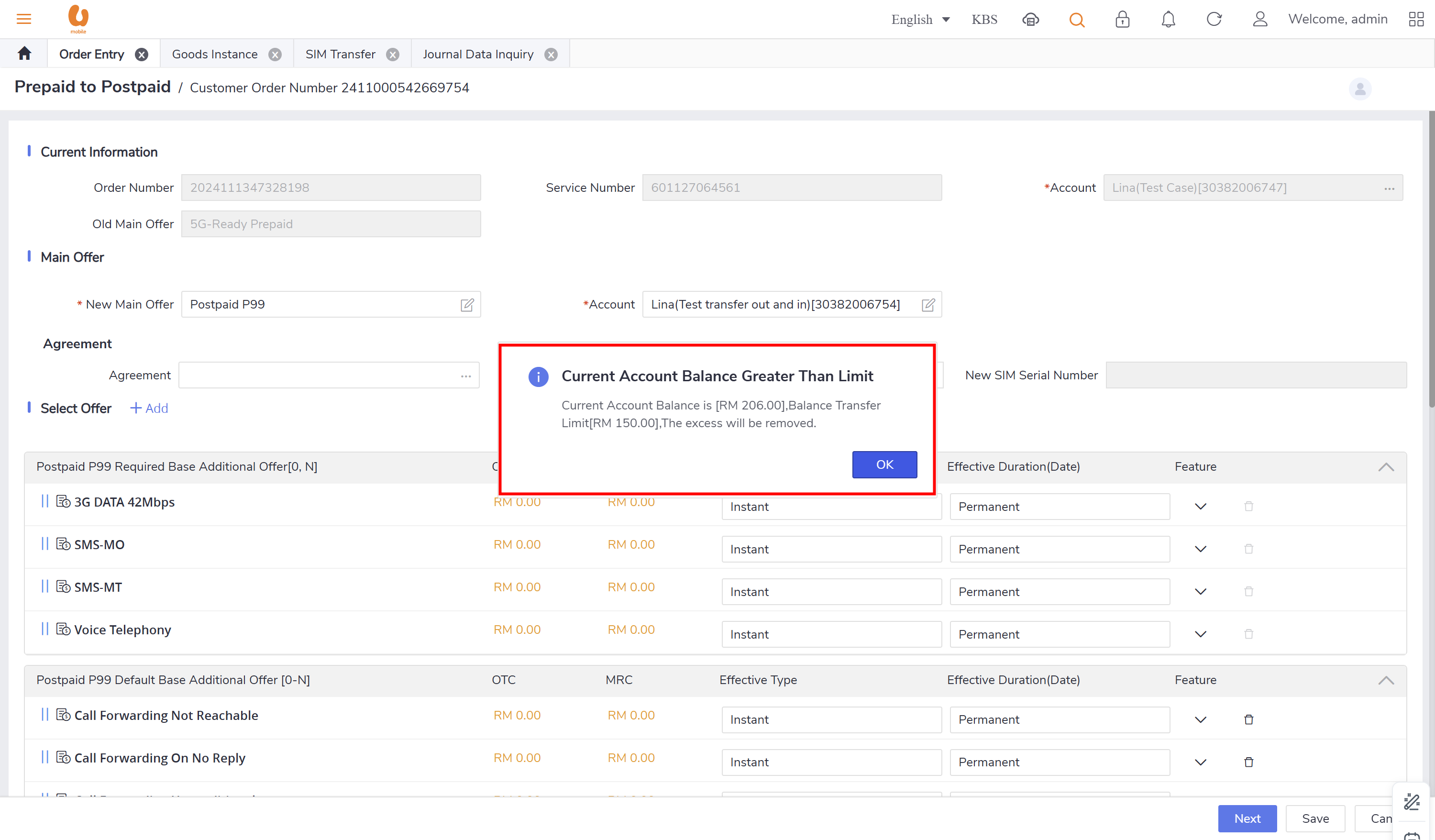
transfer out and transfer in:: it is the transaction of a customer changing their offer from prepaid to postpaid with a maximum 150rm credit, if there is more credit it will be expired. for the prepaid account it is the balance transferred out, for the postpaid it will be balance transferred in. in the below is an example to clarify the transaction of transfer out, detailing how the credit is applied and the implications for both