sodium potassium pump
- solute pump
- amino acids, some sugars, and ions are transported by solute pumps
- ATP energizes protein carriers, and in most cases, moves substances against concentration gradients
- coupled systems: more than one substance
- symport: both moved in the same direction
- antiport: moved in opposite directions
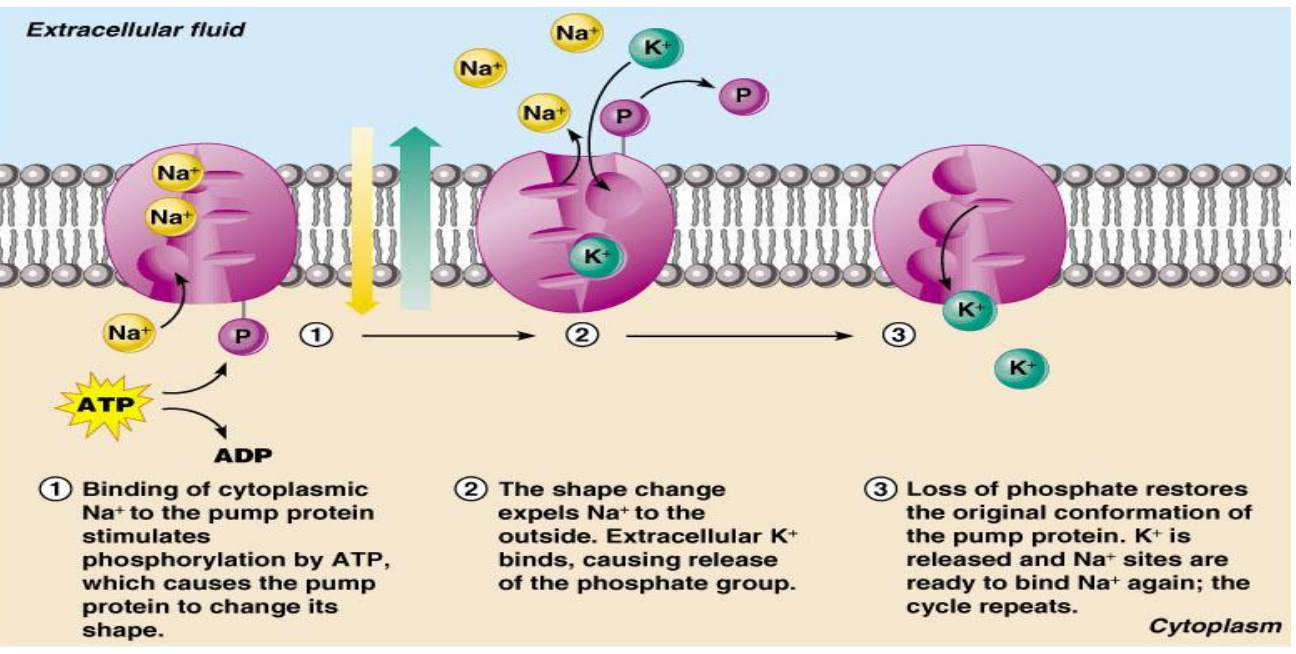
- one of the most important solute pumps is the Na+/K+ pump (sodium potassium pump)
- it is an antiport
- sodium potassium pump
- Na+ and K+ are necessary for water balance of all cells
- important for normal function of muscle and nerve cells
- the pump has an order of operation
- primary active transport: where energy is provided by the hydrolysis of ATP
- secondary active transport/co-transport: which is driven indirectly by passive ion gradient created by the operation of the primary transport
- primary active transport : Na+-K+ pump
- K+ needs 10-20 times higher on the inside of the cell as compared to the outside
- Na+ needs to be 10-20 higher on the outside of the cell as compared to the inside
- each ion will slowly leak passively across the membrane due to their concentration gradients
- thus, the pump is needed to maintain their concentration differences driving Na+ out of K+ into the cell
- because they are being moved against their concentration gradients, it will require the use of ATP
- thus, Na+-K+ ATPase is an enzyme within the pump protein that hydrolyzes ATP to get the energy to operate the pump
- secondary active transport: co-transport
- occurs as a result of the gradient created by primary active transport step out of the pump
- Na+ will leak back into the cell by facilitated diffusion, other substances (amino acids, glucose, ions) get dragged along with it
- they make use of their electrochemical gradient PE stored up across the membrane
- they can even move against their own concentration gradients
- why the Na/K pump is super cool
- it creates a polarized cell membrane: one side is net positive, the other side is net negative
- the polarized membranes established a resting membrane potential
- this is PE created by ion concentration and distribution of net charge
- it establishes an electrochemical gradient: an electrochemical potential for an ion
- made of 2 parts
- chemical PE: the PE due to a difference in chemical concentration
- electrical PE: the electrochemical energy built up because of the uneven distribution of the positive charges
- this gradient allows for some substances to move against their concentration gradients without the use of ATP