TOPIC 5: Price Elasticity, Income Elasticity, Cross Elasticity, & Elasticity of Supply
Price Elasticity
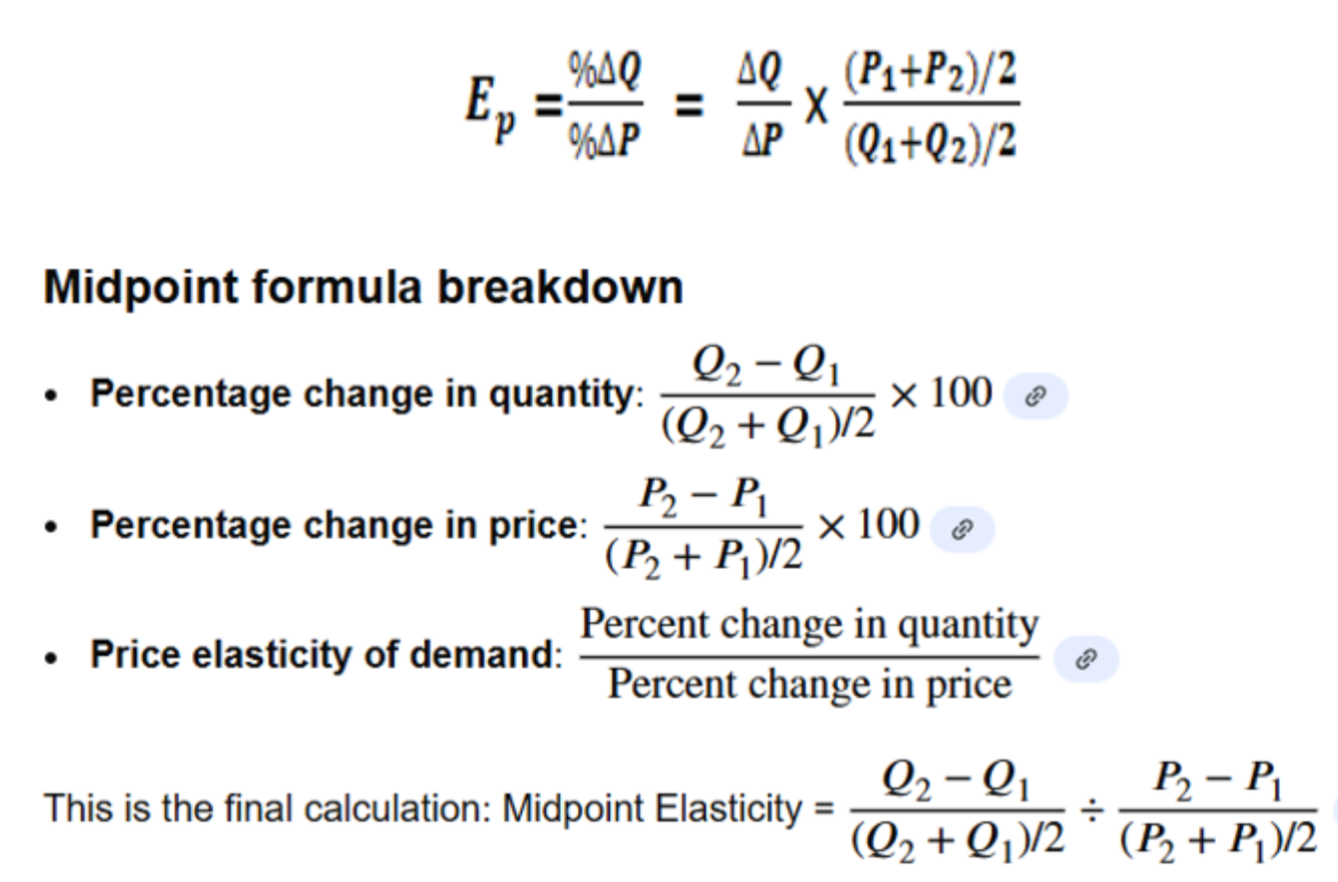
Elastic when the percentage change in price resulted in a larger percentage change in quantity demanded or supplied (responsive)
Inelastic when the percentage change in price resulted in a smaller percentage change in quantity demanded or supplied
Unit Elastic when the percentage change in price resulted in an equal percentage change in quantity demanded or supplied
Perfectly elastic when a small change in price might cause the consumers or producers to be highly responsive
Perfectly inelastic means consumers and producers are not responsive at all to any price changes
