Week 1 Pulse-Echo Technique
Diagnostic Ultrasound
Uses the Pulse-echo technique:
Transducer sends ultrasound pulses into the body.
Pulses interact with tissues/interfaces.
Echoes return to the transducer and generate B-mode (grey scale) ultrasound images.
Pulse-echo Principle
Analogous to Echolocation:
Calculate distance between the transducer and tissues/interfaces using the speed of sound.
Based on the round-trip time of the echo.
\text{Velocity} (\nu) = \frac{d \times 2}{t}Where:
d = distance to tissue/interface
t = time taken for the echo to return.
Factors Affecting Echolocation
Key dependencies include:
Speed of sound in tissue
Time of travel of sound
Direction of sound propagation
Scan Lines in Imaging
Sonographic images consist of scan lines:
More scan lines lead to improved image quality.
Real-time imaging requires many frames per second for effective visualization.
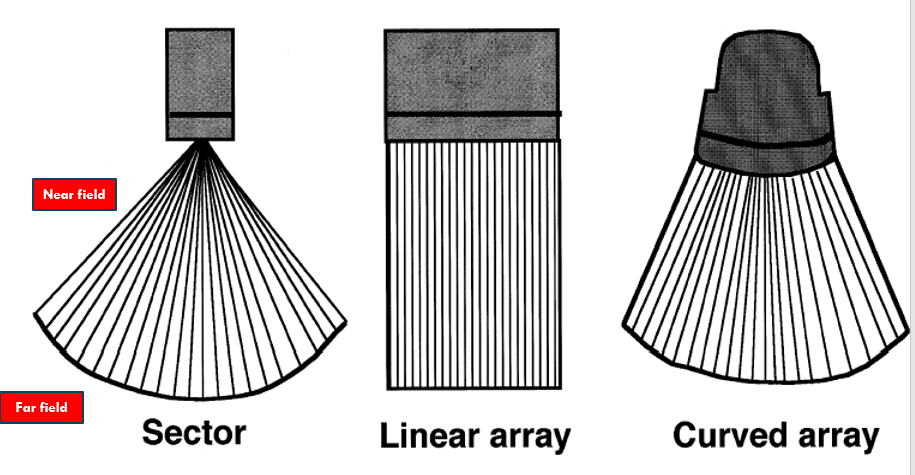
Types of Imaging Formats
Basic transducer formats include:
Linear array - broad near and far field image; not good for viewing large areas
Curved array - larger near field and an even larger far field
Sector format - small near field but larger far field
Modes of Imaging
B-mode ultrasound
Displays 2D images, providing a gray-scale representation of tissue.
M-mode ultrasound
Uses a single beam path, particularly useful for cardiac and fetal imaging.
3D imaging
Provides volumetric representations of structures.
Doppler Imaging Types
Doppler Ultrasound is used for measuring the flow of blood:
Pulsed Wave (PW) Doppler
Types:
PW Spectral Doppler
PW Colour Doppler
PW Power Doppler
Continuous Wave (CW) Doppler
Used to demonstrate continuous flow information.
PW Colour Doppler
Color displays provide valuable information:
Indicate the direction and velocity of blood flow.
PW Power Doppler (CPD)
Information is based on the amplitude/strength of blood cell motion:
Superimposed over a 2D image.
Does not indicate direction of flow but is sensitive to slow flows.
PW Spectral Doppler
Demonstrates waveforms of different flow types:
differentiates between arterial and venous waveforms, indicating flow direction (forward/reverse).
Conclusion
Enhanced understanding of ultrasound technology and its various applications can significantly improve diagnostic capabilities in clinical practice.
Special acknowledgment to Dr. Michelle Fenech for contributions to the content.