
NURS 1001- Nurses Role in Organziational Safety
NURS 1001- Nurses Role in Organizational Safety
Content
- Quality Care
- Safety
- Discrimination in Healthcare
Quality Care
- Patient-centered
- Safe
- Effective
- Timely
- Equitable
- Collaborative
- Comprehensive
- Continuous improvement
Accrediation Canada
“Accreditation is an ongoing process of assessing health care and social services organizations against standards of excellence to identify what is being done well and what needs to be improved” (Accreditation Canada, 2023).
- Accreditation process
- Standards
- Continuous improvement
Professional Standards
“Authoritative statements that a profession uses to describe the responsibilities for which its practitioners are accountable (Kily, 2005; Peters, 1995).

- College of Nurses of Ontario (CNO)
- Practice Standards
- Practice Guidelines
Best Practice Guidelines
Best practice guidelines (BPG) are systematically developed, evidence-based documents that include recommendations for nurses, interprofessional health teams, educators, leaders and policy-makers on how to improve outcomes for people and their support networks.” (RNAO, 2023)

- >50 BPG
- 9 Health sectors
Nurse Sensitive Outcomes
Patient outcomes that are directly influenced by nursing care
Examples:
- Patient satisfaction
- Patient safety
- Medication errors
- Length of hospital stay
- Readmission rates
Leadership Impacting Quality Care
Effective leadership impacts quality care by:
- Prioritizing quality improvement
- Promoting safety culture
- Strong communication
- Being accountable
- Using evidence informed decision making
- Being regulatory compliant
- Being a role model
Safety
Patient Safety
“the reduction of risk of unnecessary harm associated with healthcare to an acceptable minimum” (Potter & Perry, 2022).
Healthcare Excellence Canada (2020) Six Core Safety Competencies for HCP
- Patient safety culture
- Teamwork
- Communication
- Safety, risk and quality improvement
- Optimize human and system factors
- Recognize, respond to and disclose patient safety incidents
Nurse Safety
Well-being and protection of nurses in the workplace
Strategies to promote nurse safety:
- Safe staffing levels
- Training and education
- PPE
- Ergonomics
- Violence prevention
- Physical safety
- Fatigue management
- Professional development
Organizational Safety
Creating a culture that prioritizes safety at all levels, across all departments
Strategies to promote organizational safety:
- Proficient leadership
- Safety commitment
- Safety policies and procedures
- Reporting systems
- Root cause analysis for critical events
- Performance metrics
- Audits
- Infection control
Positive Workplace Culture
Characteristics of positive workplace culture:
- Respect and inclusivity
- Clear communication
- Teamwork and collaboration
- Empowerment
- Recognition and appreciation
- Fairness and equity
- Organizational values
- Conflict resolution
- Safety
Sentinel Event
“A sentinel event is a patient safety event that results in death, permanent harm, or severe temporary harm. Sentinel events are debilitating to both patients and health care providers involved in the event.” (The Joint Commission, 2023).
Safety Culture (Nurse)
- Zero violence policies
- Prevention of nurse-fatigue
- Foster key values
- Staff health and well-being
Safety Culture (Patient)
Everyone involved is committed to maintaining a safety environment.
Three components:
- Just culture
- Reporting culture
- Learning culture
Nurses Role in Safety Culture
- Assessing risks
- Patient safety
- Reporting incidents
- Collaboration
- Advocacy
- Personal safety
- Research
RNAO HWE BPGs
- Collaborative Practice Among Nursing Teams
