Year 8 Geography Study Notes
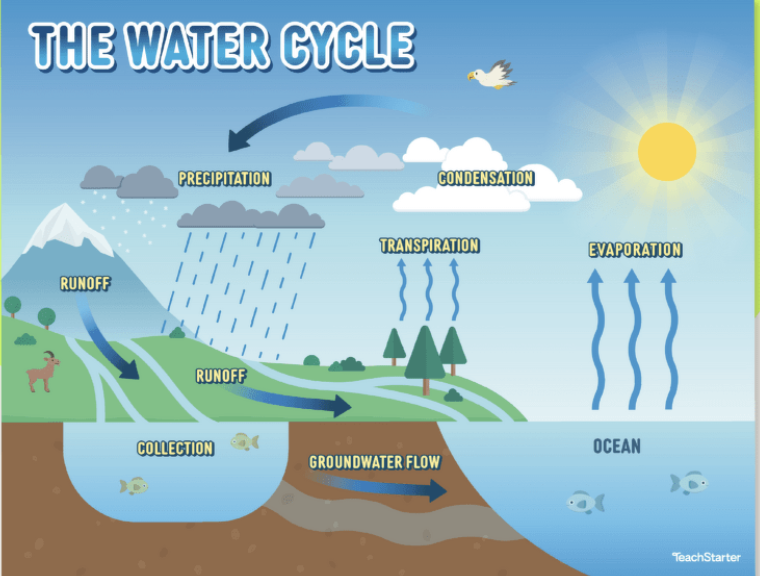
Processes:
Evaporation: Water turns into vapor due to heat.
Condensation: Water vapor cools and forms clouds.
Precipitation: Water falls back to Earth as rain, snow, hail or sleet.
Infiltration: Water seeps into the ground.
Runoff: Flows downward until reaching rivers, lakes, or oceans.
These processes are important because they regulate climate, support ecosystems, and provide drinking water.
2. Types of Water Bodies
Freshwater: Found in Rivers, lakes, groundwater and glaciers. It is only 3% of Earth's water, 2% of it is locked in ice caps or aquifers.
Saltwater: Found in oceans and seas, makes up the remaining 97% of Earth’s water.
Importance of Freshwater: Drinking, agriculture, sanitation.
Importance of Saltwater: Crucial for regulating Earth's climate, supporting marine ecosystems, and providing livelihoods through fishing and tourism.
3. Global Water Distribution
Statistics: 97% saltwater, 3% freshwater (2% is frozen).
Access to Water: Disparities in water access around the world.
Physical Scarcity: Lack of sufficient water resources.
Economic Scarcity: Lack of investment in water infrastructure. Causes include overuse, climate change, pollution, and population growth.
4. Water Management
Issues: Pollution, overuse, water scarcity.
Solutions: Conservation, sustainable practices, technology.
Sustainable Water Use: Methods to manage water resources effectively.
Conservation: Reducing water waste.
Recycling: Treating wastewater for reuse.
Desalination: Turning saltwater into freshwater.
6. Case Study: Murray-Darling Basin
Australia’s largest river system.
Used for irrigation, but also faces issues with drought and overuse.
Sustainable practices are needed to protect it from long-term damage.
My creation took long so be thankful 😇
I’m so done with highlighting, someone else finish
Interconnections
Human Interaction with Water
Uses: Domestic, agricultural, industrial.
Impacts: Pollution, habitat destruction, climate change effects.
Global Connections
Trade and Resources: Water-intensive products (e.g., cotton).
Transboundary Water Issues: Conflicts and cooperation over shared water resources.
Cultural Significance
Religious and Social: Water’s role in cultural practices and traditions.
Globalization
The increasing interconnectedness of the world due to trade, communication, transport, and cultural exchange.
Trade: The exchange of goods and services globally.
Communication: Advances in technology (e.g., the internet) that connect people.
Transportation: Air travel, shipping, and rail networks making the movement of people and goods faster.