Income Elasticity
Income elasticity of Demand is the percentage change in quantity demanded caused by a 1 percent change in income. Y = income
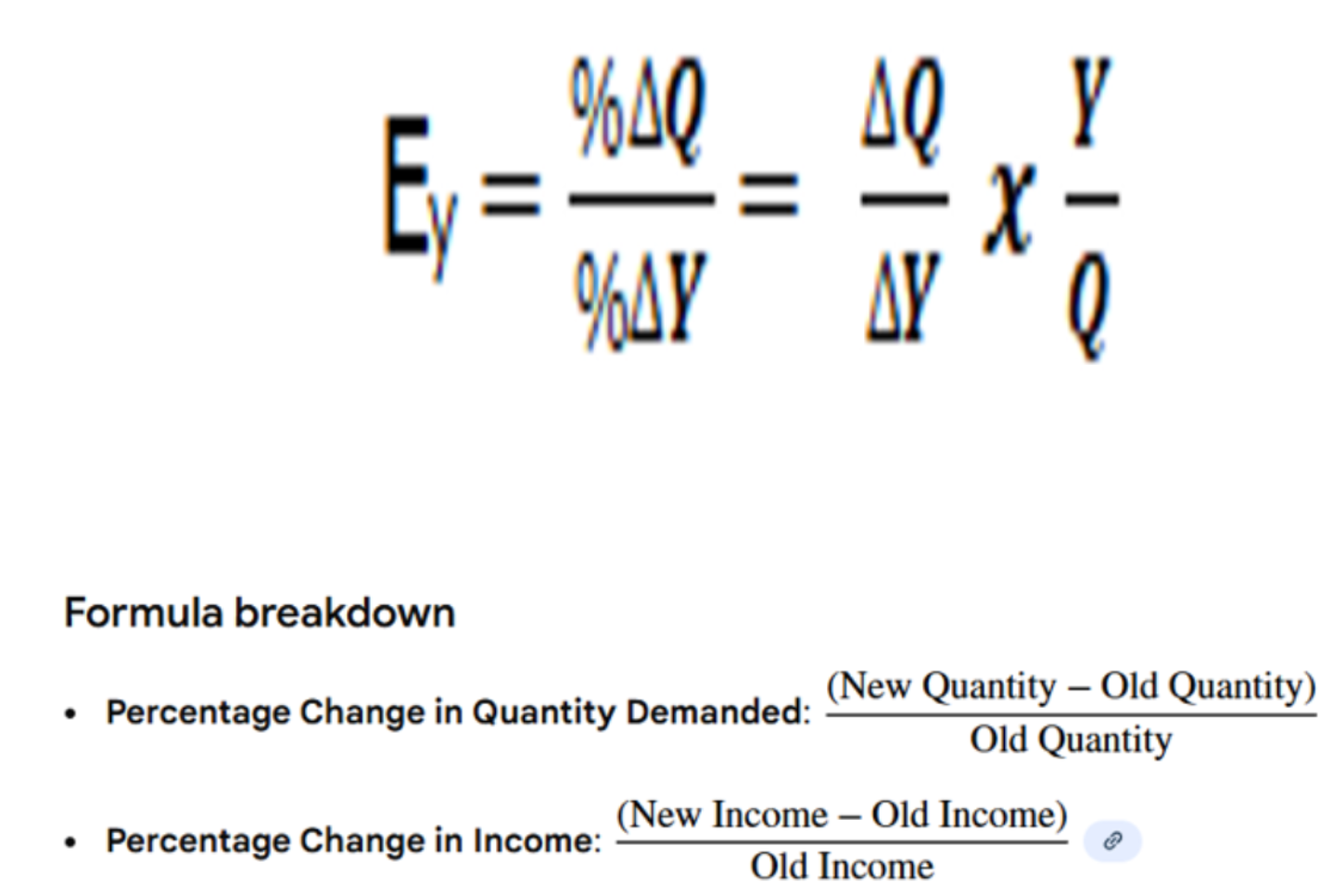
Income-Elastic: positive income elasticity (normal good - luxury)
Ey > 1
(%) Quantity demanded > (%) Income
Income-Inelastic: positive income elasticity (normal good - necessity)
0 < Ey < 1
(%) Quantity demanded < (%) Income
Negative Income Elasticity: inferior good
Ey < 0
When quantity demanded decreases as income increases
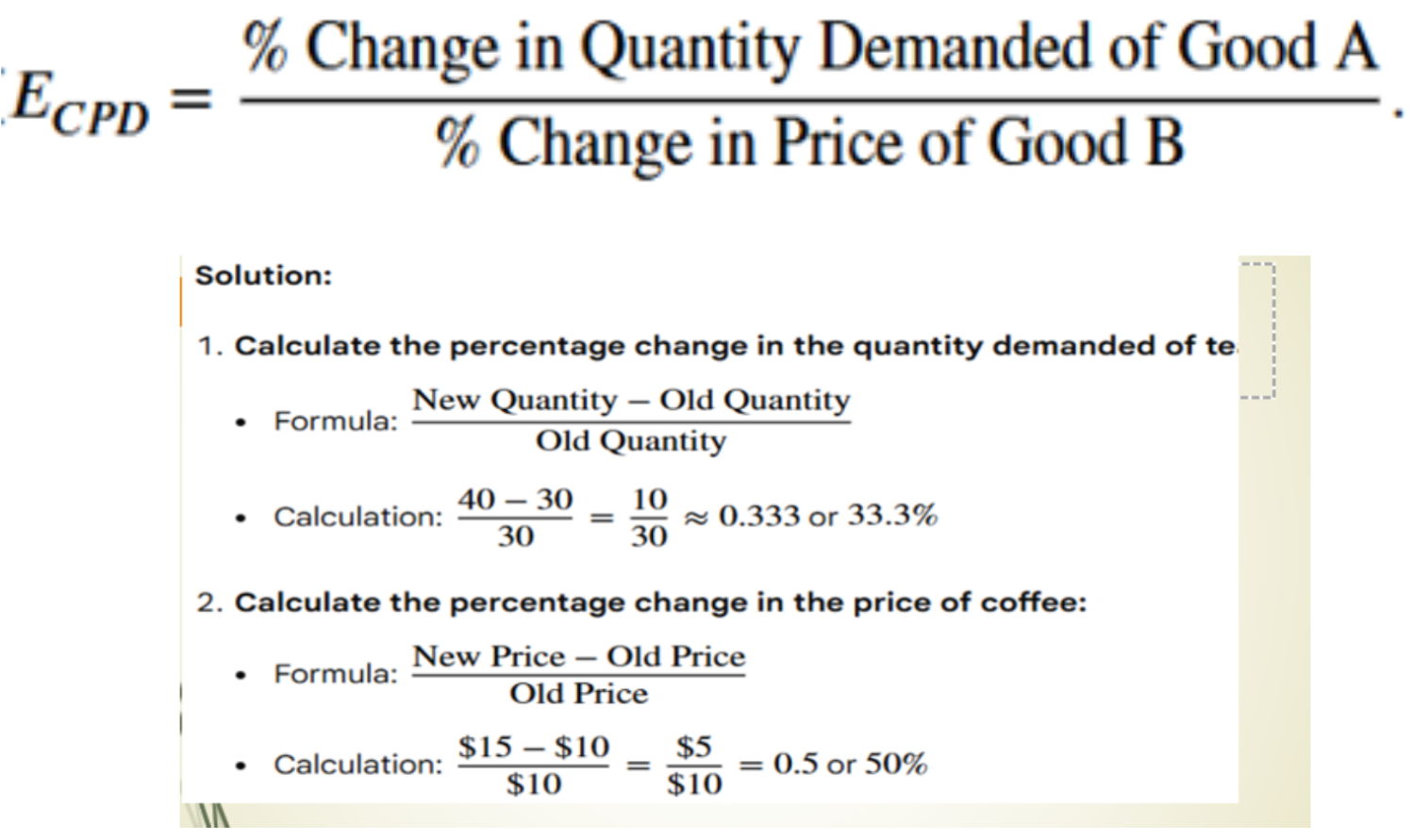
Cross Elasticity
Cross Elasticity of demand shows the percentage change in the quantity demanded of one good when the price of another good changes