- Developing and Sustaining Effective Staffing and Workload Practice
- Developing and Sustaining Nursing Leadership
- Embracing Cultural Diversity in Health Care: Developing Cultural Competence
- Professionalism in Nursing
- Workplace Health, Safety and Well-being of the Nurse
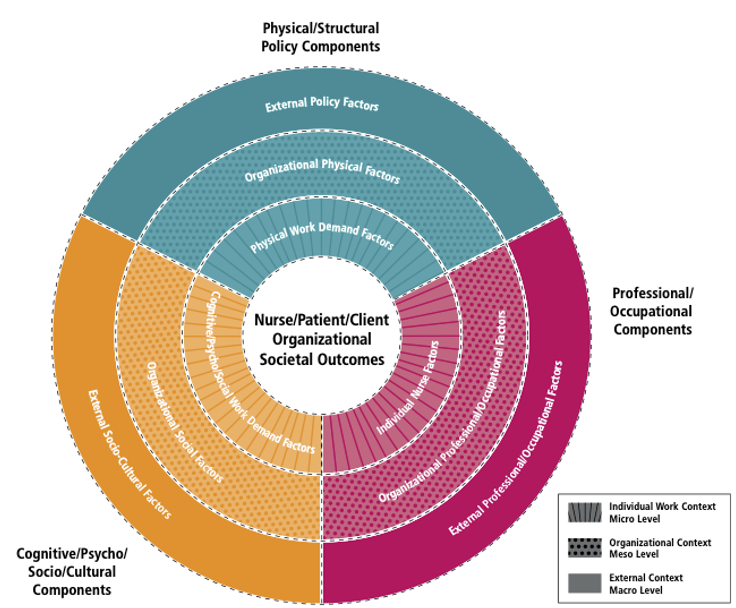
HWE Framework
Occupational Health Nurse
- Disability management
- Health and safety programs
- Health promotion initiatives
- TB maintenance
- Health assessment
- Health education
- Outbreak surveillance
Discrimination in Healthcare
Cultural Safety
- Cultural awareness and competence
- Self- reflection
- Respect for cultural identity
- Equity and social justice
- Non-discrimination
- Recognition of trauma and historical context.
- Reporting and accountability
“Othering”
“Othering, is described as a social process whereby a dominant group or person uses negative attributes to define and subordinate others” (Roberts & Schiavenato, 2017).
Impact on patient safety
- Miscommunication
- Bias and stereotyping
- Patient engagement
- Access to care
- Disparities in care
Gender Discrimination
Women
- Less likely to have senior/leadership roles
- Pay inequities
- Workplace violence and sexual harassment
Men
- Disproportionate heavy lifting assignment
- Exclusion from some areas of nursing
- Mistaken identity
Racism
Impacts of racism in healthcare
- Health disparities
- Access to care
- Quality of care
- Implicit bias
- Maternal mortality
- Mental health disparities
- Structural racism
Systemic Racism
- Attitudes and structures
- Early colonization values
- Unconscious bias
- Confronting stereotypes
Nurses Role in Preventing Discrimination
What is the nurses role to address racism and discrimination?
- Self awareness
- Advocate
- Cultural Competence
- Report incidents
- Anti-racism education
- Support for colleagues
- Policies and procedures
- Promote equity
- Engage with community
CNO’s Code of Conduct
Principle 2 : Nurses provide inclusive and culturally safe care by practicing cultural humility
Empowering Nurses to Change the System
A Call to Action
- Acknowledge the problem
- Become educated
- Make a commitment
Summary
We have explored many issues related to safety, racism, discrimination, and patient care. We discussed the specific impact to nurses and patients when in unsafe healthcare organizations. We highlighted the importance of the nurses role when eliminating stereotypes and systemic racism. Workplace safety culture can impact the overall wellness and role satisfaction for nurses and positively impact patient care.
NURS 1001- Nurses Role in Organziational Safety
NURS 1001- Nurses Role in Organizational Safety
Content
- Quality Care
- Safety
- Discrimination in Healthcare
Quality Care
- Patient-centered
- Safe
- Effective
- Timely
- Equitable
- Collaborative
- Comprehensive
- Continuous improvement
Accrediation Canada
“Accreditation is an ongoing process of assessing health care and social services organizations against standards of excellence to identify what is being done well and what needs to be improved” (Accreditation Canada, 2023).
- Accreditation process
- Standards
- Continuous improvement
Professional Standards
“Authoritative statements that a profession uses to describe the responsibilities for which its practitioners are accountable (Kily, 2005; Peters, 1995).

- College of Nurses of Ontario (CNO)
- Practice Standards
- Practice Guidelines
Best Practice Guidelines
Best practice guidelines (BPG) are systematically developed, evidence-based documents that include recommendations for nurses, interprofessional health teams, educators, leaders and policy-makers on how to improve outcomes for people and their support networks.” (RNAO, 2023)