prepaid and postpaid accounts. first a prepaid new connection is made and a top-up is preformed to make the account has a balance more than 200rm, to see the expiry and movement of the credit.
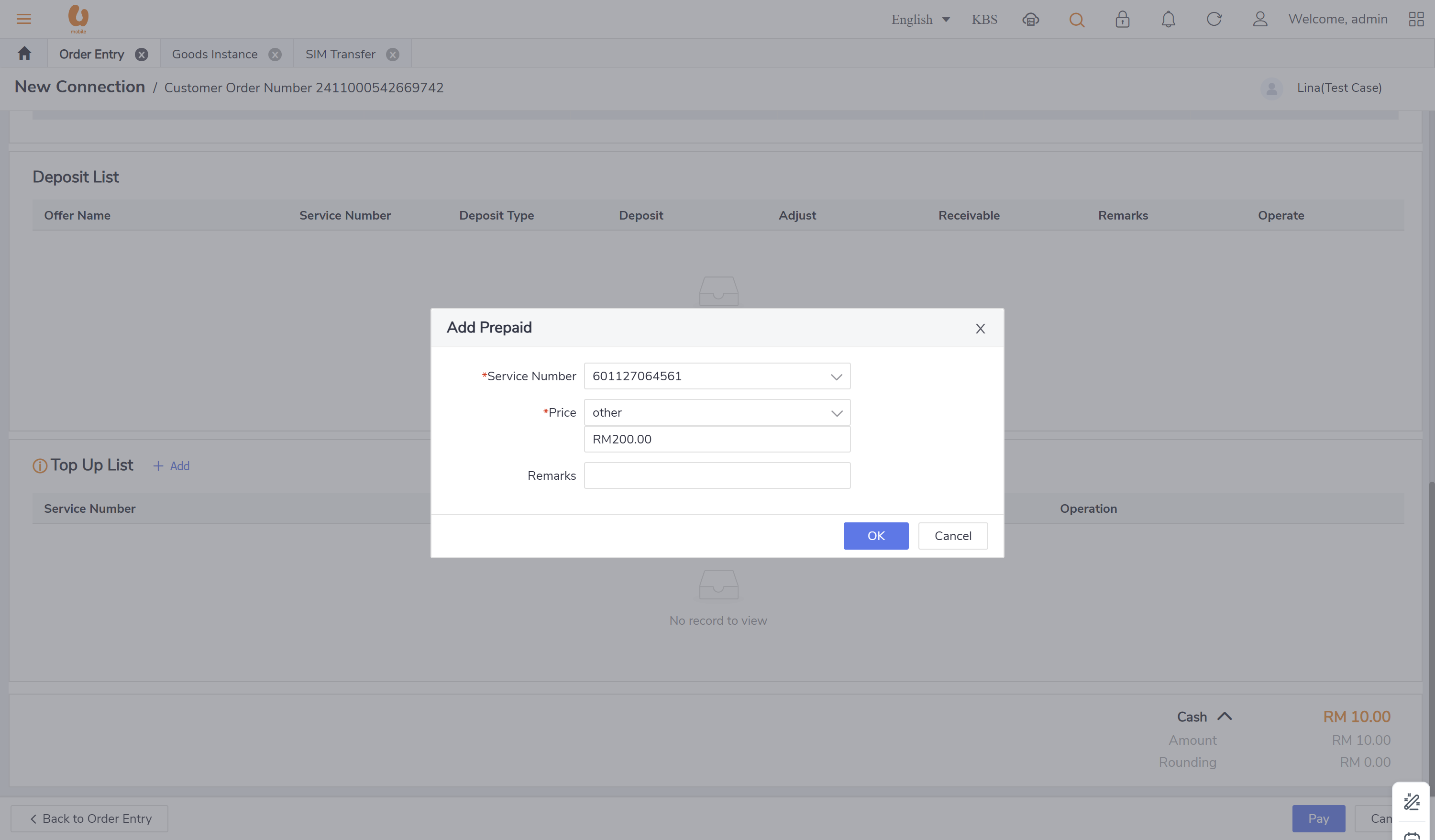
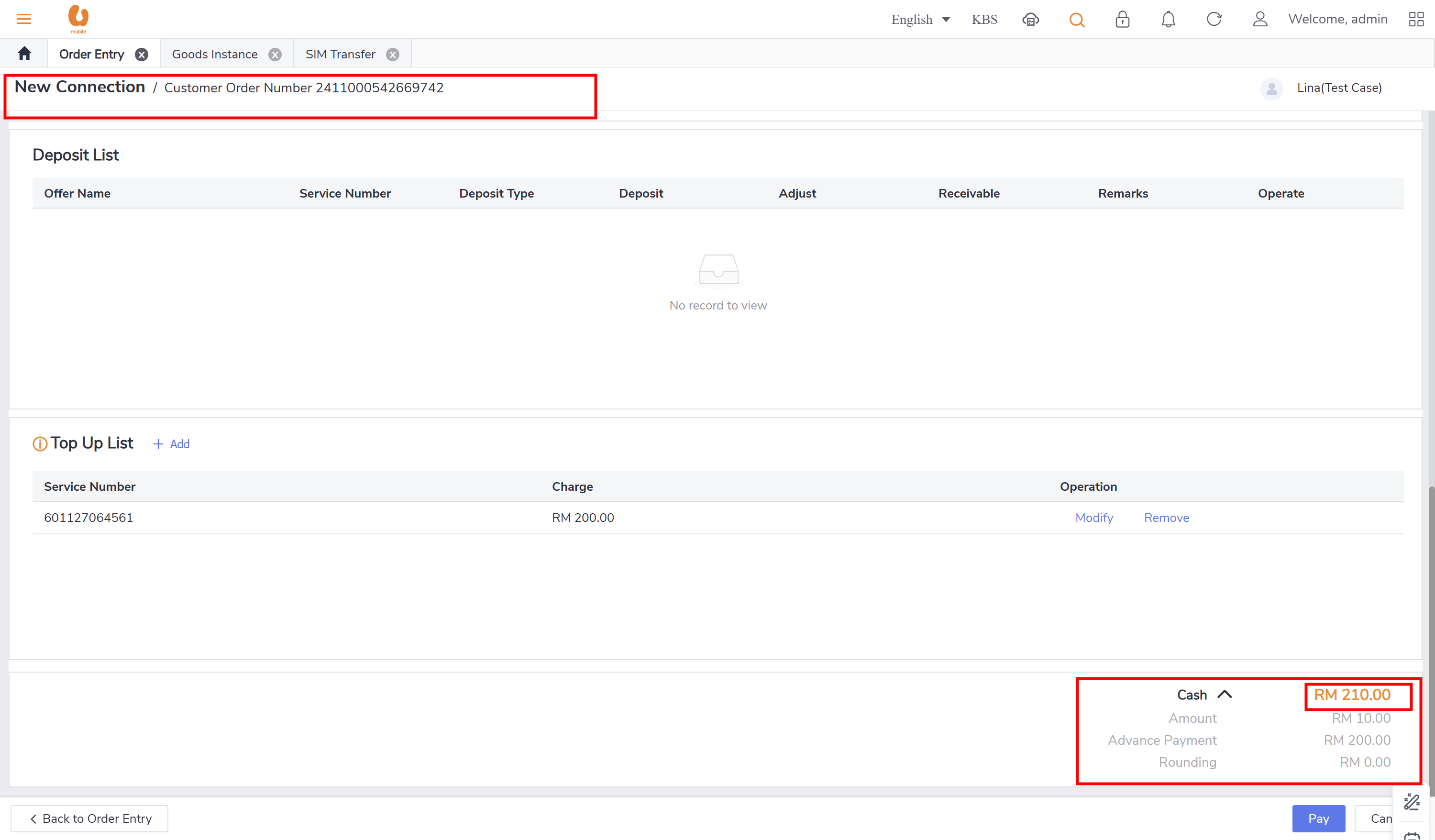
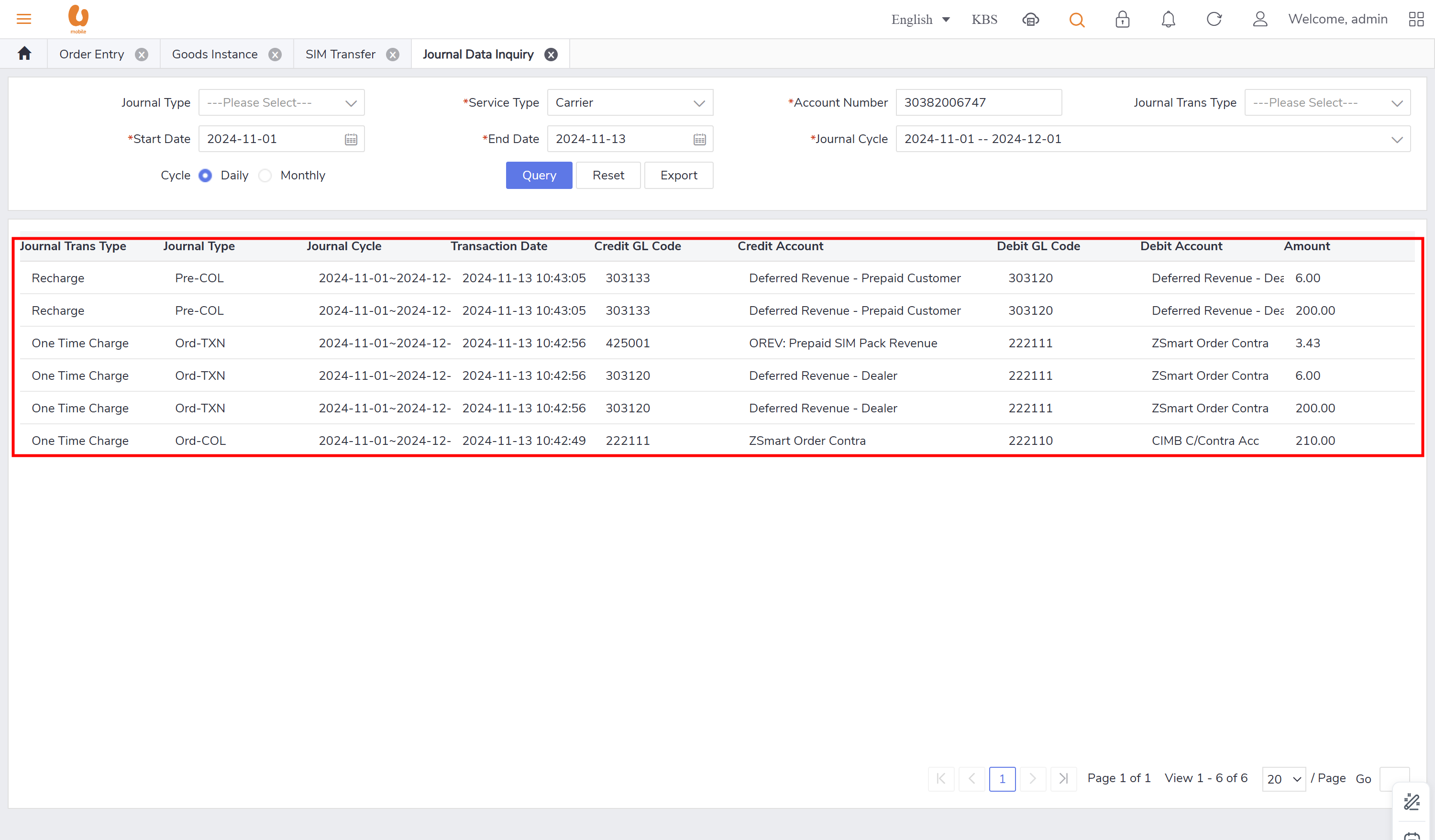
Solution Description:
GL management solution:
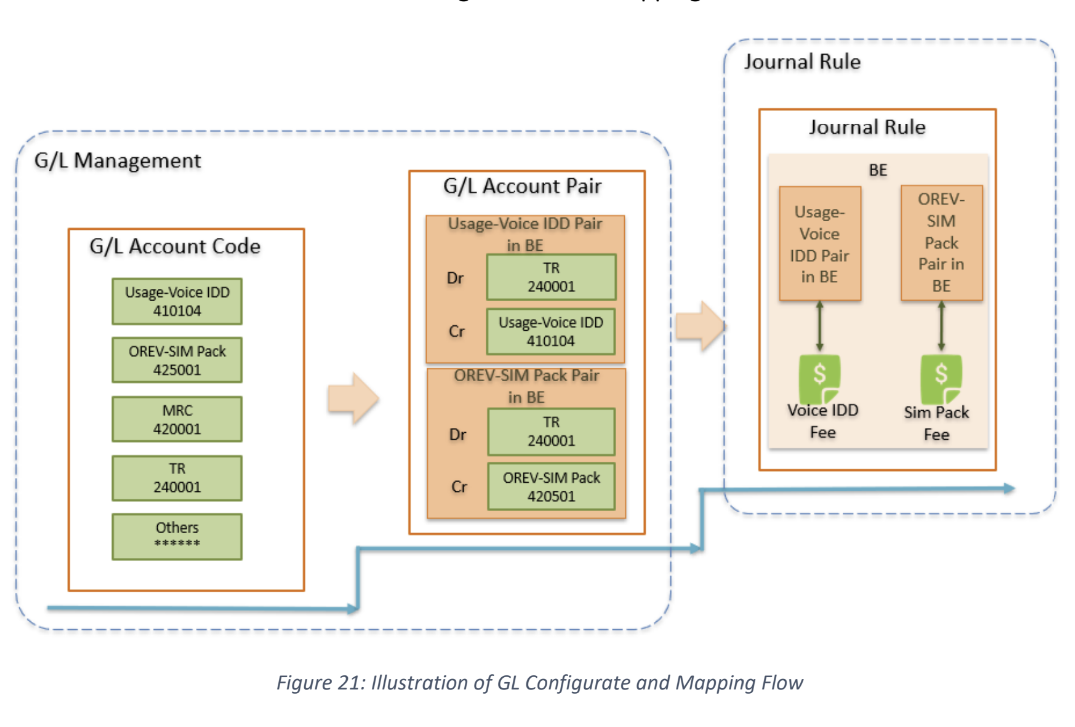
create GL account code : solution GUI (journal account configuration).
