24. Regulation of Kidney Function
Glomerular filtration rate is maintained within a tight range, primarily accomplished by dilation of the afferent (incoming) arteriole
distal convoluted tubule is tucked right in by the incoming anf outcoming tubules
if dilation of afferent arteriole does not increase GFR, the kidney releases renin into the blood
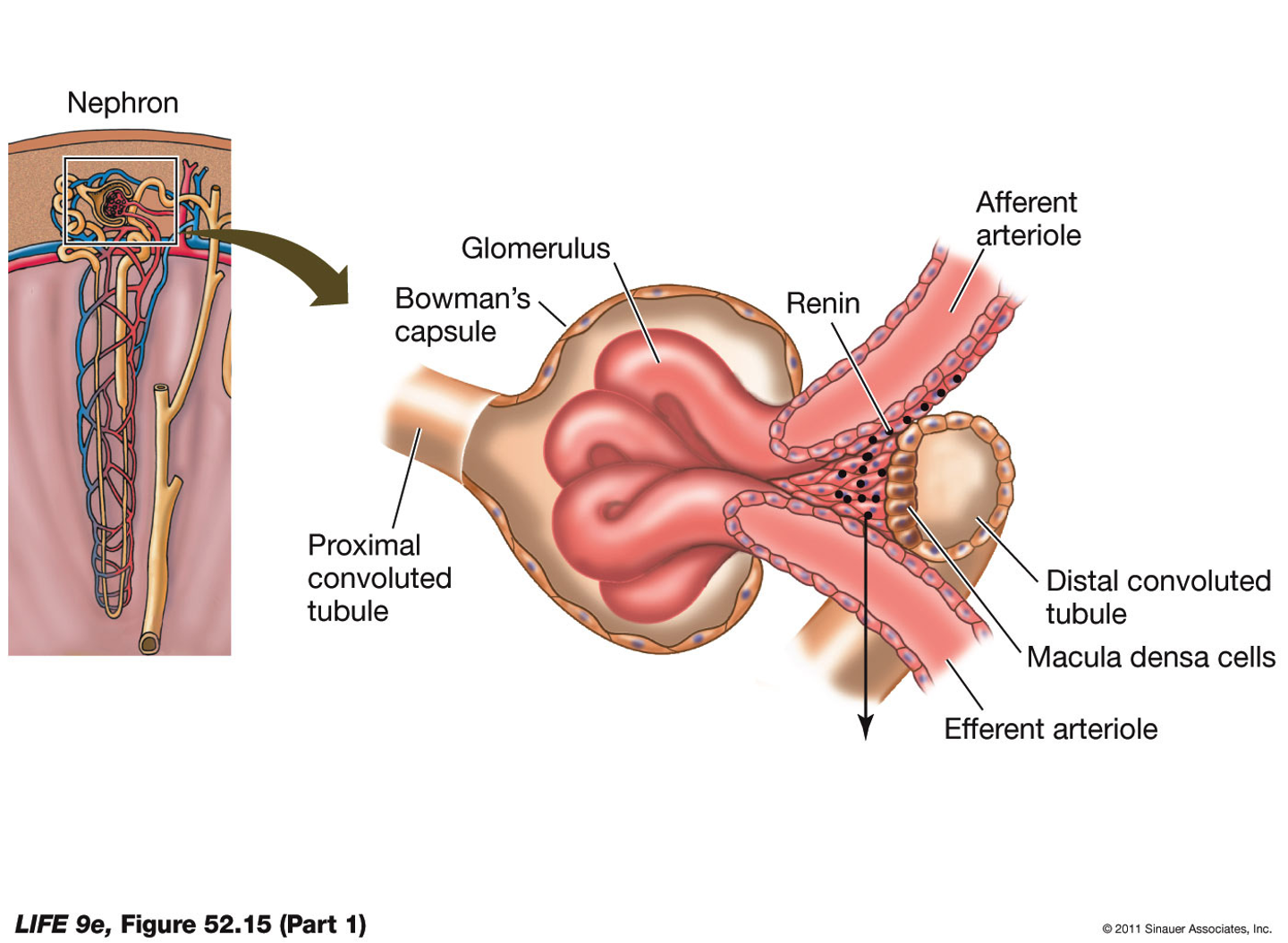