- >50 BPG
- 9 Health sectors
Nurse Sensitive Outcomes
Patient outcomes that are directly influenced by nursing care
Examples:
- Patient satisfaction
- Patient safety
- Medication errors
- Length of hospital stay
- Readmission rates
Leadership Impacting Quality Care
Effective leadership impacts quality care by:
- Prioritizing quality improvement
- Promoting safety culture
- Strong communication
- Being accountable
- Using evidence informed decision making
- Being regulatory compliant
- Being a role model
Safety
Patient Safety
“the reduction of risk of unnecessary harm associated with healthcare to an acceptable minimum” (Potter & Perry, 2022).
Healthcare Excellence Canada (2020) Six Core Safety Competencies for HCP
- Patient safety culture
- Teamwork
- Communication
- Safety, risk and quality improvement
- Optimize human and system factors
- Recognize, respond to and disclose patient safety incidents
Nurse Safety
Well-being and protection of nurses in the workplace
Strategies to promote nurse safety:
- Safe staffing levels
- Training and education
- PPE
- Ergonomics
- Violence prevention
- Physical safety
- Fatigue management
- Professional development
Organizational Safety
Creating a culture that prioritizes safety at all levels, across all departments
Strategies to promote organizational safety:
- Proficient leadership
- Safety commitment
- Safety policies and procedures
- Reporting systems
- Root cause analysis for critical events
- Performance metrics
- Audits
- Infection control
Positive Workplace Culture
Characteristics of positive workplace culture:
- Respect and inclusivity
- Clear communication
- Teamwork and collaboration
- Empowerment
- Recognition and appreciation
- Fairness and equity
- Organizational values
- Conflict resolution
- Safety
Sentinel Event
“A sentinel event is a patient safety event that results in death, permanent harm, or severe temporary harm. Sentinel events are debilitating to both patients and health care providers involved in the event.” (The Joint Commission, 2023).
Safety Culture (Nurse)
- Zero violence policies
- Prevention of nurse-fatigue
- Foster key values
- Staff health and well-being
Safety Culture (Patient)
Everyone involved is committed to maintaining a safety environment.
Three components:
- Just culture
- Reporting culture
- Learning culture
Nurses Role in Safety Culture
- Assessing risks
- Patient safety
- Reporting incidents
- Collaboration
- Advocacy
- Personal safety
- Research
RNAO HWE BPGs
- Collaborative Practice Among Nursing Teams
- Developing and Sustaining Effective Staffing and Workload Practice
- Developing and Sustaining Nursing Leadership
- Embracing Cultural Diversity in Health Care: Developing Cultural Competence
- Professionalism in Nursing
- Workplace Health, Safety and Well-being of the Nurse
HWE Framework

Occupational Health Nurse
- Disability management
- Health and safety programs
- Health promotion initiatives
- TB maintenance
- Health assessment
- Health education
- Outbreak surveillance
Discrimination in Healthcare
Cultural Safety
- Cultural awareness and competence
- Self- reflection
- Respect for cultural identity
- Equity and social justice
- Non-discrimination
- Recognition of trauma and historical context.
- Reporting and accountability
“Othering”
“Othering, is described as a social process whereby a dominant group or person uses negative attributes to define and subordinate others” (Roberts & Schiavenato, 2017).
Impact on patient safety
- Miscommunication
- Bias and stereotyping
- Patient engagement
- Access to care
- Disparities in care
Gender Discrimination
Women
- Less likely to have senior/leadership roles
- Pay inequities
- Workplace violence and sexual harassment
Men
- Disproportionate heavy lifting assignment
- Exclusion from some areas of nursing
- Mistaken identity
Racism
Impacts of racism in healthcare
- Health disparities
- Access to care
- Quality of care
- Implicit bias
- Maternal mortality
- Mental health disparities
- Structural racism
Systemic Racism
- Attitudes and structures
- Early colonization values
- Unconscious bias
- Confronting stereotypes
Nurses Role in Preventing Discrimination
What is the nurses role to address racism and discrimination?
- Self awareness
- Advocate
- Cultural Competence
- Report incidents
- Anti-racism education
- Support for colleagues
- Policies and procedures
- Promote equity
- Engage with community
CNO’s Code of Conduct
Principle 2 : Nurses provide inclusive and culturally safe care by practicing cultural humility
Empowering Nurses to Change the System
A Call to Action
- Acknowledge the problem
- Become educated
- Make a commitment
Summary
We have explored many issues related to safety, racism, discrimination, and patient care. We discussed the specific impact to nurses and patients when in unsafe healthcare organizations. We highlighted the importance of the nurses role when eliminating stereotypes and systemic racism. Workplace safety culture can impact the overall wellness and role satisfaction for nurses and positively impact patient care.