religion
\n
Interfaith Dialogue
The challenges of interfaith dialogue 27/10/22
Conversations are held between different types of people, theology, atheists etc
First challenge is a lack of focus
All parties must be clear on the goal of the conversations, this helps people decide which conversation they belong in
It is necessary to hold multiple different types of conversations, each geared to a different audience
The second challenge is when people feel the need to water down/compromise their identity to fit in
Interfaith dialogue is supposed to help each participant better understand their own religion and discover the area in which their religion is unique. In the situation described, both parties should agree to disagree. They should accept that differences exist and seek to understand them without compromising their own beliefs
The third challenge is proselytising, or attempting to convert others
In interfaith dialogue, participants should enter the conversation in order to learn about other religions beliefs, not promote their own
\n
2.1 Examining the religious profile of the Australian community within a global context
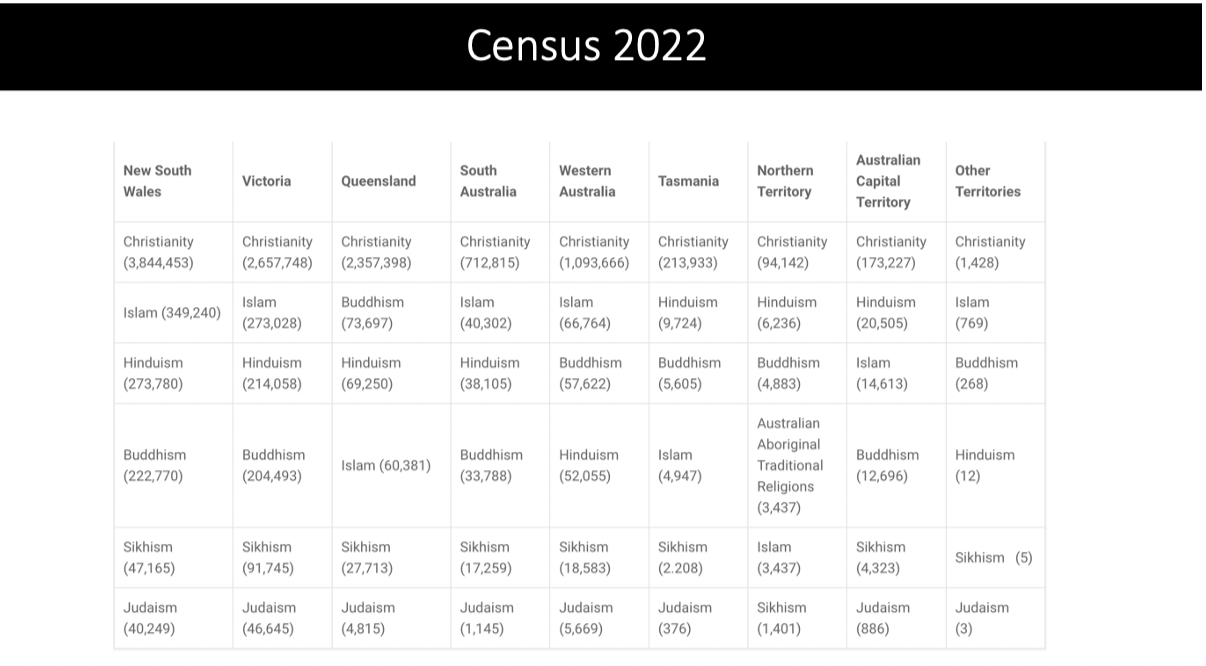
Census 2022
\n
Christianity
Australias major religion is christianity with its denominations (catholoc, anglican, uniting church, eastern orthodox, presbyterian & reformed, baptist and Pentecostal, high to low)
30% of population claimed to be catholic or anglican in 2021
\n
Other religions
Non christian religion in Australia include Islam, Hinduism, Buddhism, Sikhism and Judaism.
Islam is the largest non-christian religion with followers comprising 3.2% of the total population
Followers of hinduism, the second largest non-christam religion represented in Australia, make up about 2.7% of the total population.