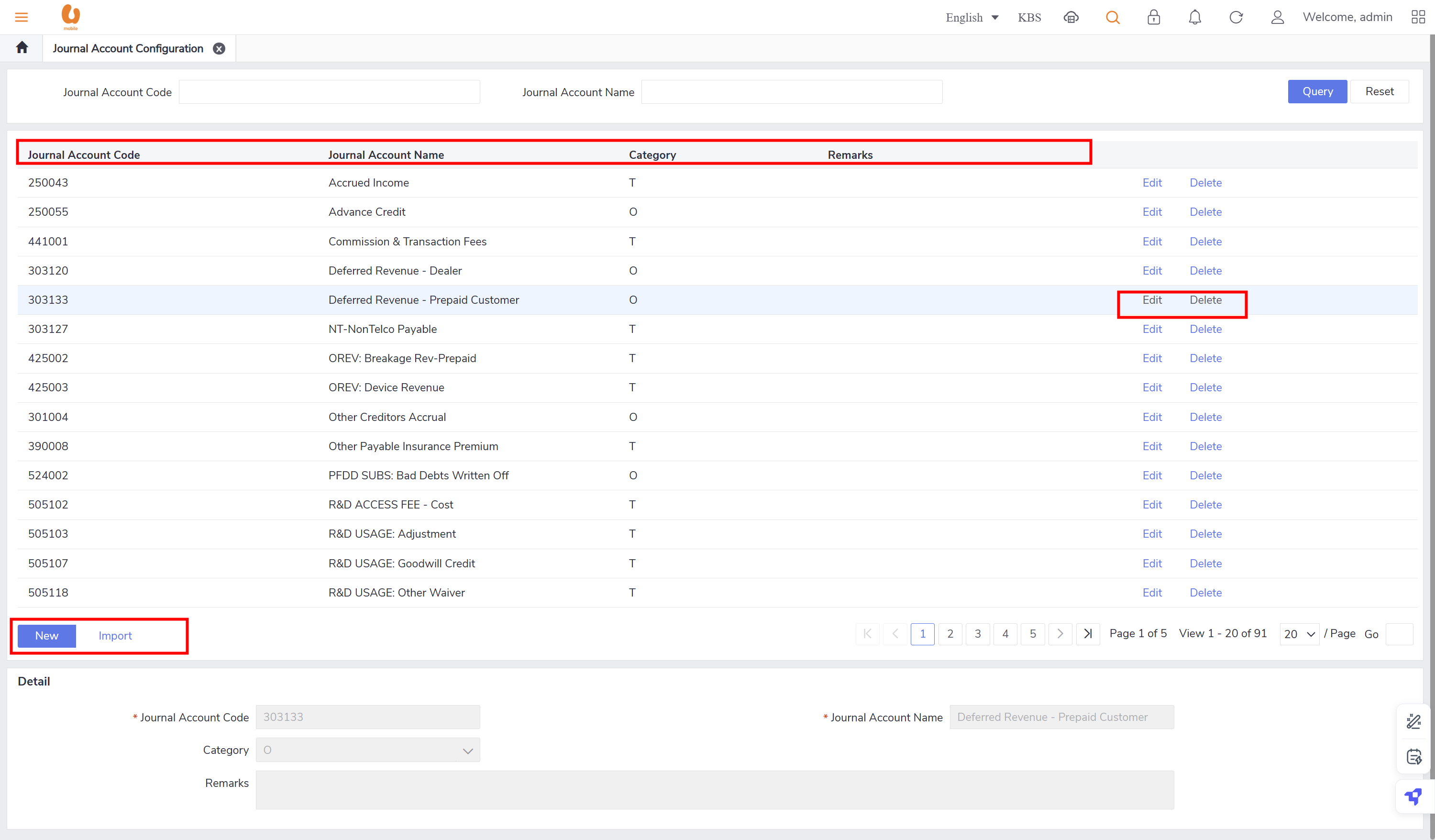
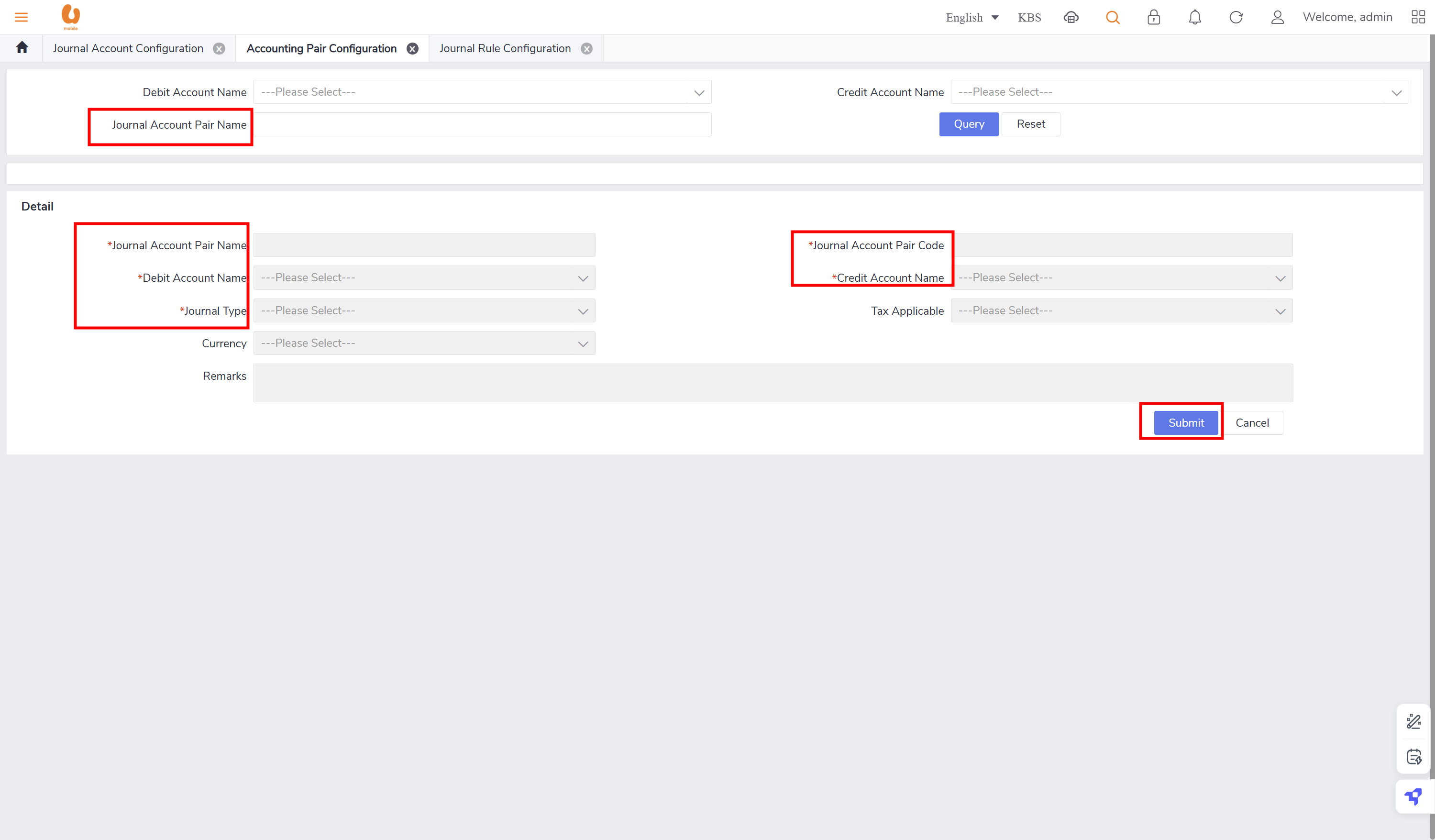
create GL account pair: solution GUI (journal account pair configuration).