Cultural Exchange: The spread of ideas, customs, and social behavior between countries.
Interconnected Economies
Supply Chains: How products are made from materials sourced globally.
Multinational Corporations: Companies that operate in multiple countries, connecting economies through production and jobs.
Tourism
Tourism connects people to different places.
Positive Impacts: Economic growth, employment, cultural exchange.
Negative Impacts: Environmental damage, overcrowding, cultural erosion.
Transport and Technology
Advancements in transport and technology have made the world more connected.
Transport: Airplanes, high-speed trains, and shipping have reduced travel time.
Technology: Smartphones and the internet allow instant communication.
Case Study: Global Fashion Industry
Fashion items are designed in one country, made in another, and sold worldwide.
Impacts include environmental pollution from manufacturing and the exploitation of workers in developing countries.
Skill Interpretation Study Notes
1. Map Reading Skills
Types of Maps: Topographic, thematic, political.
Scale: Understand how to interpret scale (e.g., 1:50,000).
Legend/Key: Know how to read symbols and what they represent.
2. Grid References
Understanding Grid Systems:
Latitude and Longitude: How to identify locations using these coordinates.
Map Grid References:
4-figure grid references: Identifies a square on the map.
6-figure grid references: More precise location within that square.
Example: How to find a location using a grid reference on a map.
3. Interpreting Data
Graphs and Charts: Be able to read and interpret various forms of data representation (bar graphs, pie charts, etc.).
Infographics: Analyze information presented visually to understand trends and relationships.
4. Analyzing Spatial Patterns
Identifying Features: Recognizing patterns like population density, resource distribution, or environmental changes.
Connections: Understanding how geographic features influence human activity and vice versa.
Practice Activities
Map Exercises: Use practice maps to find grid references and identify features. ( the skills booklet is full of these)
Data Interpretation: Look at sample graphs and charts, practice summarizing the information they present.
Just practice and focus on what you got wrong and keep doing it until you not only get it right but can’t get it wrong
Glossary
Murray-Darling Basin: A large geographical area in Australia that includes the Murray and Darling Rivers, crucial for agriculture and biodiversity.
Biodiversity: The variety of plant and animal life in a particular habitat, important for ecosystem health.
Water Management: The process of planning, developing, and managing water resources to meet the needs of people and the environment.
Sustainability: The ability to maintain ecological balance by avoiding depletion of natural resources.
Fast Fashion: A business model that produces inexpensive clothing rapidly to meet the latest trends, often leading to environmental harm.
Ethical Sourcing: The practice of ensuring that products are obtained in a responsible and sustainable manner, considering the welfare of workers and the environment.
Circular Fashion: A model that promotes the reuse and recycling of clothing to minimize waste and environmental impact.
Urbanization: The process by which rural areas become urbanized as a result of population migration to cities.
Environmental Justice: The fair treatment and involvement of all people in environmental policies and practices, regardless of race, color, or income.
Data Analysis: The process of inspecting, cleansing, and modeling data to discover useful information and support decision-making.
Exam Preparation Tips
Section Breakdown:
Multiple Choice (15 marks):
Review key definitions and concepts.
Skill Interpretation (5 marks):
Familiarize yourself with maps, graphs, and data tables.
Short Answers (15 marks):
Prepare concise definitions and explanations.
Use examples to support your answers.
Extended Response on Interconnections (15 marks):
Structure: Introduction, body paragraphs, conclusion.
Key points to address: Human impact on water, case studies, and global connections.
Use specific examples and evidence.
Equipment Checklist for Exam Day
Ruler
Pens (blue/black)
Calculator
Study Strategies
Group Study: Discuss concepts with classmates.
Flashcards: Create flashcards for key terms.
Practice Past Papers: Get familiar with exam format and question types.
Reminder
Due Dates: Remember your exam is on 22/10/2024 and 23/10/2024, depending on your class.
Weighting: This exam is worth 60% of your Semester 2 grade, so take it seriously!