Ecology & Ecosystems
Ecology
a branch of the biological science that studies the interaction’s between an organism & its environment
Layers of organization
Organisms>Population>Communities>Ecosystems>Biomes>Biosphere
Biosphere
The Lithosphere
The Atmosphere
The Hydrosphere
A terrarium (sealed/closed system)
Reason:
The plants & the soil in the terrarium release water vapour - essentially recycling water
The vapour is then collected unto the walls of the vessel & flows down to the soil
→ Terrariums are self-nourishing, which is why they require little maintenance if sealed
one input: the sun & it’s sunlight
Biomes
Terrestrial part of the biosphere
Diff. Biomes are distinguished by their climates & the soils & species they support (moisture & temp. defines most biomes)
Aquatic Life Zones
Like a biome but in the ocean
Defined by temp., nutrients, & light
Richest regions are estuaries (where river dumps into the ocean, shallow areas)
Lots of penetration & nutrients
Most productive area; good for fisheries
Ecosystems
2 parts of ecosystem: living - biotic & nonliving - abiotic
Abiotic Factors:
Physical - rock
Chemical - minerals
Range of Tolerance - taking in physical and chemical energy
Biotic Factors:
Other species in ecosystem
food supply
preparation
competition
has a range of tolerance
Habitat & Ecological Niche
Habitat: where a species is found
Niche: where it is found & what it does
Deer lives in Assiniboine forest - Habitat
Deer lives on Assiniboine forest, eats grass, & feeds coyotes - Niche
Now TWO have the same niche (one will always outperform the other)
Deer & Elk, Owl & Hawk (although similar they hare clear differences that separates them)
Food Chains & Webs
Producers (basic system;base of all food)
organism that can take sunlight & turn it into carbohydrates
algae, etc.
Consumers
consumes producers
Decomposers
trapped nutrients; when you die it gets released back into the ecosystem
Other terms -
Omnivore - multiple levels of feed
Herbivore - only eats plants
Ex:
Carnivore - only eats meat
ex:
energy flows in 1 way -
ex: Cod is a stable food system - when it breaks down, cant be rebuild but losing a single factor wouldn’t
Energy
Energy: capacity to do work
Two Types of Energy:
Potential energy: stored in the object
Ex: Ball on top of hill or chemical bond
Kinetic Energy: energy of motion
1st Law of Thermodynamics:
Energy can be neither created or destroyed, but only charged from one form to another
2nd Law of Thermodynamics:
In any energy conversion, there will be some loss as heat (from one type of energy to another)
Efficiency in the Food Chain
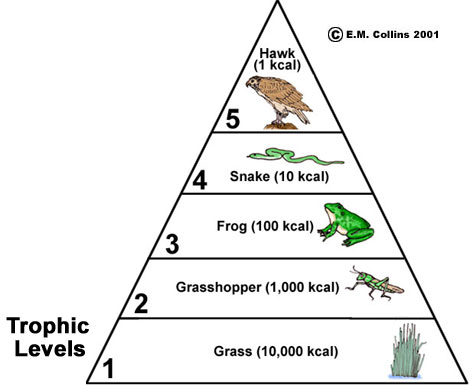
Nutrient Cycles
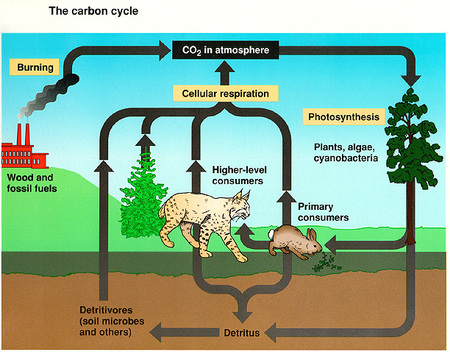
Nutrients unlike energy are recyclable
Cycles that moves chemicals around the biosphere are called biogeochemical
driven by life process
Carbon Cycle
Balance & Imbalance in Ecosystems
Ex: Lake Victoria & Nile perch
Lake Victoria have been for a long time; Nile perch
British: added Nile Perch and it ate all of the Cichlids
Nile Perch (oily fish) preserved
resulted in a disruption of ecosystem
Ex: Water hyacinth in Florida
around 1920s, Florida Everglades now becomes closed because there was no competitor
Stable Ecosystem: things changed a little from day to day, or month to month, or in annual cycles, but generally stay the same
Dynamic equilibrium: doesn’t stay exactly the same but oscilates around a central point
Ecosystem Stability
Total # of living species is constant (or almost) year after year
The same species are present every year; &
The population (P) of each species is roughly the same every year
Population Growth in Ecosystems
Populations of various species are controlled by many factors, some of them are biological or biotic, & some of them not or abiotic
Biotic Growth Factors:
Reproductive rate
Ex: High Reproductive Rate: Rats & Bunnies & Dandelions & Mosquitoes
Adaptability:
Ability to migrate:
Ex: Dandelions; mobile seeds
Competitiveness
Ex: Nile Perch & Water Hyacinth
Food Supply:
Ability to eat & survive
Ex: Pandas & Koalas
Abitic Growth Factors:
Favourable Light: Plants under Water Hyacinth
Favourable Temp. or moisture
Etc
Biotic Reduction Factors:
Predators
Ex: Nile Perch
Parasites
Presence or absence of parasites
Ex: Moose population is decreasing in Quebec due to Ticks
Food Shortage
Not enough grass-decrease in pop.
Loss of Habitat
Ex: Less sea ice in Manitoba = decrease in Polar Bears
Abiotic Reduction Factors
Bad Weather
Mosquitoes
Water Shortage
Ex: A pond has lessened water = affects frog pop.
Pollution
Resisting Change
If an ecosystem is stable. it resists change, & the system is said to have inertia
If it changes significantly,& then bounces back to something like its original state, it is said to have resilience
Ex: Singapore’s cold weather is 24 and the hottest is 31
Human Impact on Ecosystems
Introducing new species
Ex. Nile perch, (human introduction)
Africanized killer bees
Rabbits, displacing natural herbivores in Australia
ate all the food sources
Rabbits that did survive had a resistance to virus (bred like rabbits)
Removing a species
Kaibab Plateau in Arizona (modification of an ecosystem)
Introducing parasites
Bacillus thuringiensis (BT)
natural pesticide