Ch 4 - Elasticity Of Demand
Price elasticity of demand: measure of the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a price change. if a price is elastic, it is very responsive, if it is inelastic, it’s not responsive
Key words:
Ed = elasticity of demand
Qd = quantity of demand
P = price
%△ = percentage change
Ed = %△Qd / %△P
Steps:
% change in Qd : New quantity - old quantity * 100 Old quantity
% change in price : New price - Old price * 100Old price
%△Qd / %△P
Ignore negative sign
If the answer is:
Between 0 and 1: price inelastic demand
1: unitary price elastic demand
Above 1: price elastic demand
Inelastic demand curve:
When a product’s PED is inelastic and the price falls, the firm will face loss in revenue

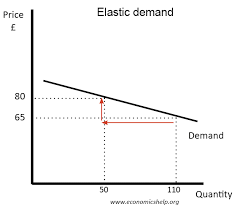
Elastic demand curve:
When the selling price of a product that has an elastic PED is decreased, the revenue increases (they sell more)
Perfectly elastic demand curve:
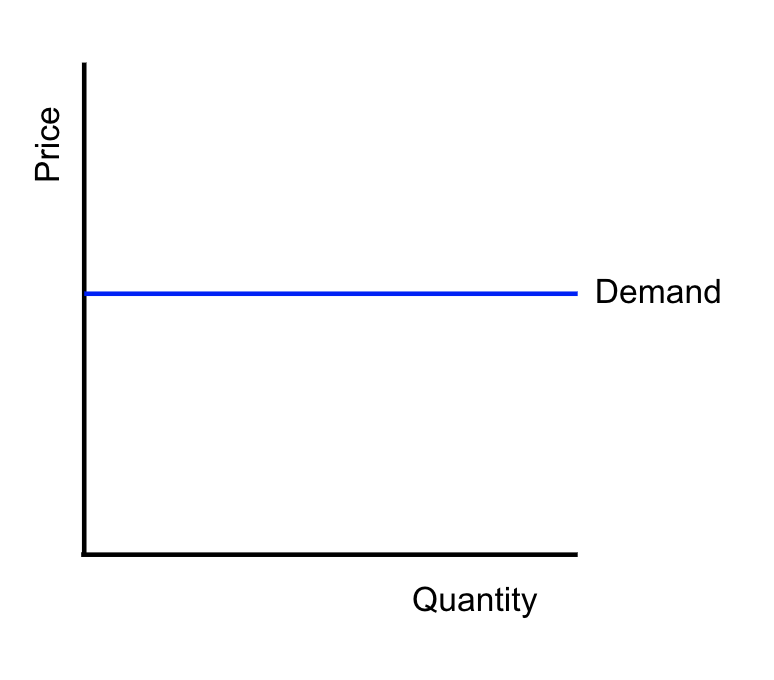
The PED (price of elasticity of demand) will reduce as the price falls
Demand becomes less elastic
Determinants of PED:
Availability of substitutes (too many choices)
Time
Luxury
Proportion of income is spent on a good
Income elasticity of demand: measures the extent to which the quantity demanded of a product is affected by an income
IED = %△Qd / %△ in income
For most normal accounts:
Rise in consumer income = rise in demand
Fall in consumer income = fall in demand
Normal goods = positive YED
Normal necessities = income inelastic
Normal luxuries = income elastic
Inferior goods: as income rises, demand falls (consumers look for more affordable substitutes)
Has negative IED, less than zero
Normal goods YED > 0:
Increased income = higher demand
Positive elasticity
Luxury goods YED > 1:
Increased income
Bigger % increase in demand
Inferior goods YED < 0:
Increase income leads to fall in demand
Negative elasticity
Unitary IED: perfectly proportional, Ey = 1
Zero income IED: consumer’s income doesn’t affect demand on product, Ey = 0
An Engel curve shows the relationship between demand for a good (x-axis) and income level (y-axis)
Positive slope: normal good
Negative slope: inferior good
PES price elasticity of supply: a measure of how much the quantity supplied of a product changes when there's a change in its price
PES = %△ quantity supplied of the product / %△in price of the product
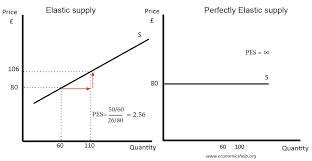

More time being considered = increased elasticity of a product
If total costs rise, supply will not be raised
Cross elasticity of demand (XED): measure of how much the demand of a product changes when there's a change in the price of another product
XED = %△in quantity demanded of X / %△ in price of product Y
If value of XED = positive, goods are substitutes for each other
If value of XED = negative, goods are complements of each other
If value of XED = 0, goods are unrelated
 Knowt
Knowt