2.4% of australia follow buddhism
Less than 1& of the total population follow Sikhism and Judaism respectively
\n
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islanders
For aboriginal and torres straitnislander people, the concept of ;spirituality refers to a more holistic view of life, in particular ones link with the land, sea and air
Consequently, this relationship confirms one's identity and place as an aboriginal person and/or a torres strait islander person
In 2021 census, 7887 people were recorded as practising Australian Aborginal traditional religions
Northern Territory had the highest number of people recorded as practising Aboriginal traditional religions (3437), followed by NSW (1422), Western Australia (1096) and Queensland (979)
\n
2016 to 2021 census
- The diversity of religious affiliation has increased across the Australia population
- The percentage of Australians reporting no religious affiliation continues to grow. Its now at 38.9& of the population identifying as Christian, a decrease from 52.1% in the 2016 census
- The top 5 religions outside of Christianity are Islam, Hinduism, Buddhism, Sikhism and Judaism
- The religion question
2.2 Considering come of the core elements common to the major religious traditions
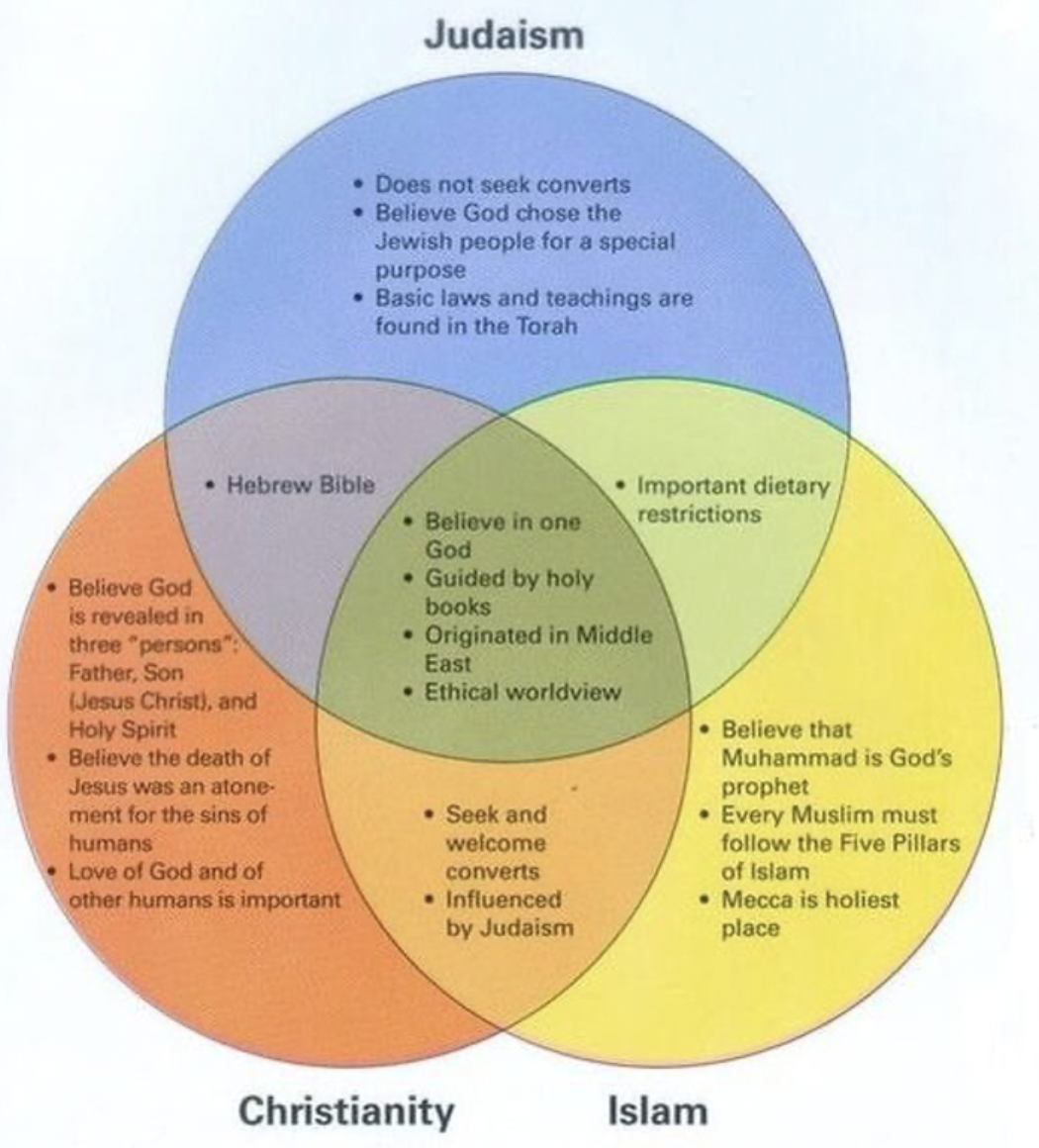
Who is Abraham
The Israelites believed they descended from a man named Abraham
The Hebrew Bible says that God told Abraham and his people to leave Mesopotamia and settle in Canaan
Abraham's grandson Jacob (also called Israel) raised 12 sons in Canaan. His family then divided into what is known as the 12 tribes of Israel
\n
\n
Things/features to know about interfaith
Different between interfaith + ecumenism
Census stats (biggest religion in Aus, is religion on the up/down)
Specific examples of interfaith dialogue
Challenges of interfaith dialogue
\n
Gospel of Mark
Short answer Mark question
- What apostle did Mark take notes from?
Apostle peter, he knew jesus' well
\n
- Is mark the smallest or largest gospel out of Matthew, Mark, Luke and John?
Smallest
\n
- What are recurring themes of Jesus in mark?
Jesus authority is shown, there is an emphasis on Jesus being the son of god
\n
Things/features to know about Mark
Audience of Mark's gospel
- gentiles, non-jews
Chiastic structure
- A - The wilderness
- B - Galilee
- C - the way
- B - Jerusalem
- A - The Tomb
Themes of Marks Gospel
- messianic secret
- jesus’ desire to keep his identity a secret
- discipleship
- 6 stories of discipleship in Mark
- parables
- one of the ways Jesus taught/told stories
- the kingdom of god
- not a geographical or political kingdom, but a church that belongs to people whose hearts are set on goodness
jesus is:
- servant leader
- son of god
- messiah
- suffering messiah
1st gospel written
Shortest gospel of the 4
\n
Features to know about the gospels
- Synoptic gospels: Matthew, Mark and Luke
- 4 gospels: Matthew, Mark, Luke and John
- Purpose is to spread news of Jesus, tell good news, preach Jesus promises, tell us what Jesus did, persuade readers to follow Jesus