Blood Pressure and Circulatory system flashcards
Pulmonary and Systemic Pressures
Pulmonary Artery Pressure (PAP):
The pressure within the pulmonary arteries.
Blood Pressure (BP):
The arterial pressure exerted by the blood on the walls of the systemic circulatory system.
Left Heart and Systemic Circulation
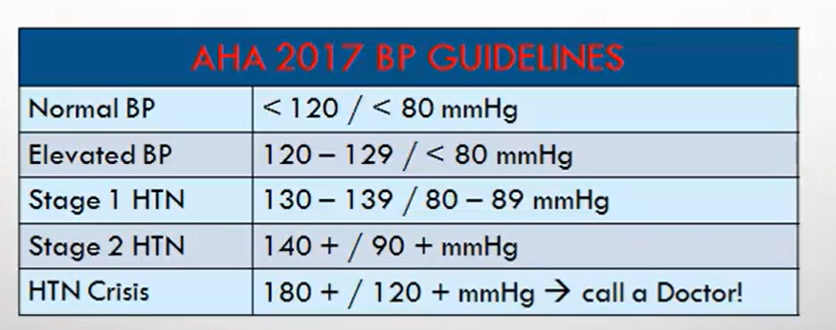
Guidelines from the American Heart Association (AHA) in 2017.
Left Heart Association:
Associated with the systemic circulatory system.
High pressure, high resistance system.
High oxygenation with an O_2 saturation rate of approximately 98%.
Left Heart Function:
Receives oxygenated (arterial/red) blood from the pulmonary circulatory system.
Pumps oxygenated blood to the systemic circulatory system.
Oxygenated Blood and Systemic Circulation
Oxygenated Blood:
Rich in oxygen.
Delivered to all tissues in the body via the arterial system.
Deoxygenated Blood:
Returns to the right heart after oxygen is utilized by the tissues.
The cycle then repeats.
Blood Pressure (BP) Explained
Blood Pressure Definition:
Arterial pressure exerted by the blood on the walls of the systemic circulatory system.
Measurement:
Manually with a BP cuff and stethoscope.
Automatically with an automatic BP cuff and monitor.
Systolic BP:
The upper number.
Pressure when the heart is contracted.
Diastolic BP:
The lower number.
Pressure when the heart is relaxed.
BP Reading:
Systolic BP and Diastolic BP are read as a fraction (e.g., 114/72 mmHg).
Example: \frac{114}{72} mmHg (millimeters of mercury) indicates the pressure during heart contraction (systolic) over the pressure during heart relaxation (diastolic), providing crucial insights into cardiovascular health.
American Heart Association (AHA) Blood Pressure Guidelines
Equipment for Acquiring BP
BP cuff
Stethoscope
Automatic BP monitor with cuff
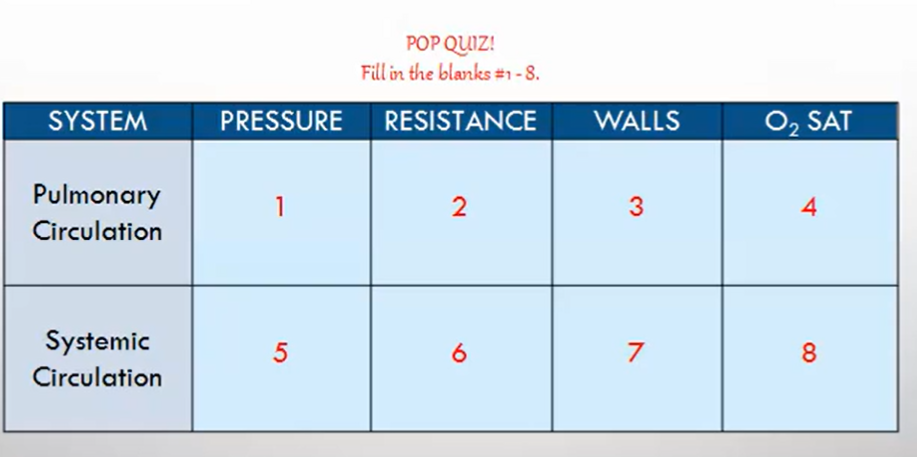
Pulmonary vs. Systemic Circulation Quiz
Pulmonary Circulation:
Pressure: Low 1
Resistance: Low 2
Vessel Walls: Thin 3
O_2 Saturation Rate: 75% 4
Systemic Circulation:
Pressure: High 5
Resistance: High 6
Vessel Walls: Thick 7
O_2 Saturation: Approximately 98% 8