What To Memorize: Chapters 1-3
Chapter 1
Elements and Symbols
Name | Symbol | Name | Symbol |
|---|---|---|---|
Antimony | Sb | Iron | Fe |
Aluminum | Al | Lead | Pb |
Argon | Ar | Lithium | Li |
Arsenic | As | Magnesium | Mg |
Barium | Ba | Manganese | Mn |
Beryllium | Be | Mercury | Hg |
Bismuth | Bi | Neon | Ne |
Boron | B | Nickel | Ni |
Bromine | Br | Nitrogen | N |
Cadmium | Cd | Oxygen | O |
Calcium | Ca | Phosphorous | P |
Carbon | C | Platinum | Pt |
Cesium | Cs | Potassium | K |
Chlorine | Cl | Radium | Ra |
Chromium | Cr | Rubidium | Rb |
Cobalt | Co | Silicon | Si |
Copper | Cu | Silver | Ag |
Fluorine | F | Sodium | Na |
Gallium | Ga | Strontium | Sr |
Germanium | Ge | Sulfer | S |
Gold | Au | Tin | Sn |
Helium | He | Titanium | Ti |
Hydrogen | H | Uranium | U |
Iodine | I | Zinc | Zn |
Metric Prefixes
Prefix | Symbol | Numerical Value |
|---|---|---|
Giga | G | 109 |
Mega | M | 106 |
kilo | k | 103 |
centi | c | 10-2 |
milli | m | 10-3 |
micro | u | 10-6 |
nano | n | 10-9 |
1 mL = 1 cm³
Equations

Converting Celsius to Kelvin: K = C + 273.15
Equation for work:
w=F\times d
w = work
F = force
d = distance
Chapter 2
The following widely used metals have several common oxidation states:
Vanadium V
Chromium Cr
Manganese Mn
Iron Fe
Cobalt Co
Nickel Ni
Copper Cu
Gold Au
Mercury Hg
Antimony Sb
Tin Sn
Lead Pb
Uranium U
Metalloids
B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te
Average Mass
The formula for calculating the average mass of isotopes is:
Average mass = (mass₁ × % abundance₁) + (mass₂ × %abundance₂) + ... + (massₙ × %abundanceₙ)
Where:
mass₁, mass₂, ..., massₙ are the masses of the isotopes
abundance₁, abundance₂, ..., abundanceₙ are the relative abundances of the isotopes
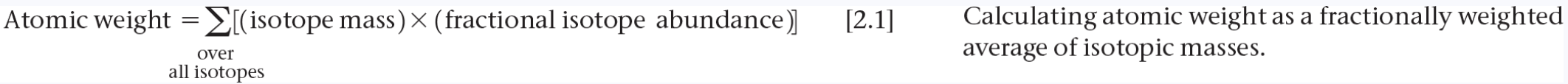
Groups of the periodic table
Alkali metals (1A)
Alkaline-earth metals(2A)
Transition metals (3-12)
Halogens (7A)
Noble gases (8A)
Polyatomic Ions
Name | Equation | Name | Equation |
|---|---|---|---|
Hydroxide | OH^{-} | Bicarbonate | HCO_{3}^{-} |
Hydronium | H_{3}O^{+} | Cyanide | CN^{-} |
Ammonium | NH_{4}^{+} | Sulfate | SO_{4}^{2-} |
Nitrate | NO_{3}^{-} | Sulfite | SO_{3}^{2-} |
Nitrite | NO_{2}^{-} | Phosphate | PO_{4}^{3-} |
Perchlorate | ClO_{4}^{-} | Hydrogen Phosphate | HPO_{4}^{2-} |
Chlorate | ClO_{3}^{-} | Dihydrogen Phosphate | H_{2}PO_{4}^{-} |
Chlorite | ClO_{2}^{-} | Phosphite | PO_{3}^{3-} |
Hypochlorite | ClO^{-} | Acetate | C_{2}H_{3}O_{2}^{-} |
Carbonate | CO_{3}^{2-} | Permanganate | MnO_{4}^{-} |
Important Molecules
Water: (H2O)
Ammonia: (NH3)
Hydrogen Sulfide: (H2S)
Acids
Strong:
Hydrofluoric acid (HF)
Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
Hydrobromic acid (HBr)
Hydroiodic acid (HI)
Chloric acid (HClO3)
Perchloric acid (HClO4)
Nitric acid (HNO3)
Sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
Weak:
Acetic acid (C2H4O2)
Organic/Base Molecules
Methane (CH4)
Ethane (CH3-CH3)
Propane (CH3-CH2-CH2) as base molecules
Change ending to –ol for alcohols
Strong Bases
Group 1A metal hydroxides
Heavy group 2A metal hydroxides ( Ca(OH)2 ) and down.
Chapter 3
Symbols for Chemical Reactions
(g) = gas
(l) = liquid
(s) = solid
(aq) = dissolve in aqueous (water) solution
(Δ) = heat needed for reaction.
Reactions
Be able to recognize/name Combination, Decomposition, and Combustion reactions.
Formula for Percent Composition
 Avogadro’s Number:
Avogadro’s Number:
6.022×1023 particles/mols
Formula for Percent Yield