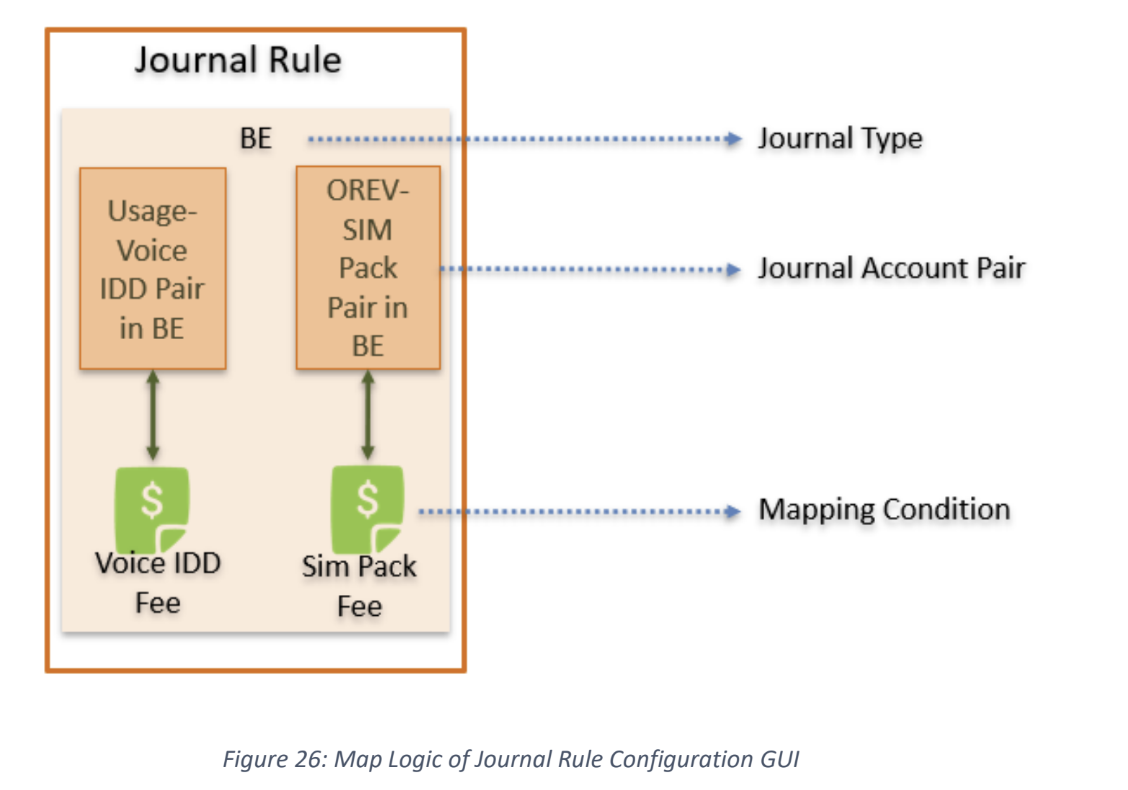
configure journal rule to map GL account code with charge item: solution GUI (journal rule). it will uses journal mapping mechanism, in which it will map data to different GL according to the information recorded in the billing, and then map the GL to specific journal object type. the common mapping