Computer Science Cheat Sheet
hey all, notes in order of the exam spec (the syllabus), nothing extra, concise and handy, covers key definitions of ALL topics, including some helpful formulas. Good Luck :))
Topic 1: Fundamentals of Algorithms
What is an ==algorithm==? :: set of instructions used to solve a problem or complete a task
What is ==decomposition==? :: breaking larger problems into smaller, sub-problems so that each accomplish an identifiable task, which might itself be further subdivided
What is ==abstraction==? :: Abstraction is the process of removing unnecessary detail from a problem
Topic 2: Fundamentals of Data Representation
@@Data structure@@ :: way of storing and organizing a set of data, that can easily be edited/changed @@Subroutine@@ :: named block of code which can be run by calling its name in a program
@@Function@@ :: a procedure which has a return value Parameter – input variable for a subroutine @@Assembler@@ :: converts assembly language (low level) into machine code
@@Interpreter@@ :: converts high level programming into machine code (line by line)
@@Compiler@@ :: converts high level programming into machine code (whole program at once)
@@Scope@@ :: which part of a program can see variables/constants/data structures
here’s a neat little comparison table between assembler, interpreter and compiler:
| Feature | Interpreter | Compiler | Assembler |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input | A High-Level Language | A High-Level Language | Assembly Language (Low Level) |
| Output | No output, program runs straight away | Machine Code | Machine code |
| How it works | Translates source code and immediately runs it | Compiles source code so it can be run later | Assemble source code so it can be run later |
| Speed of execution | Slow as it needs to be translated each time it is run | Fast, as CPU runs the machine code | Fast, as the CPU runs the machine code |
| What users need to run program | End users need the interpreter and the program | Users need just the compiled program | Users need just the compiled program |
| Source Code | End users can see the source code | End users cannot see the source code | End users cannot see the source code |
Bit :: one unit of data
Character set :: defined list of characters recognized by computer’s hardware and software
Pixel :: single dot of colour in an image
Bitmap :: graphical image made up of pixels
Pixel resolution :: number of pixels in an image
Colour depth :: bits used per pixel
Sample :: measure of amplitude at a point in time
Sampling rate :: number of samples taken per second
Sample resolution :: number of bits used per sample
here are the important formulas for this topic:
File size of image (in bits) = width (pixels) x height (pixels) x colour depth (bits)
think of this one as a formula triangle, with file size at the top, and the three others below
File size of sound (bits) = sample rate (Hz) x time (sec) x sample resolution (bits)
again, file size is the top of the triangle, with the three others below
Topic 4: Computer Systems
%%Computer system%% :: combination of hardware and software used to perform tasks
%%Hardware%% :: physical part of a computer
%%Software%% :: programs that are downloaded/installed onto a computer
%%System software%% :: programs which help run and maintain a computer system
%%Application software%% :: programs which help the user perform day to day tasks
%%Operating system%% :: platform for hardware to use the software
%%Volatile memory%% :: temporary storage that is lost when power turns OFF (RAM)
%%Non-volatile memory%% :: permanent storage that is kept when the power turns OFF (ROM, HDD)
%%Cloud storage%% :: secondary storage, at a remote location which is accessible via the internet
%%Embedded System%% :: computer system with a specific purpose, built into another system/machine
%%RAM%% :: stores running applications while the computer is ON
%%ROM%% :: stores the BIOS (instructions needed to turn on the computer and cannot be edited) %%Cache%% :: stores the most frequently accessed instructions from the RAM (Level 1, Level 2, L3)
here is the memory pyramid
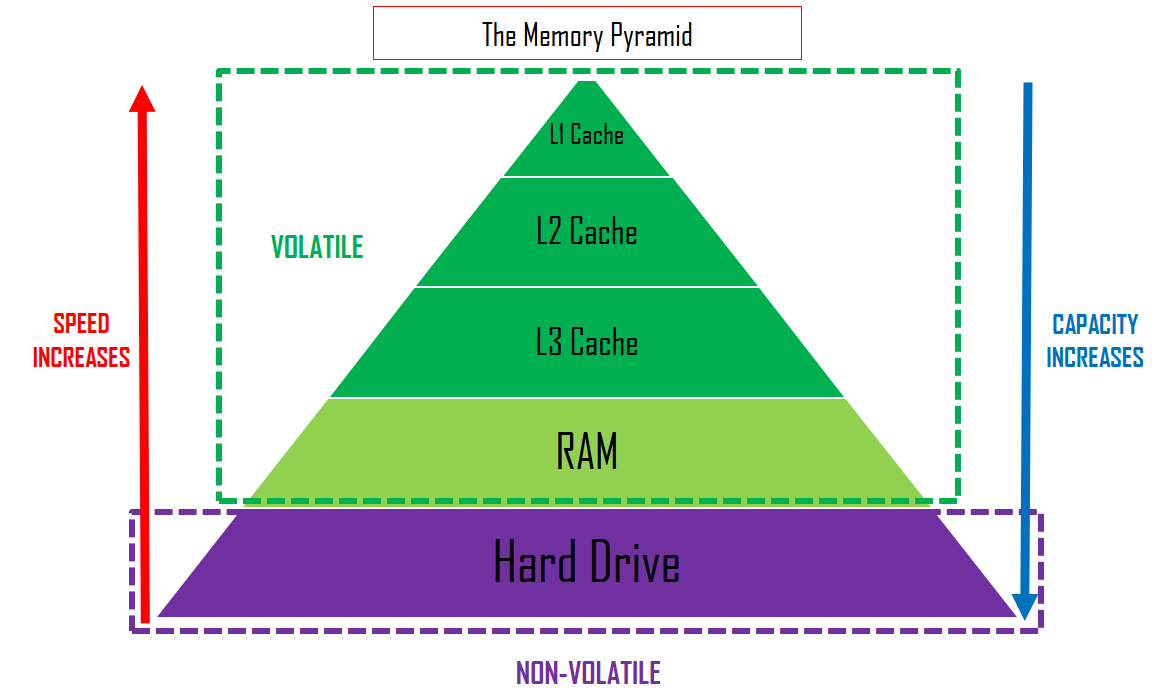 Level 1 cache is used around 50% of the time, Level 2 90%, so its no doubt that cache makes a big difference in the computer’s performance speed, as it is fast access memory location that is quicker to access than RAM and slower than registers.
Level 1 cache is used around 50% of the time, Level 2 90%, so its no doubt that cache makes a big difference in the computer’s performance speed, as it is fast access memory location that is quicker to access than RAM and slower than registers.
Topic 5: Computer Networks
==Computer Network== :: a group of computers connected together to share resources
==Network Protocol== :: a set of rules which allow devices to communicate
==Network Security== :: methods which protect networks from unauthorised access and harm
==Authentication== :: verifying the user’s identity when accessing data/network, to prevent unauthorised access
==Firewall== :: protects network from unauthorised access by controlling incoming/outgoing network connections
==Encryption== :: scrambling data to change how it looks to prevent unauthorised access (only people with decryption key can access original)
Topic 6: Cyber Security
^^Cyber security^^ :: methods which prevent data/programs from Attack, Damage and Unauthorised access
^^Penetration Testing^^ :: testing the security of a system/network to find any vulnerabilities.
^^Black-box testing^^ :: stimulates external hacking or cyber warfare attack
^^White-box testing^^ :: stimulates malicious insider (spy) who knows something about the target system
^^Social engineering^^ :: art of manipulating people to give up personal information/details ^^Malware^^ :: malicious software/code