Substitutes (+) A price increase in one leads to a rise in demand for the other
Exy > 0
Complements (-) A price increase in one leads to a decrease in demand for the other
Exy < 0
Non-related: A change in the price of one does not affect the demand for the other
Exy = 0
Elasticity of Supply
Price elasticity of supply is the measure of the responsiveness of the quantity supplied of a good to changes in price
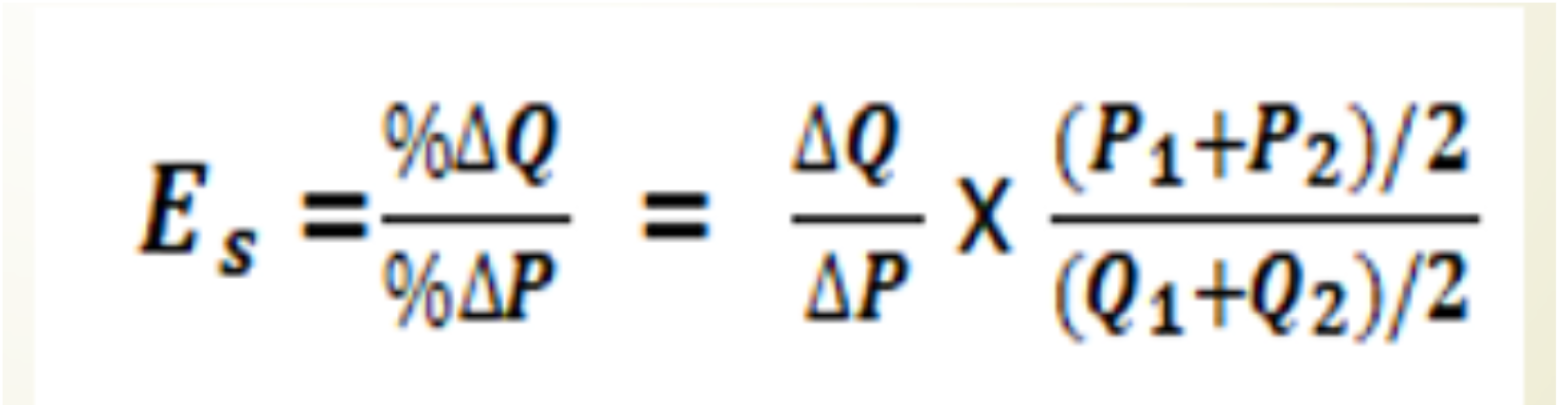
Perfectly Inelastic Supply
Es = 0 (absolutely unresponsive)
Unique Goods that have no substitutes or alternatives
Inelastic Supply: the producers limit their production even if the price increases
The percentage change in price is insignificant
0 < Es < 1
(%) Quantity demanded < (%) Price
Unit Elastic
Es = 1
Elastic Supply: There is an increase in output produced, even if the cost incurred by the entrepreneur in making the good increases
There is a considerable increase in the price of goods being sold
Es > 1
(%) Quantity demanded > (%) Price
Perfectly Elastic Supply
Es = ∞
Determinants of the Price Elasticity of Supply
Length of Time: the shorter the time period, the more inelastic the supply for a product, because it is harder to get additional inputs to increase production. Inversely, a longer time period results in an elastic supply
Production Capacity:
A flexible production capacity is more elastic
An inflexible production capacity is more inelastic