condition are (account item type name, payment method, payment channel, reason code, deposit type, prepaid to postpaid, etc.)
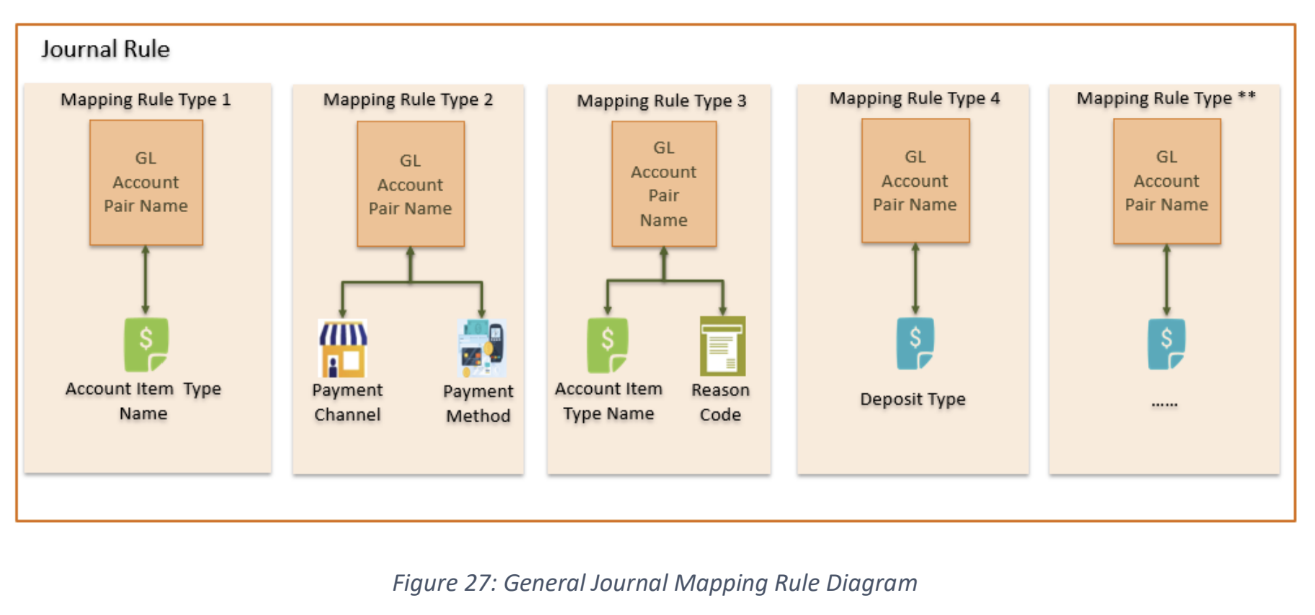
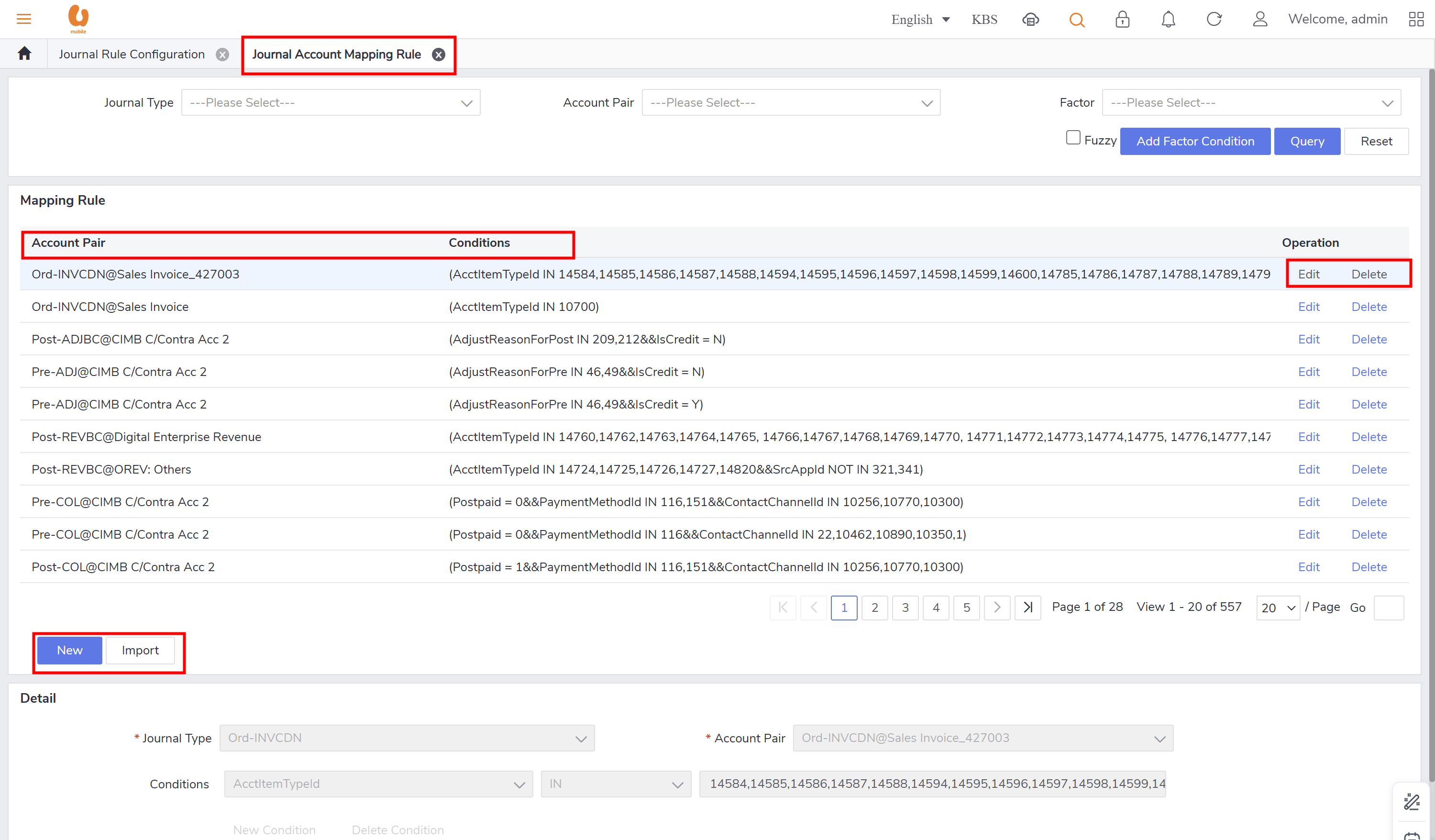
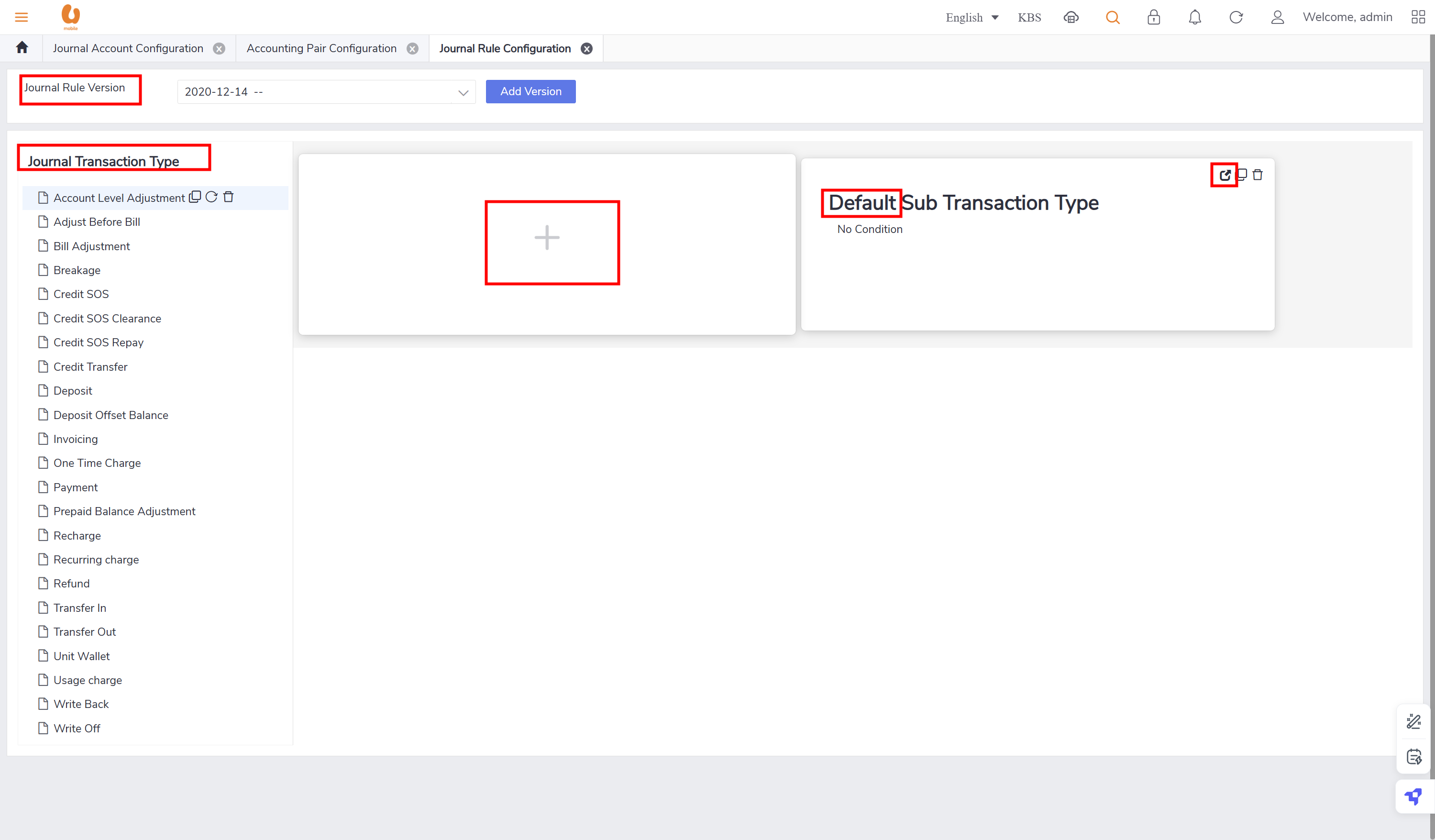
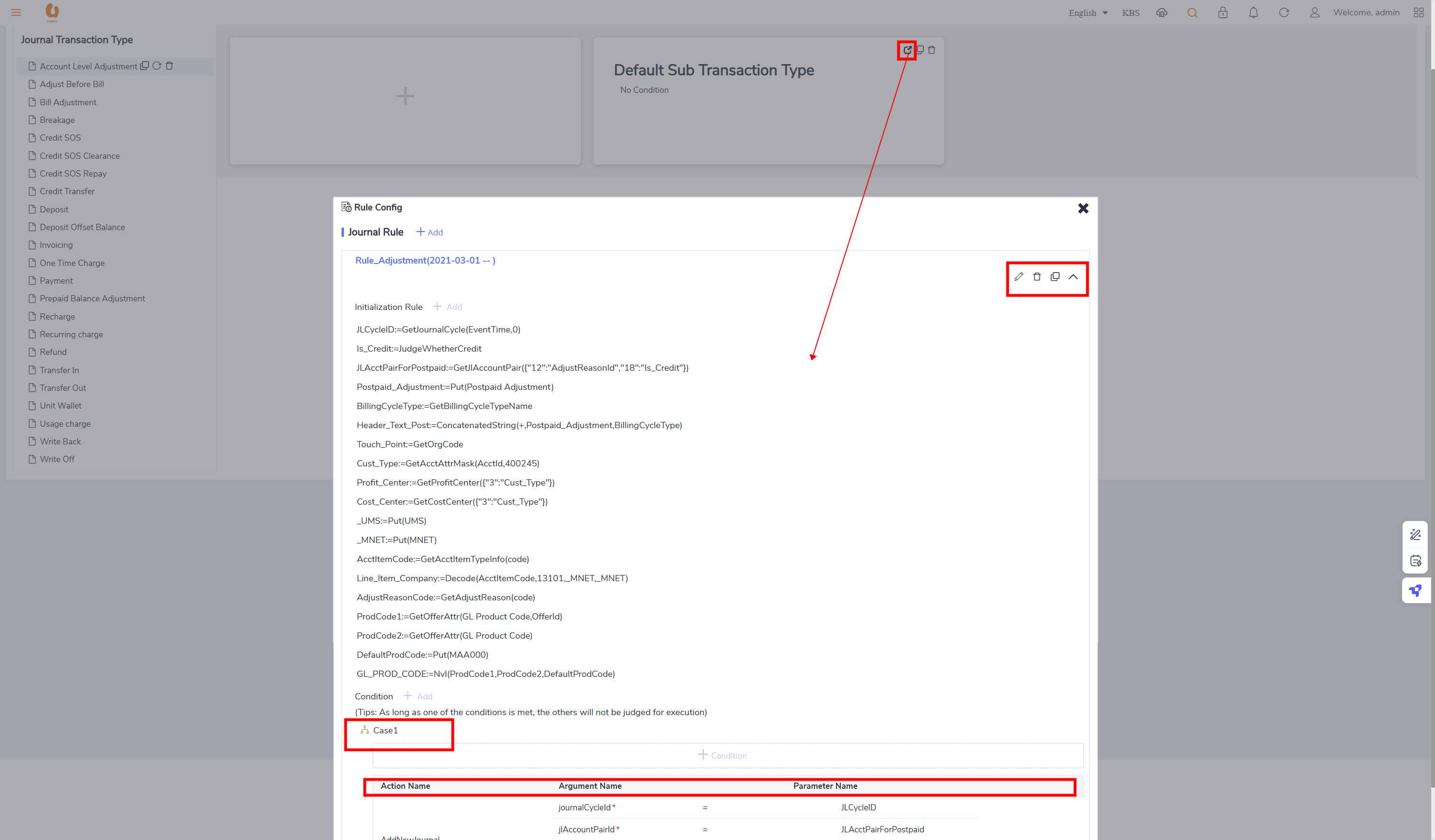
Other Configurations
configuration of additional fields.
