unit 4 genetics pre ap biology 1
protein synthesis happens as a result id RNA and RNA helps DNA makes proteins
RNA ribosomes nucleic acid is a single strand of DNA that carries the genetic information necessary for the synthesis of proteins, playing a vital role in translating the instructions encoded in DNA into functional molecules.
with RNA a=u instead of a=t, which means that adenine pairs with uracil instead of thymine.
Furthermore, this pairing is crucial as it allows for the correct transcription and translation of genetic information, ultimately guiding the formation of specific amino acid sequences that form proteins necessary for various cellular functions. In addition to this process, there are three primary types of RNA involved in protein synthesis: messenger RNA (mRNA), which conveys the genetic blueprint from DNA; transfer RNA (tRNA), which brings the appropriate amino acids to the ribosome; and ribosomal RNA (mRNA), which forms the core of the ribosome's structure and catalyzes the assembly of amino acids into polypeptide chains. This intricate process of protein synthesis is fundamental to cellular function and underscores the importance of accurate RNA synthesis, as any errors in this process can lead to mutations affecting overall organism health. Additionally, post-transcriptional modifications can further refine the RNA molecules, ensuring their readiness for the transnational process, thereby enhancing the fidelity of protein synthesis. DNA→RNA→ protein is central dogma of molecular biology, illustrating the flow of genetic information and the intricate steps involved in gene expression. with a DNA strand its inside of a chromosomes which is inside of a cell
transcriptions- mRNA copies DNA instructions
location:nucleus
players involved:DNA and RNA
DNA: The molecule that contains the genetic instructions necessary for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all known organisms.
RNA: Serves as the intermediary that conveys the genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes, where proteins are synthesized.
Translation- ribosomes uses mRNA to make proteins
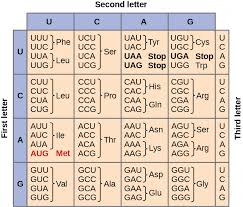
genetic code is the sequence of nucleotide in mRNA that determines the order of amino acids in a protein, effectively translating the information stored in DNA into functional molecules.
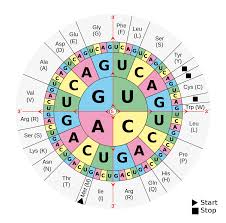
this is the chart used for genetic code deciphering
DNA RNA with DNA the only difference between the two is obliviously RNA is one
A=T A=U strand but DNA is two strand but also instead of matching A(adenine) with
C=G C=G T(Thymine) it matches with U (Uracil)
T=A T=A
G=C G=C