cause more vasodilation of aferent arteriole, whcih forces more blood across glumerulus into bowmans capsule, low NaCL = large blood volume
causes renin release from adjacent cells, low NaCl stimulates to dump renin into the blood
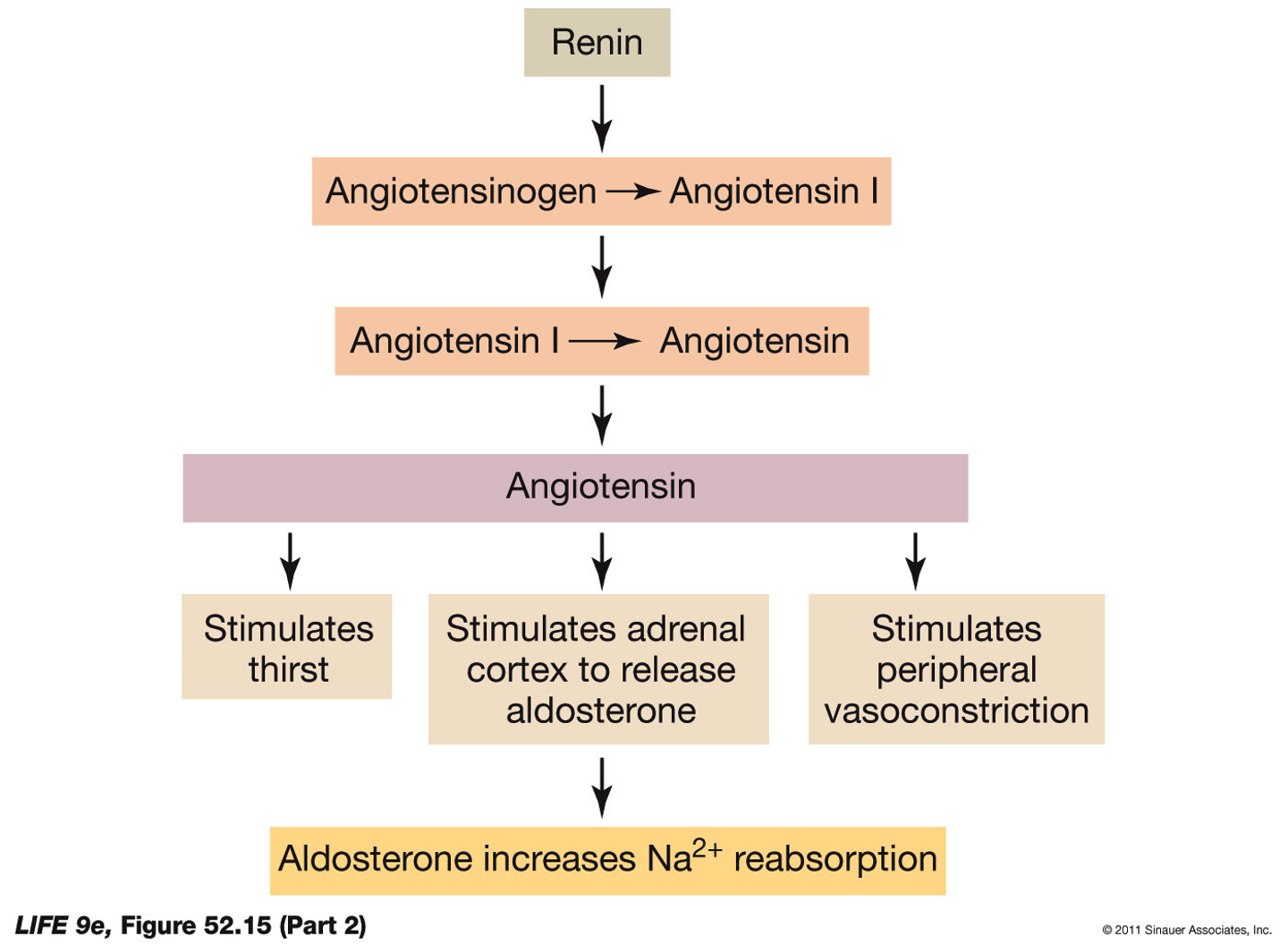
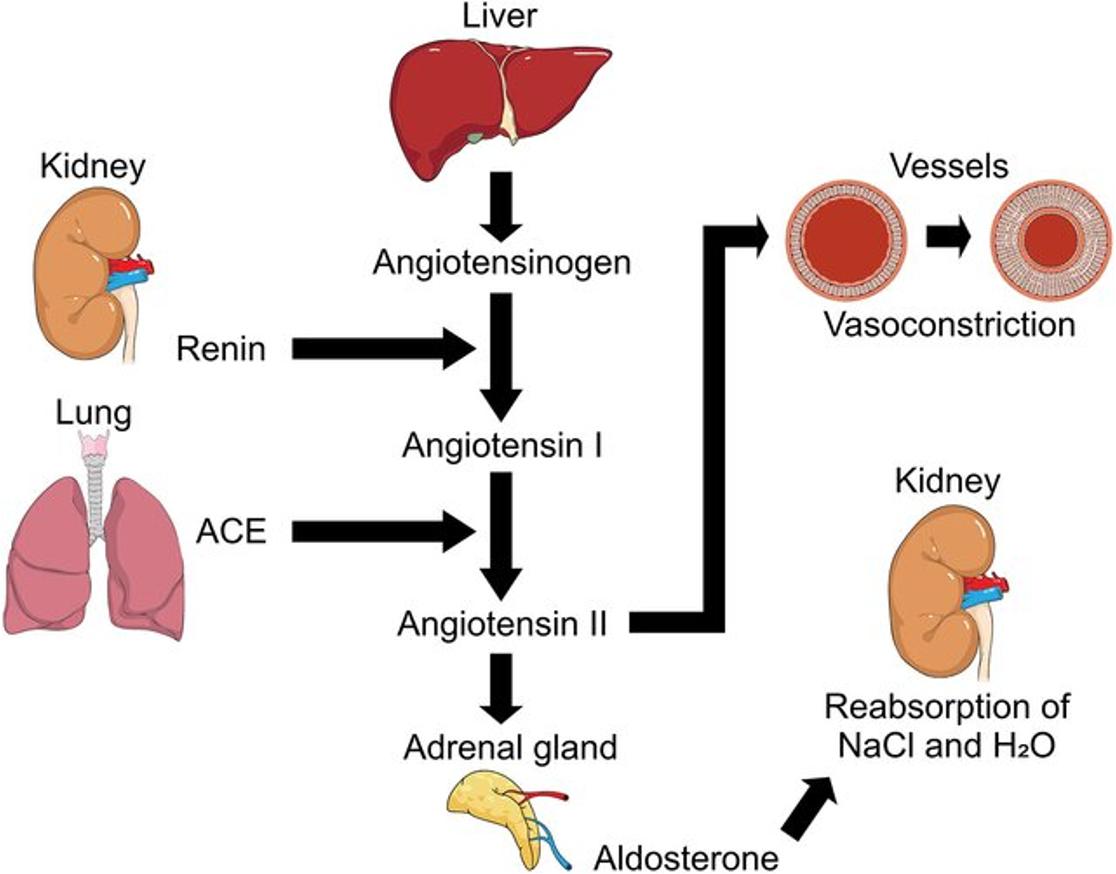
RENIN
major role in cascade of a compound called angiotensin
angiotensin- hormone
stimulates thirst
stimulates
stimulates peripheral vasoconstriction (not critical body parts)
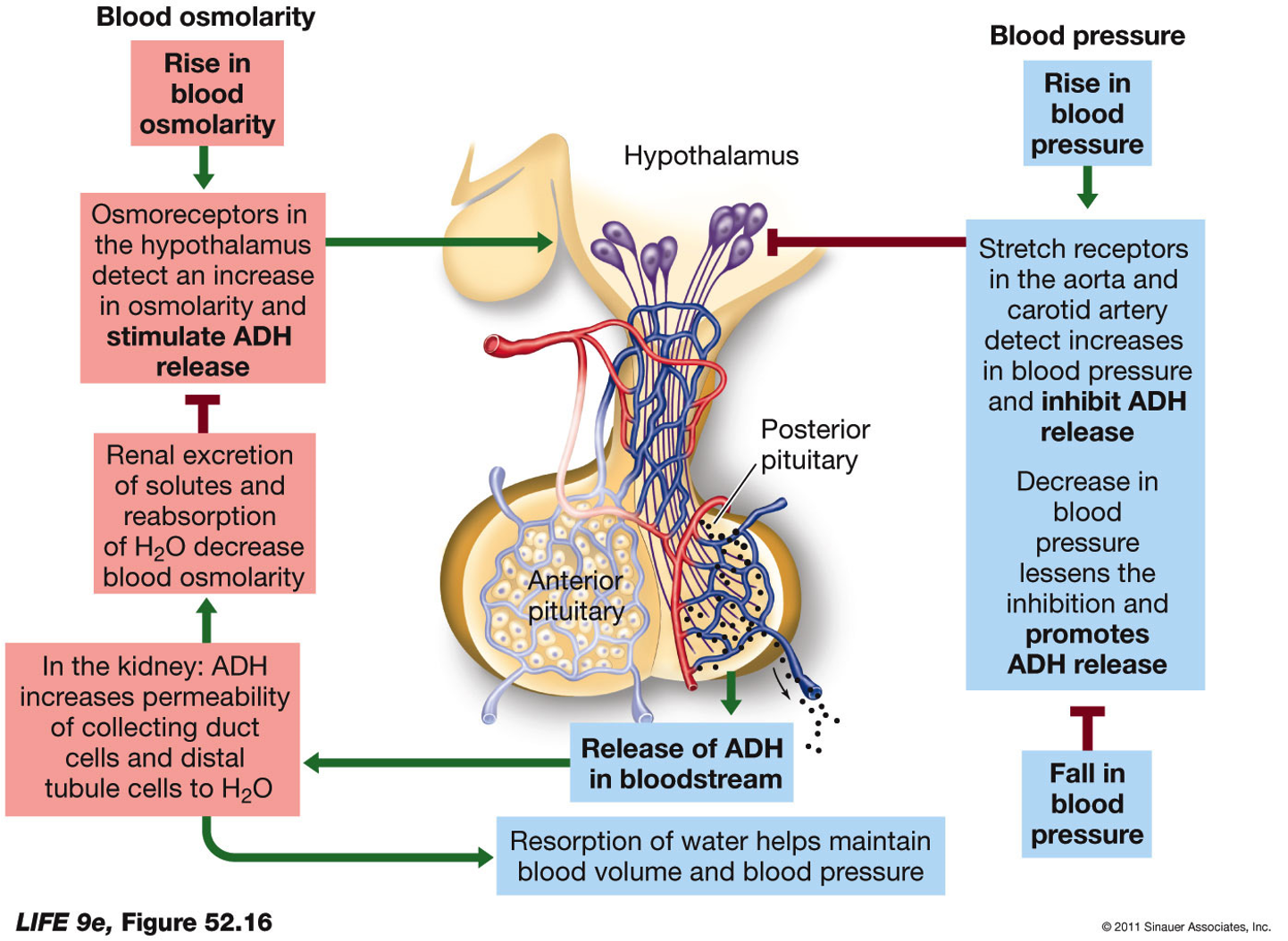