Set up for profit center/cost center management.
Journal Feed File
Generation of feed files for SAP that requires specific naming conventions and layouts.
the journal feed file has a specific naming rule (GL_< Journal Type >-< YYYYMMDD >-<HHMMSS>.csv) . the journal type refers to the journal types (pre- /post- ). the HHMMSS (running number sequence of the day) and it refreshes daily. for example (GL_Pre-COL-20200501-113020.csv).
the journal feed file has specific file format which ASCII-format.
the transaction types> journal data process > finance system
process steps :
daily aggregation: the journal will get consumption/transaction & payment data based on the accounting/billing cycle. according to the journal rule definition, journal center will maps the original transaction of CRM and Billing to the GL (general ledger). journal accumulates the data of the same category together based on the rule definition (daily).
monthly aggregation: the journal will accumulate the data of the same category based on the rule definition (monthly).
the generation of feed file requires the use of the stat tool, in which it will extract the aggregated data from the journal center, it will use the daily aggregation data for daily journal file, and the monthly aggregation data for monthly journal file.
aggregation rule key factors are (journal type, debit/credit account code).
posting the rule happens when the stat tool extract all the aggregation data from journal center every morning, and then generate the feed file based on the frequency of each journal type based on the definition rule.
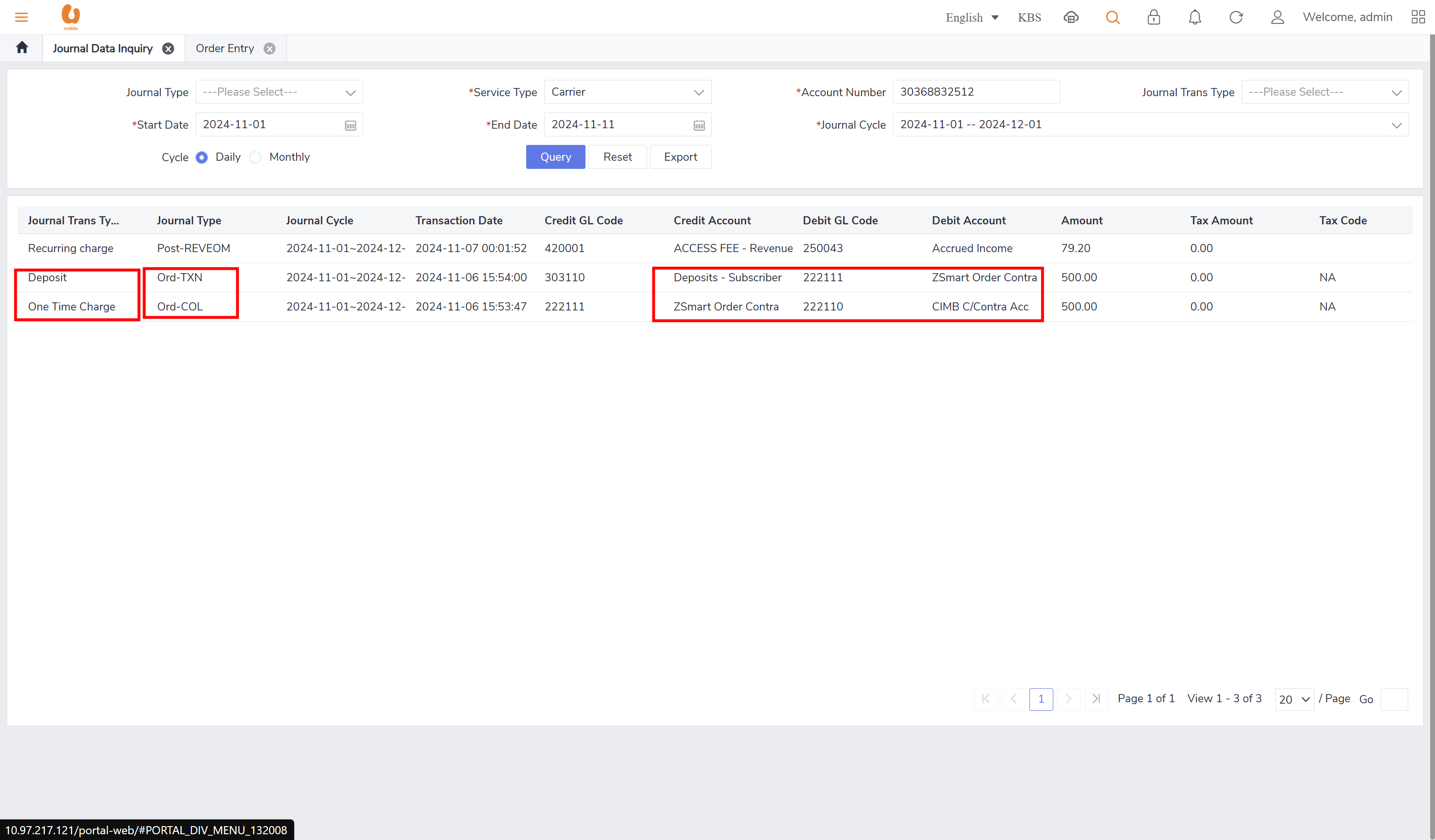
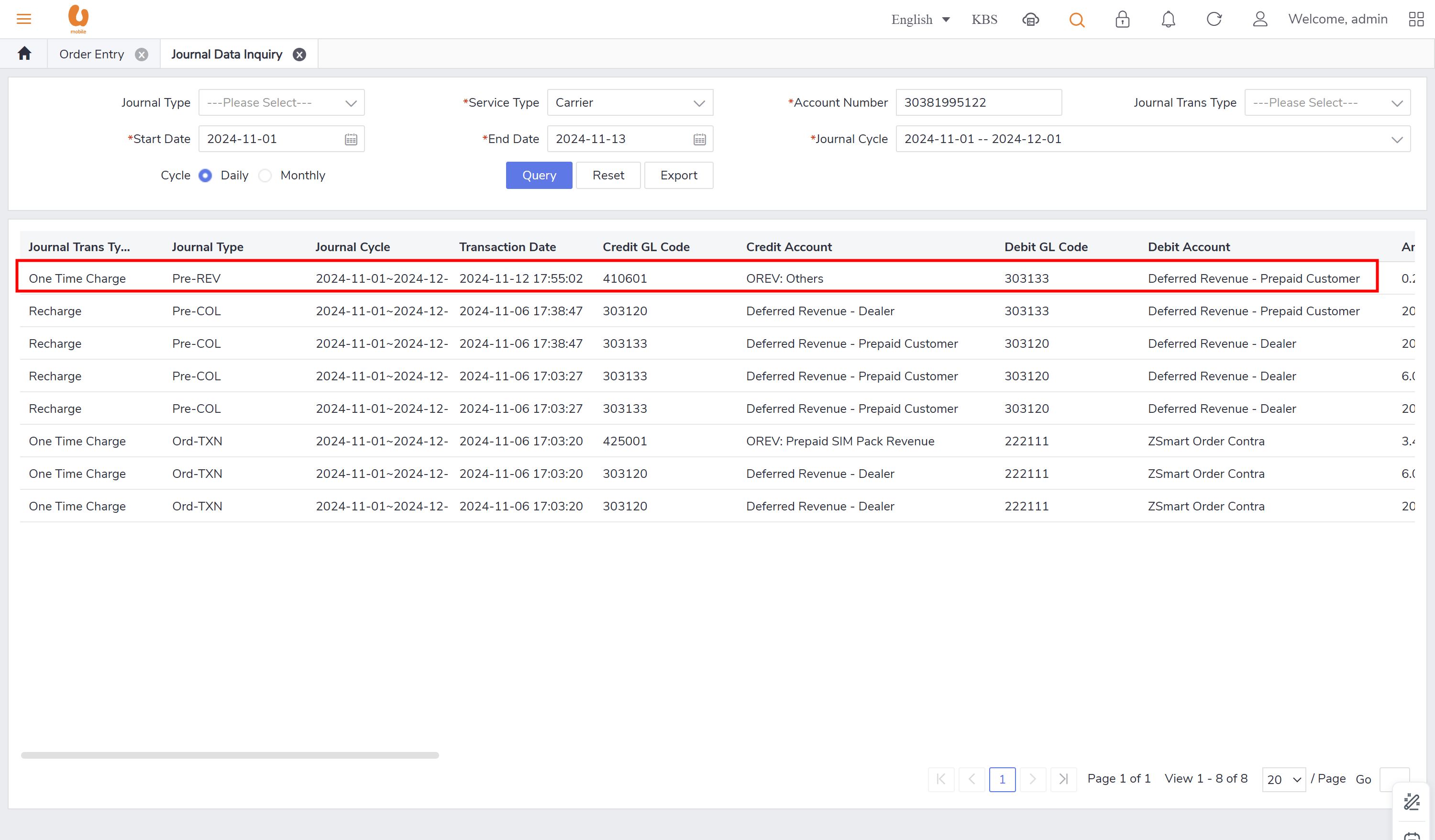
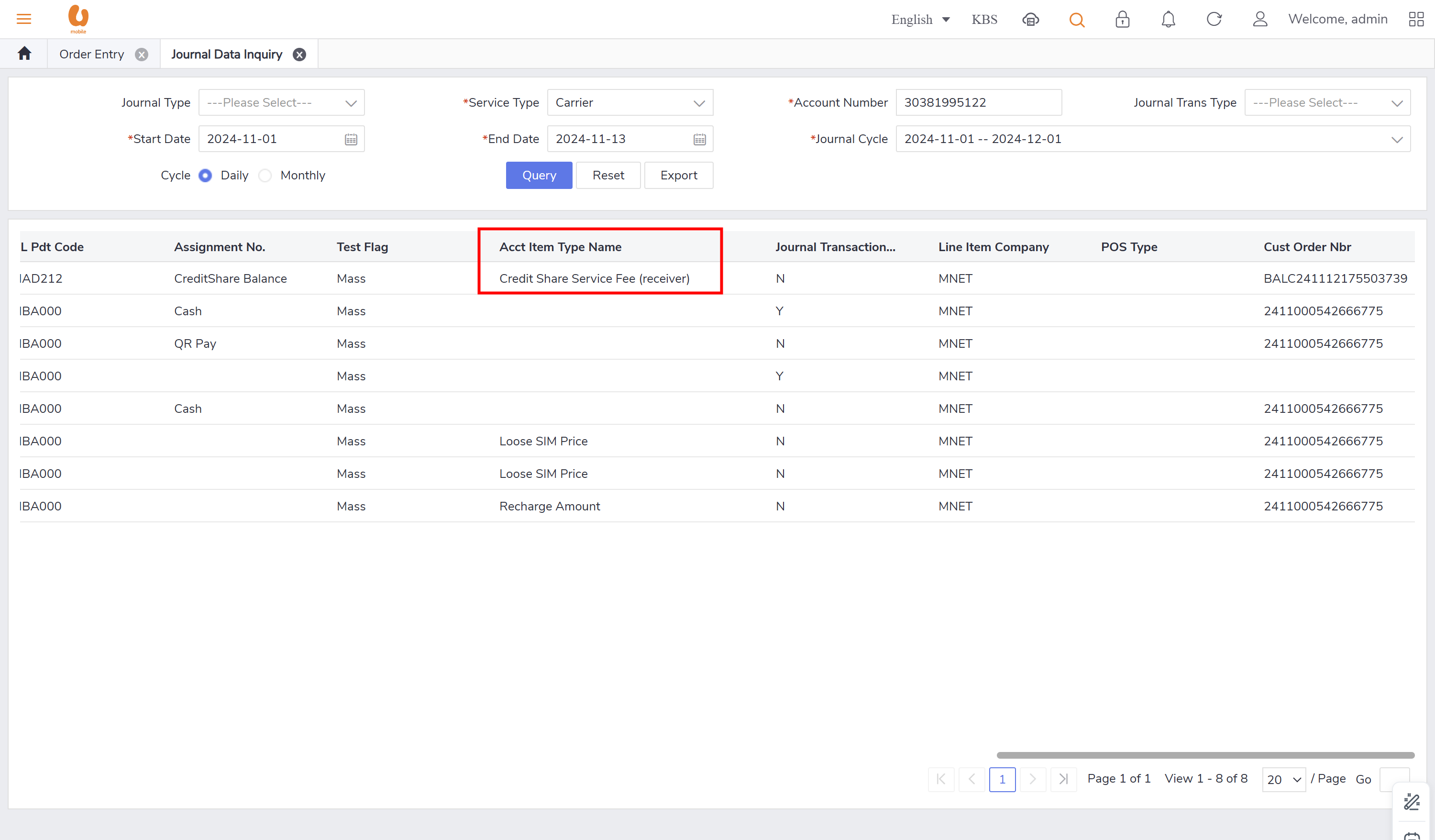
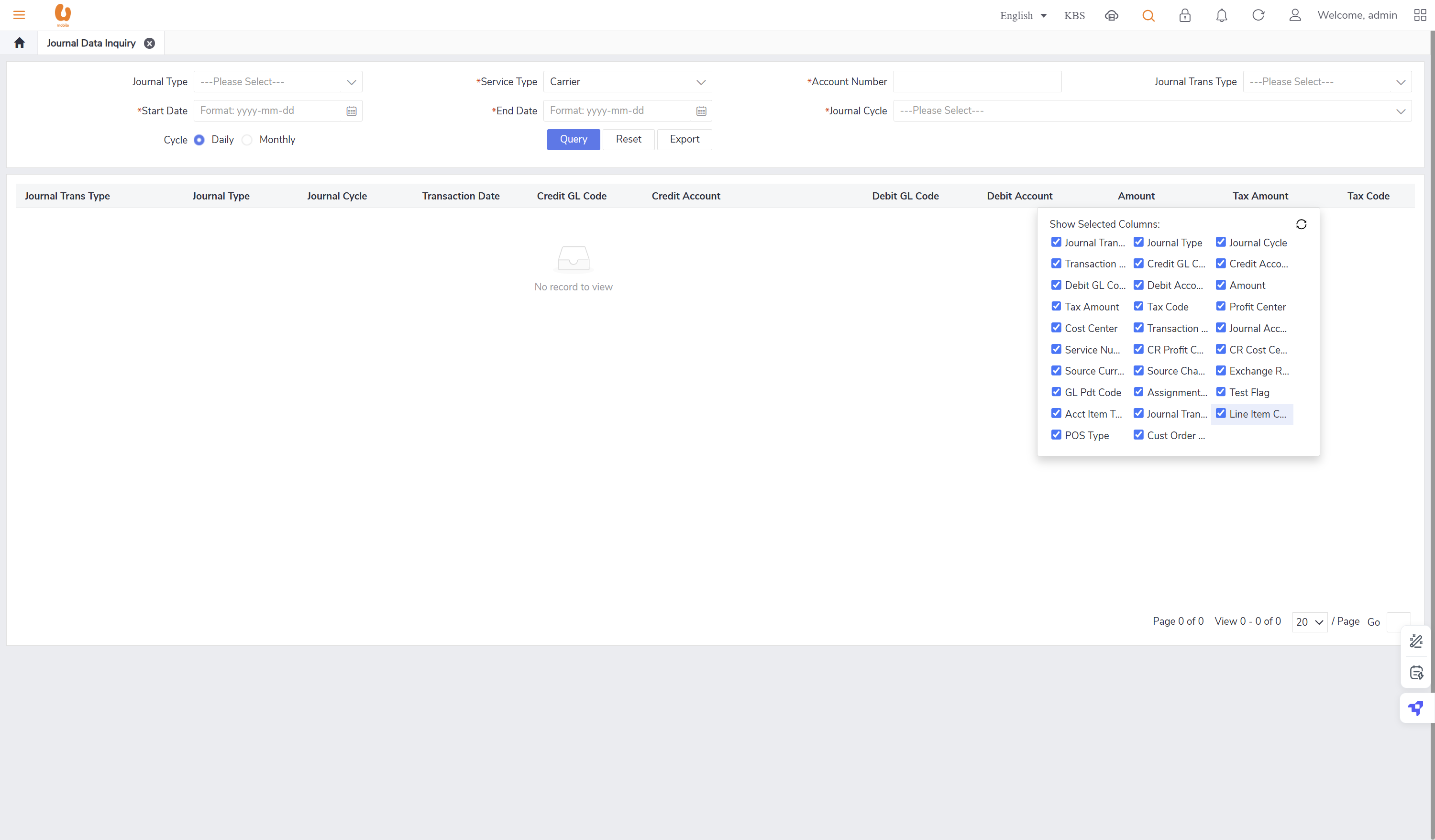
Journal Data Inquiry
Query functionalities supporting operational teams in daily/monthly inquiries.
