Note
0.0(0)
Explore Top Notes Note
Note Studied by 500 people
Studied by 500 people Note
Note Studied by 15 people
Studied by 15 people Note
Note Studied by 16 people
Studied by 16 people Note
Note Studied by 11 people
Studied by 11 people Note
Note Studied by 15 people
Studied by 15 people Note
Note Studied by 6 people
Studied by 6 people
AP World 5.2 - Atlantic Developments
5.0(7)
SCIENCE TEST ;DD
5.0(1)
Chapter 35-40 Notes
5.0(1)
Chemistry Honors: Final Review
5.0(1)
taalnormen vs taalgebruik
5.0(1)
Hunters in the Snow
5.0(1)
DNA Replication Assessment 2-2-23
Helicase unwinds the double helix and seperate the two strands by breaking ==HYDROGEN BONDS==
DNA polymerase links nucleotides together to form a new strand using ==preexisting strand as a template.==
Helicase
- separates two (2) polynucleotide strands
- ==breaking hydrogen bonds==
- that exist between complementary base pairs
- the two (2) separated polynucleotide strands act as templates
- for synthesis of ==new complementary strands==
DNA Polymerase
- synthesis new strands from (2) parental strands
- free DN triphosphates align ==opposite their complementary base partner==
- leaves (2) excess phosphates
- ==uses the energy released to link the nucleotide to new strand==
(1) UNWINDING →the DNA strand is unwound to allow replication to occur
- coiled DNA uncoils creating ==SWIVEL POINT==
- Enzymes are involved in this indication phase
- unwinding and unzipping
- stabilizing strands so copying can occur
(2) ELONGATION → new DNA strands are made using original strands as template
- unwind DNA ==(parent strands)==
- new DNA is formed by adding ==FREE NUCLEOTIDES==
- the new strand is called the daughter strands
(3)TERMINATION →DNA synthesis is completed and ea. new DNA molecule goes back to its double helix structure
- when DNA synthesis is completed
- (2) new strands coil into the helix as CHROMOSOME
Leading Strand
→ enzymes can build strands in 5’ to 3’ direction
==→ leading strand is synthesized as one continuous strand==
Lagging Strand
==→ constructed in fragments==
→ later joined together (Okazaki fragments)
Enzymes 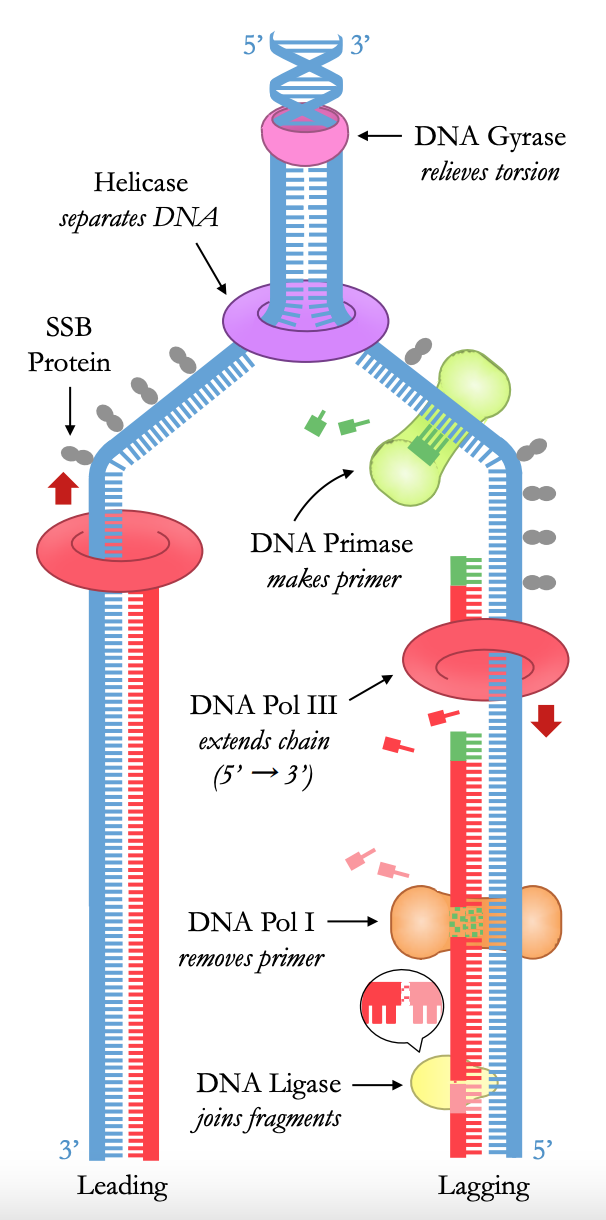
Helicase
separates DNA to form ==replication fork==
- breaks HYDROGEN BOND between comp. base pais
DNA gyrase
reduces torsional strain created by helicase
- prevents DNA from ==supercoiling==
DNA Primase
- short RNA primer on each strand
- provide indication point for polymerase III
DNA Polymerase III
- Free nucleotides (dNTPs) line up opposite complementary bases
- DNA polymerase III covalently joins free nucleotides together
Okasaki fragments
- DNA strands anti-parallel (5’ → 3’)
- synthesis is continuous on ==LEADING STRAND==
DNA polymerase I
- removes RNA primers and replaces them w/ DNA
DNA Ligase
- covalently joins okasaki fragments
Note
0.0(0)
Explore Top Notes Note
Note Studied by 500 people
Studied by 500 people Note
Note Studied by 15 people
Studied by 15 people Note
Note Studied by 16 people
Studied by 16 people Note
Note Studied by 11 people
Studied by 11 people Note
Note Studied by 15 people
Studied by 15 people Note
Note Studied by 6 people
Studied by 6 people
AP World 5.2 - Atlantic Developments
5.0(7)
SCIENCE TEST ;DD
5.0(1)
Chapter 35-40 Notes
5.0(1)
Chemistry Honors: Final Review
5.0(1)
taalnormen vs taalgebruik
5.0(1)
Hunters in the Snow
5.0(1)