Regulation of blood osmolarity involves the kidney too!
rise in blood osmolarity is detected by osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus (detects ions in blood)
this then results in a signal to the pituitary to release anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) into blood
ADH then travels to the kidneys where it can cause insertion of aquaporins in the walls of the collecting duct
How does ADH increase H2O permeability in collecting duct?
insertion of channels (called aquaporins) allow H2O molecules through
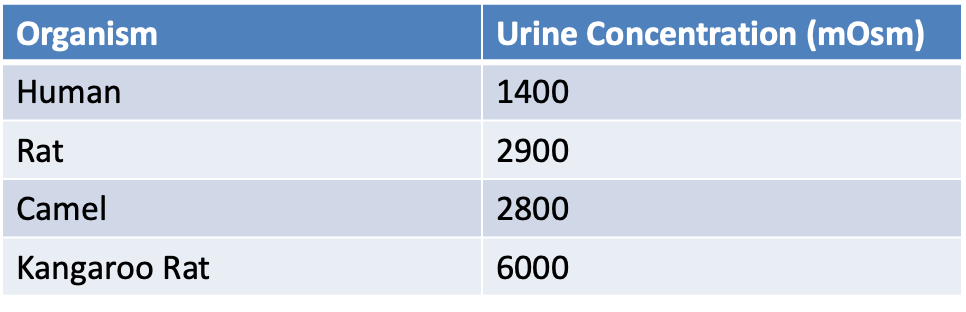
How can the kangaroo rat survive without drinking water?
countercurrent multiplier in the loop of henle
the loop of henle is extremely long
carry seeds to their burrows where they absorb moisture from surrounding soil
Organism
Urine Concentration (mOsm)
Human
1400
Rat
2900
Camel
2800
Kangaroo Rat
6000