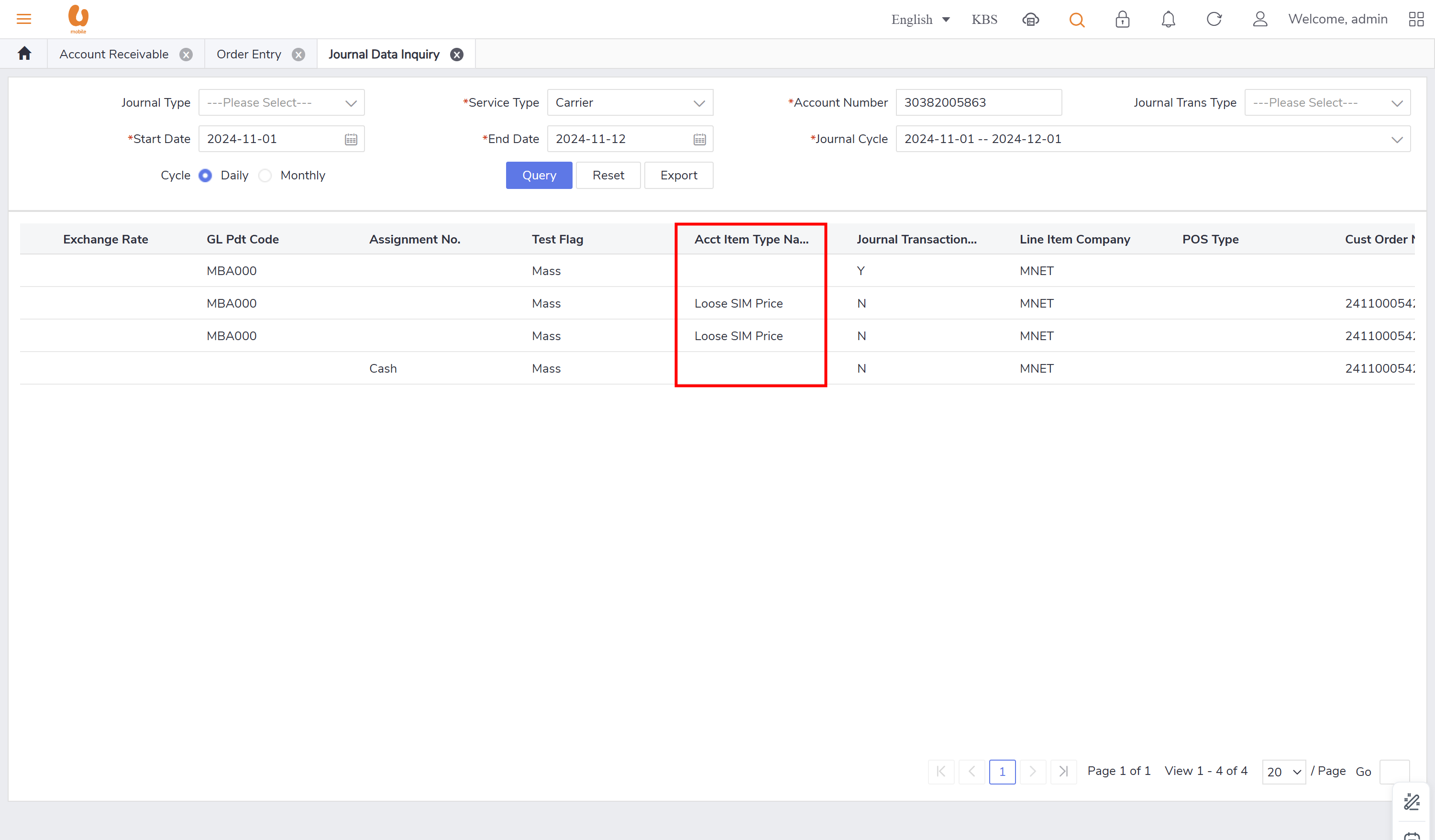
includes important fields like (credit and debit fields, Journal transaction sub type, journal type, account item type name, journal transaction type).
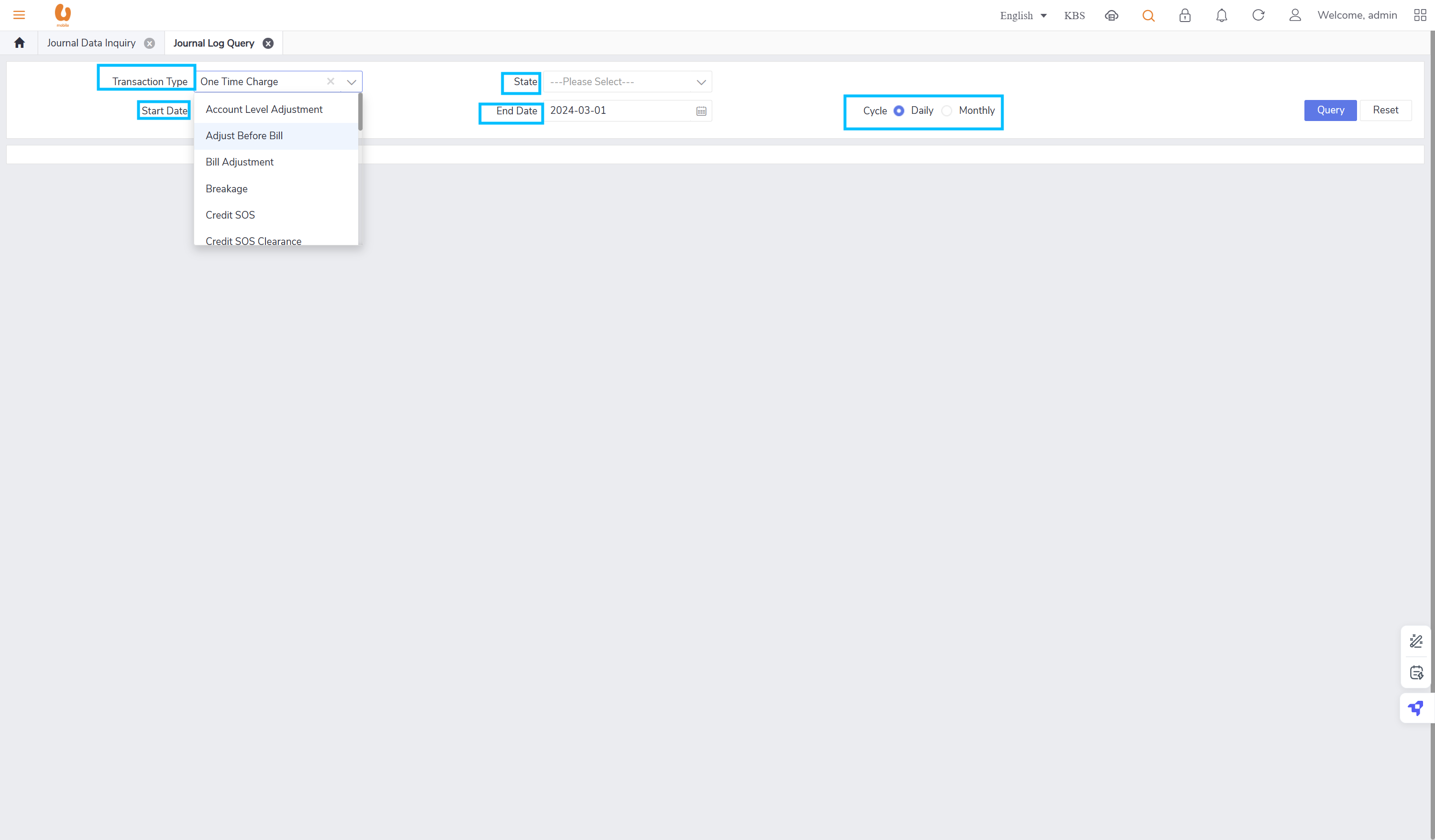
journal log query, shows the important information like transaction type, date, data quantity, state , etc.
Journal Audit
Reconciliation points established for journal transactions with oversight from different modules, daily/monthly/BC aggregation in journal center, stat tool and SAP.
Journal Reprocess
Specifications for the flow to reprocess : journal > stat tool > SAP.
Journal Misposting
if one of the customer ( complains regarding a misposting from account B to account A, the transaction first will tracked by the conditions, date, posting channel, and amount, and there is a possibility of 2 scenarios:
account A and account B belongs to the same customer, the customer agreed not to reallocate because a future payment may happen for account A.
account A and account B belongs to the same customer, the customer refused to not to reallocate, in this case “payment transfer” will preformed with non-used/unconsumed/ remained amount. for example, if the customer wrongly paid 100rm for account A , and it has been partially used then like around 60rm then remaining 40rm will only be transferred to account B, this transaction type is called “payment reversal”.
Reporting
Report Name | Description |
PFDD Report | A report to capture outstanding including ETP or customer was flagged with Confirm Fraud. |
Write Off Report | A report to capture the detail write off & write back transaction. |
Top Up Report | A daily top up summary report by payment mode and wallet type. |
Prepaid EOM Report | EOM KPIs list in the Return at 1st day of each month for Prepaid transaction. |
Postpaid EOM Report | EOM KPIs list in the Return at 1st day of each month for Postpaid transaction |
Journal Summary Report | Summarized transactions extracted from JNL DB. |
Journal Detail Report | Detailed transactions extracted from JNL DB. |